- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 07 DECEMBER 2024
PLACES IN NEWS 07 DECEMBER 2024
07-12-2024
Antarctica
Why in news?
- A study led by Tom Roland (University of Exeter) and Olly Bartlett (University of Hertfordshire) highlights significant greening on the Antarctic Peninsula due to warming, with mosses dominating areas below 1,000 feet, particularly on the western side and South Shetland Islands.
About Antarctica:
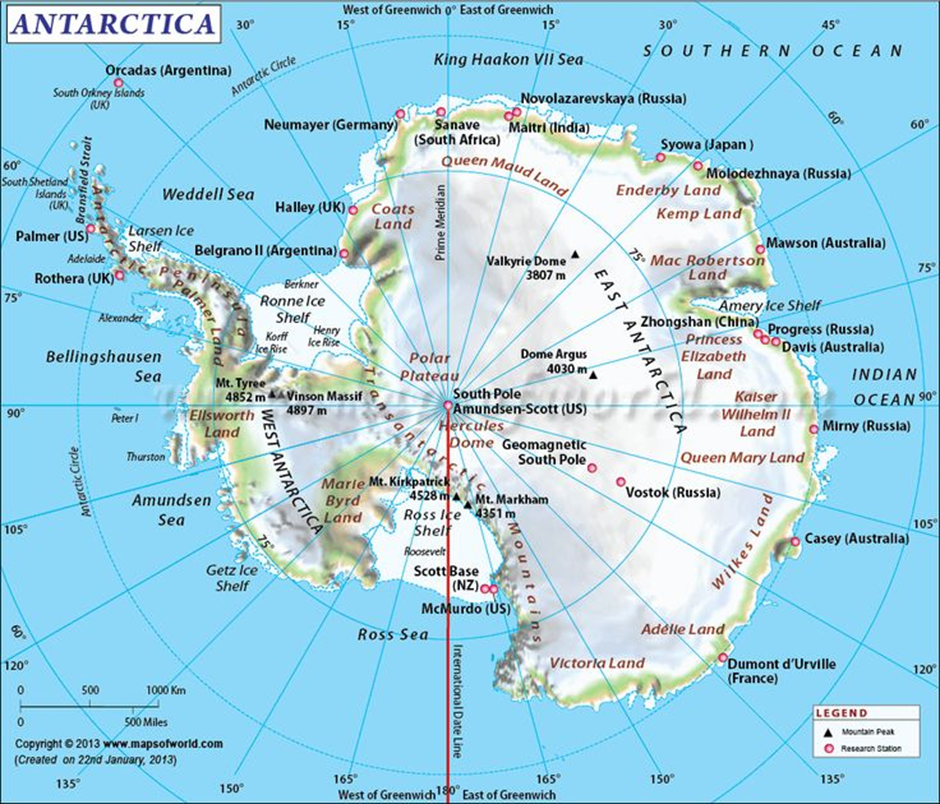
- Antarctica is the southernmost continent, which is characterised by vast ice-covered landmasses, making it the coldest, driest, and windiest region on Earth. It spans 14 million square kilometres, covering about 98% of its surface with ice.
- Key geographical features include prominent ice sheets like the East Antarctic Ice Sheet and West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
- The Transantarctic Mountains divide the continent into eastern and western sections. These mountains extend for over 3,500 kilometres, exposing some of the continent’s rare ice-free regions.
- Notable glaciers include the Lambert Glacier, the world's largest glacier, stretching approximately 400 kilometres. The Pine Island Glacier and Thwaites Glacier, known for their rapid melting, are significant contributors to global sea level rise.
- Antarctica is surrounded by the Southern Ocean, which helps regulate its harsh climate. It includes numerous islands like the South Shetland Islands, known for their volcanic activity, and Ross Island, which is home to Mount Erebus, the southernmost active volcano on Earth.
- The Weddell Sea and the Ross Sea are vital parts of Antarctica’s coastline, hosting unique marine ecosystems. Ice shelves like the Ross Ice Shelf and Ronne Ice Shelf play critical roles in stabilising the glaciers feeding them.
- Research stations: India has two active research stations in Antarctica: Maitri, established in 1989 and located in the Schirmacher Oasis, and Bharati, operational since 2012 in the Larsemann Hills. These stations focus on glaciology, atmospheric sciences, and environmental monitoring.
- Despite its inhospitable environment, Antarctica’s pristine ecosystem and geological features make it a key area for studying climate change and biodiversity, underscoring its global importance.
Ghana
Why in news?
Ghanaians head to the polls Saturday, deciding between economic revival promises from Vice President Bawumia and reform pledges from ex-President Mahama in an election closely watched for its regional democratic significance.
About Ghana:
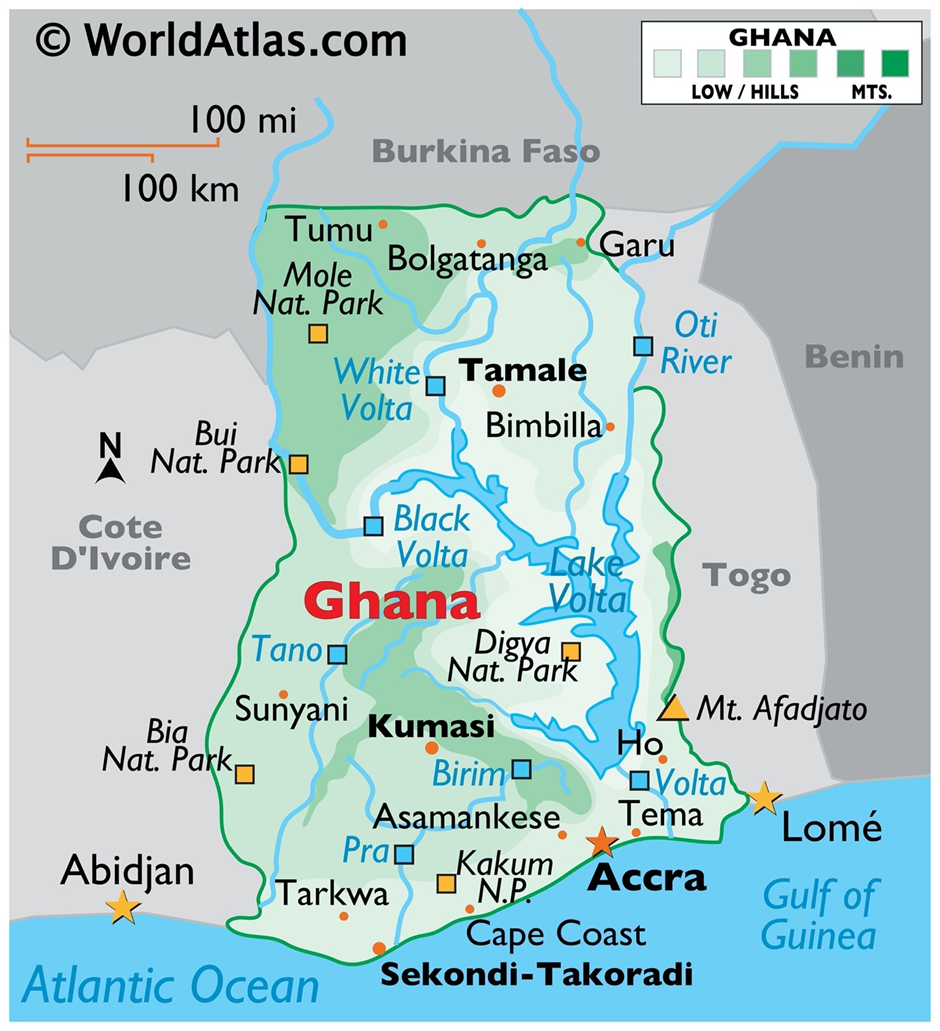
Geography
- Ghana is located in West Africa, bordered by Ivory Coast to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south.
- Covering an area of 238,533 square kilometres, the country features diverse landscapes, including coastal plains, rolling savannahs, and forested plateaus.
- The Volta River Basin, dominated by the massive Lake Volta, one of the world’s largest artificial lakes, is a key geographical feature.
- Its coastline stretches over 560 kilometres, with sandy beaches and lagoons.
- The Kwahu Plateau in the south-central region provides cooler climates and scenic beauty.
- The country is bisected by the Greenwich Meridian, making it geographically significant.
Natural Resources
- Ghana is endowed with abundant natural resources, making it a hub for mining and agriculture.
- It is the world’s second-largest cocoa producer, supporting its agricultural economy.
- The country is rich in gold, ranking among the top producers globally, and hosts significant deposits of bauxite, manganese, and diamonds.
- Recently, oil and natural gas reserves discovered off the coast have boosted Ghana’s economic prospects, with fields like Jubilee contributing to exports.
- Its forest reserves provide valuable timber, while arable land supports crops like yams, maize, and palm oil.
- Inland, salt mining is a traditional industry, and the Volta Basin holds potential for hydropower generation.
Paraguay
Why in news?
- Paraguay expelled Chinese diplomat Xu Wei for alleged interference in domestic affairs, accusing him of undermining ties with Taiwan. Local reports claim Xu lobbied Paraguayan lawmakers to recognise China over Taiwan, promising economic benefits.
About Paraguay:
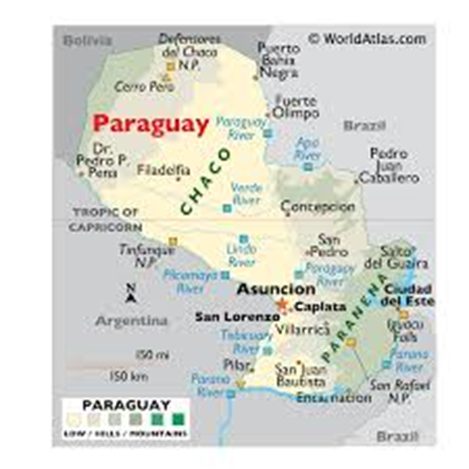
- Geography
- Paraguay is a landlocked country in the heart of South America, bordered by Argentina to the south and west, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest.
- It covers an area of 406,752 square kilometres and is divided by the Paraguay River into two distinct regions: the Eastern Region (Paranena), featuring rolling hills and fertile plains, and the Western Region (Chaco), characterised by arid lowlands and extensive grasslands.
- The Chaco Boreal occupies over 60% of Paraguay’s land but supports only a small portion of the population due to its harsh climate.
- The country is crisscrossed by numerous rivers, including the Paraná River, a major waterway for trade and transport.
- Paraguay enjoys a subtropical to tropical climate, with abundant rainfall in the east and arid conditions in the Chaco. The landscape also includes savannahs, forests, and wetlands, fostering rich biodiversity.
- Natural Resources
- Paraguay is rich in natural resources, which significantly contribute to its economy. The country boasts vast tracts of arable land, supporting agriculture as its economic backbone.
- It is a leading global exporter of soybeans, corn, and beef, thanks to its fertile soils and favourable climate.
- Forest resources provide timber, particularly from the Chaco region.
- Paraguay’s rivers, including the Paraná and Itaipú, offer immense hydropower potential, making it one of the largest exporters of hydroelectric energy globally, powered by the Itaipú Dam and Yacyretá Dam.
- The country also has reserves of limestone, gypsum, and clay, essential for construction and industry.
California
Why in news?
- An earthquake of more than 7.0 magnitude struck off Northern California’s coast near Ferndale, causing widespread tremors felt in regions like San Francisco and Santa Cruz.
About Geophysical characteristics of California:
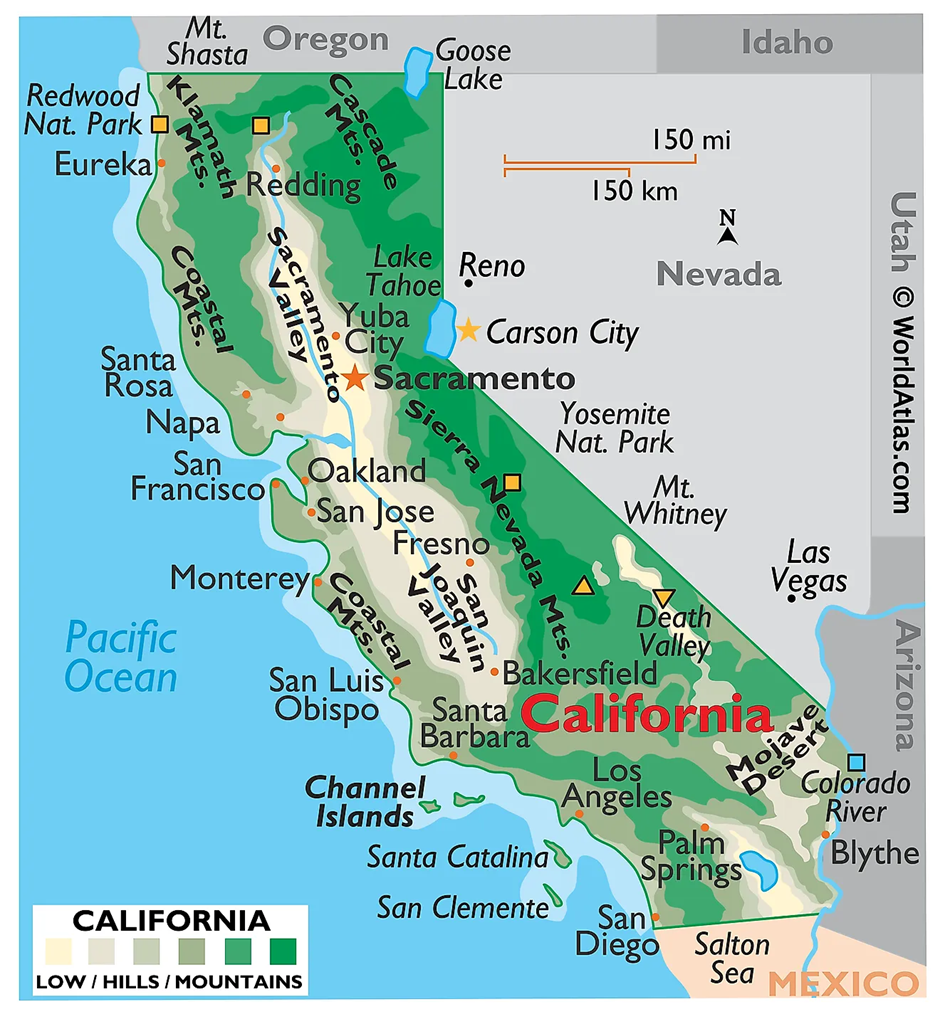
- California is geophysically diverse, featuring a wide range of landscapes, including mountains, valleys, deserts, and coastlines.
- It is located on the Pacific Plate, making it a seismically active region with frequent earthquakes.
- The San Andreas Fault, a major transform fault, runs nearly 1,200 kilometres through California, marking the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate.
- The state includes mountain ranges like the Sierra Nevada, home to Mount Whitney, the highest peak in the contiguous United States, and the Coast Ranges along the Pacific shoreline.
- Fertile valleys such as the Central Valley dominate its interior, supporting extensive agriculture.
- California’s Mojave Desert and Death Valley, the hottest and driest location in North America, showcase its arid regions.
- California is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area with intense tectonic activity characterised by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and plate subduction zones.
- This geophysical setting is responsible for the state’s seismic risks, with major historical earthquakes like those in 1906 (San Francisco) and 1994 (Northridge).
- Volcanic activity is also evident in the Cascade Range, which includes active volcanoes like Mount Shasta and Lassen Peak.
About Pacific Ring of Fire:
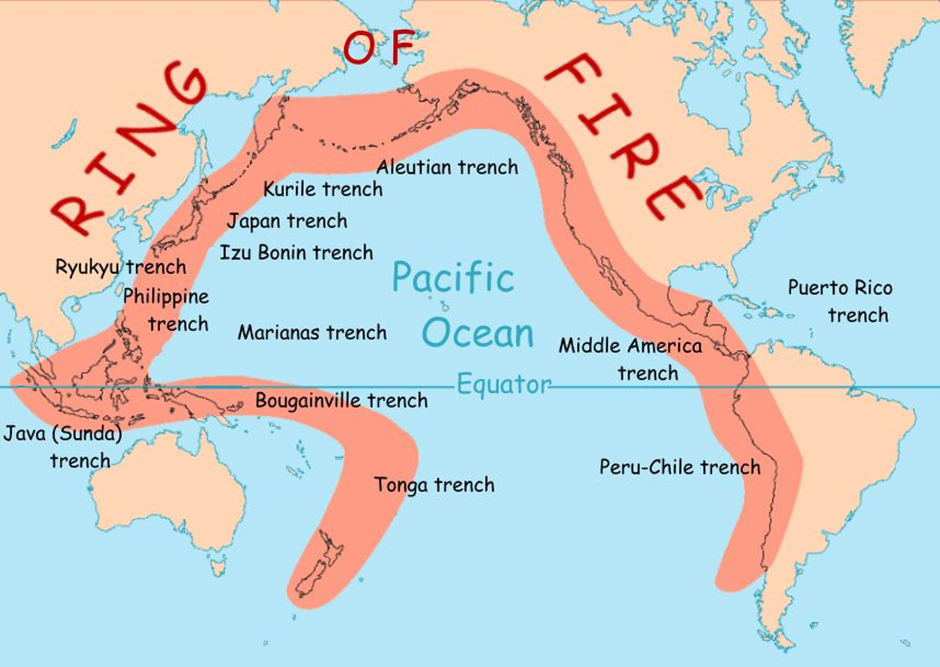
- The Pacific Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped zone encircling the Pacific Ocean, stretching from South America’s west coast to North America, Asia, and down to New Zealand.
- It spans approximately 40,000 kilometres and includes 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes.
- The Ring of Fire results from plate tectonics, where several oceanic plates, such as the Pacific Plate, interact with surrounding continental plates.
- Subduction zones, where one tectonic plate is forced under another, are common, leading to the formation of deep oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and frequent earthquakes.
- Regions along the Ring of Fire, including California, Japan, Indonesia, and Chile, experience intense geological activity due to these tectonic interactions.
- Earthquakes along faults and eruptions from both submarine and terrestrial volcanoes define this geophysical hotspot.
- California’s position on the Ring of Fire underscores its vulnerability to natural hazards, necessitating advanced monitoring systems and preparedness strategies to mitigate potential disasters stemming from its dynamic geophysical characteristics.
|
UPSC CSE PYQ Q1. Which of the following countries are well known as the two largest cocoa producers in the world? (2024)
Answer: Option C |




