- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Nano-Formulation of Melatonin: A Promising Treatment for Parkinson's Disease
Nano-Formulation of Melatonin: A Promising Treatment for Parkinson's Disease
05-01-2025
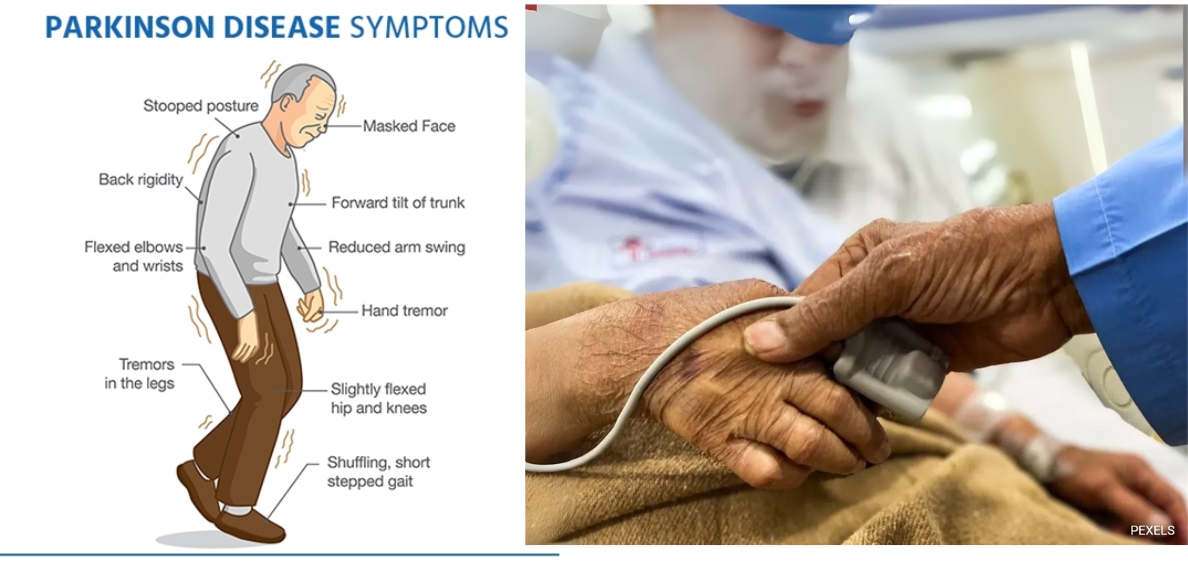
- Recent research has shown that a nano-formulation of Melatonin, a hormone produced by the brain in response to darkness, could be a new and effective treatment for Parkinson's disease (PD).
- Scientists have found that this formulation has strong antioxidant and brain-protecting properties, making it a promising option to help treat PD, a common brain disease.
What is Parkinson's Disease (PD)?
- Parkinson's disease is a brain disorder where dopamine-producing brain cells die, leading to problems with movement, such as shaking, stiffness, and trouble with balance.
- The death of these cells is caused by the build-up of a protein called alpha-synuclein.
- While current treatments help manage symptoms, they do not cure the disease, so there is a need for better treatments.
Melatonin: A Hormone with Potential Benefits
-
What is Melatonin?
- Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain, which helps control the sleep-wake cycle.
- Melatonin has natural antioxidant properties and is often used to treat sleep problems like insomnia.
-
How Melatonin Could Help with Parkinson’s Disease:
- Research has shown that melatonin may help in clearing damaged mitochondria (the energy factories in cells) through a process called mitophagy. This helps reduce oxidative stress (damage caused by free radicals) in the brain, which is one of the main factors behind Parkinson’s disease.
-
Challenges with Melatonin:
- Even though melatonin has benefits, there are some issues with its use as a treatment:
- Low bioavailability (it’s not easily absorbed or used by the body),
- Breaks down too quickly (premature oxidation),
- Difficult to get into the brain, which limits its effectiveness.
- Even though melatonin has benefits, there are some issues with its use as a treatment:
The Nano-Formulation: A New Approach
- A research team at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST) Mohali developed a nano-formulation of melatonin to solve these problems.
- The team used human serum albumin (HSA), a safe protein, as a carrier to deliver melatonin directly to the brain.
- This allows the melatonin to be more effective and better absorbed by the body.
Key Findings from the Research
-
Better Delivery and Absorption:
- The nano-melatonin formulation allows for a slow release of melatonin, keeping it active in the body for a longer time.
- This improves its bioavailability, meaning the body can use it better.
- Using nanoparticles to carry melatonin ensures that it can cross the blood-brain barrier (the protection that keeps some substances out of the brain) and reach the brain more effectively.
-
Stronger Brain Protection:
- The research showed that nano-melatonin had much better antioxidant effects compared to regular melatonin.
- This helps to reduce oxidative stress in the brain, which is a major cause of damage in Parkinson’s disease.
- The formulation also improved mitophagy, a process that helps remove damaged mitochondria from brain cells.
- This is important because damaged mitochondria play a big role in brain cell death.
-
Better Mitochondrial Health:
- In lab tests, the nano-melatonin formulation helped improve mitochondrial function in brain cells that were exposed to a toxic substance called rotenone, which causes symptoms similar to Parkinson’s disease.
- The nano-formulation also helped create new, healthy mitochondria to replace the damaged ones, improving the overall health of the brain cells.
-
Regulation of BMI1 and Mitophagy:
- One of the important findings was the increase in BMI1, a protein that helps regulate genes.
- This protein is connected to mitophagy (removing damaged mitochondria), which helps protect brain cells.
- Increased BMI1 expression promoted mitophagy, which helped reduce oxidative stress and protect the brain cells from damage.
Results from Laboratory and Animal Studies
-
In Lab Studies (In Vitro):
- In experiments with cells, nano-melatonin showed much stronger neuroprotective effects than regular melatonin.
- It helped protect dopamine-producing brain cells from damage caused by rotenone, which mimics Parkinson’s disease.
- The experiments also showed that the formulation successfully triggered mitophagy, which helped remove damaged mitochondria and reduce oxidative stress in brain cells.
-
In Animal Studies (In Vivo):
- In experiments with rats, the nano-melatonin formulation showed better protection of brain cells from damage caused by rotenone.
- The treatment helped preserve the health of brain cells and also increased BMI1 levels, which triggered mitophagy and helped protect neurons.
Implications for Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
- The study suggests that nano-melatonin could be a new treatment for Parkinson’s disease.
- By improving mitophagy and reducing oxidative stress, this formulation could help slow down the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms.
- The research also shows that nano-melatonin could be used to treat other diseases where problems with mitophagy (damaged mitochondria) are important.
- This includes conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and other brain diseases.
- Since melatonin is already used as a safe supplement, the nano-formulation improves its effectiveness while keeping it safe.
- This could make it a better treatment for Parkinson’s disease.
- More research and clinical trials will be needed to confirm how safe and effective nano-melatonin is for humans.
- But if proven successful, it could become a valuable new treatment for Parkinson’s disease and other similar conditions.
Conclusion: A Promising Step for Parkinson’s Disease
The development of a nano-formulation of melatonin represents a major improvement in treating Parkinson’s disease. This approach improves bioavailability, delivery to the brain, and effectiveness by solving the problems of regular melatonin. The research shows that it can help reduce oxidative stress, improve mitophagy, and protect brain cells, making it a promising treatment for Parkinson’s disease. If further studies confirm its effectiveness, nano-melatonin could provide a safe and effective treatment for millions of people with Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative dise.



