- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
New SEBI rules to curb F&O frenzy
New SEBI rules to curb F&O frenzy

On 2nd October, The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) introduced 6 new measures aimed at regulating the equity index derivatives market, commonly known as futures and options (F&O).
- These regulations come in response to a significant increase in trading volumes, which has raised concerns about retail investor losses and systemic risks to the economy.
Key Measures Implemented by SEBI:
-
Recalibration of Contract Size
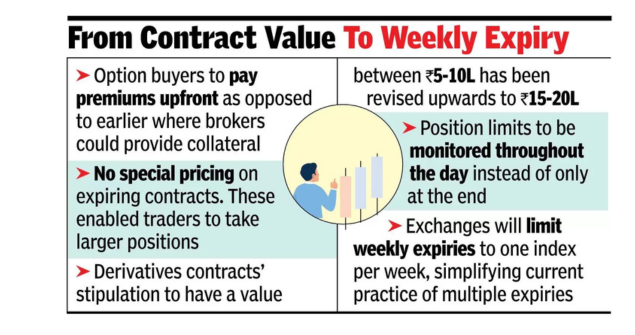
- New Minimum Contract Size: The minimum contract size for index derivatives has been raised from ₹5-10 lakh to ₹15 lakh.
- Rationale: This adjustment aims to ensure that participants take on appropriate risks and curtail speculative trading, particularly among small investors.
- Implication: This could reduce hyperactivity among small traders. Retail investors, especially from tier 2 and tier 3 cities, may need to rethink their strategies, potentially leading them to avoid high-risk index derivatives.
-
Upfront Collection of Options Premium
- New Requirement: SEBI has mandated the upfront collection of options premiums from buyers, effective February 1, 2025.
- Purpose: This measure is designed to limit excessive intraday leverage and ensure prudent risk management at the investor level.
- Implication: This will help to mitigate the risks associated with over-leveraged positions, reducing aggressive speculation.
-
Rationalization of Weekly Index Derivative Products
- Limit on Expiry Products: SEBI has directed that each exchange can only provide weekly expiry contracts for one benchmark index, effective November 20, 2024.
- Objective: This is intended to reduce speculative trading associated with multiple short-tenure options contracts that expire weekly.
- Implication: By limiting these products, the regulation aims to decrease market volatility, particularly on expiry days, and reduce naked options selling.
-
Intra-day Monitoring of Position Limits
- New Compliance Measure: Effective April 1, 2025, SEBI will require intra-day monitoring of position limits for equity index derivatives.
- Goal: This measure aims to detect and address excessive trading activity in real-time, not just at the end of the day.
- Implication: This proactive approach will help maintain orderly market behavior and prevent speculative excesses throughout the trading day.
-
Removal of ‘Calendar Spread’ Treatment on Expiry Day
- Change in Treatment: Starting February 1, 2025, the benefit of offsetting positions (calendar spread) across different expiries will not apply on the day of expiry.
- Reasoning: This is designed to address the significant basis risk that can arise on expiry days, where contract values may fluctuate unpredictably.
- Implication: This will compel traders to roll over their positions earlier, reducing speculative behavior and stabilizing pricing.
-
Increased ‘Tail Risk’ Coverage on Expiry Day
- New Margin Requirement: An additional Extreme Loss Margin (ELM) of 2% for short options contracts will be imposed to cover tail risks, effective immediately.
- Purpose: This aims to protect against unexpected market movements, particularly on volatile expiry days.
- Implication: This measure will encourage greater accountability among market participants and act as a protective buffer against sudden market downturns.
SEBI - Securities and Exchange Board of IndiaWhat is SEBI?
History of SEBI:
Objectives of SEBI:SEBI's main goals are to regulate India's securities market, safeguard investors' interests, ensure a safe investment environment, and prevent market malpractices. Organizational Structure:SEBI has a corporate structure with over 20 departments. It is managed by a Board of Directors, which includes:
Key departments include:
Functions of SEBI:SEBI's functions include:
Powers of SEBI:SEBI's powers include:
The Supreme Court of India and the Securities Appellate Tribunal oversee SEBI’s functions. |
Conclusion
SEBI's new measures to regulate the F&O segment are focused on protecting small investors, reducing speculation, and improving overall market stability. By increasing contract sizes, mandating upfront premium collections, and introducing intra-day monitoring, the regulator aims to foster a healthier trading environment that mitigates risks associated with excessive leverage and speculative trading. These changes are expected to significantly impact how retail investors participate in the derivatives market, ultimately contributing to more stable capital formation and economic growth.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus