- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
New Catalyst Revolutionises Oxygen Electrocatalysis Efficiency
New Catalyst Revolutionises Oxygen Electrocatalysis Efficiency
20-05-2025
Significance: GS III; Science and Tech;
Why in the News?
Indian Scientists from the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS) under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have developed a novel iron-doped catalyst aimed at improving oxygen-related electrocatalytic reactions.
|
What is Oxygen Electrocatalysis?
|
Catalyst Composition and Functionality: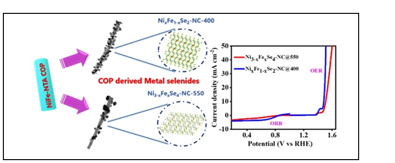
- After selenium (Se) incorporation, the researchers created two main catalyst variants: NixFe₁−xSe₂–NC and Ni₃−xFexSe₄–NC
- The most efficient variant, NixFe₁−xSe₂–NC, showed outstanding bifunctional catalytic performance for:
-
- Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER) – For OER, this catalyst exhibited lower overpotential and high durability over 70 hours, surpassing conventional ruthenium-based catalysts.
- Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) – conversion of oxygen into useful chemicals like hydrogen peroxide. For ORR, especially for H₂O₂ production, it outperformed platinum-based catalysts in terms of reaction speed, efficiency, and stability.
How has it led to innovation?
- The CeNS team developed a low-cost and efficient catalyst using nickel selenide enhanced with iron (Fe) doping, which significantly improves performance while reducing reliance on expensive precious metals.
- The catalyst was synthesised starting from a metal-organic framework (MOF), known for its high porosity and catalytic potential, but limited by poor electrical conductivity.
- Iron (Fe) doping was used to modify the MOF's electronic structure, enhancing its catalytic activity by creating more active sites and improving reaction intermediate binding.
- The MOF was further converted into a carbon-rich material using pyrolysis, a high-temperature process that enhanced the material's electrical conductivity.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




