- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) Project
Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) Project
25-12-2024

- In December 2024, the ambitious Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal (PKC) project has been initiated under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi by laying down the foundation stone for this transformative project.
- During the event, a tripartite Memorandum of Agreement (MoA) was signed between the Central Government, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- It is an inter-state river-linking initiative aimed at transferring surplus water from the Parbati, Newaj, and Kalisindh rivers to the Chambal River in Madhya Pradesh.
- The PKC project is a part of the National Perspective Plan (NPP, 1980) by the Central Water Commission and Ministry of Irrigation.
- Modified Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-ERCP (PKC-ERCP) Link Project: It is an inter-state project that merges the PKC link with the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP).
- The project aims to provide irrigation and drinking water to 21 districts in Rajasthan and 13 districts in the Chambal and Malwa regions of Madhya Pradesh, benefiting nearly 40 lakh people.
- The initiative is expected to boost agriculture and foster development in religious and tourism sectors.
- The project is expected to supply 3,000 million cubic meters (MCM) of water to Madhya Pradesh and 4,100 MCM to Rajasthan.
- It will ensure optimal utilization of the Chambal Basin's water resources, benefiting industrial and agricultural sectors in both states.
- The total estimated cost of the project is around ₹72,000 crore. The Central Government will bear the 90% cost of the project and State Governments’ Contribution will be of 10%.
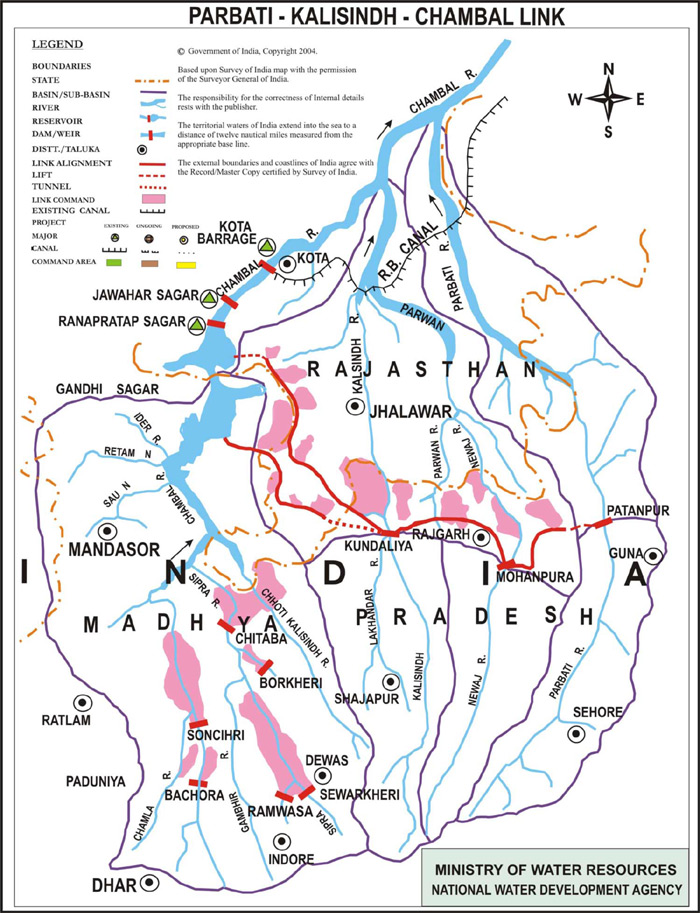
Rivers Involved in the Project
- Chambal River:
- Source: Singar Chouri Peak, Vindhya Mountains, near Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- Key Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Sipra, Parbati.
- Parvati River:
- Source: Vindhya Range, Sehore District, Madhya Pradesh.
- Kali Sindh River:
- Source: Bagli, Dewas District, Madhya Pradesh.
- Main Tributaries: Parwan, Newaj, Ahu.
Chambal River
What is Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP)?
|
|
Also Read |
|




