- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Militancy in Jammu and Kashmir
Militancy in Jammu and Kashmir
Context:
- Militancy in Jammu & Kashmir is on the rise, highlighted by the recent surprise attack on an Army vehicle by militants in Rajouri.
What is Militancy?
- Militancy is when people use force or aggression, like fighting or protests, to support their beliefs or ideas.
- It typically involves smaller, more localized acts of aggression, often carried out by non-state groups or individuals.
- A non-state actor is someone or a group that has power and influence but isn't part of a government. This could be a group like a company, an organization, or even a rebel group.
Difference between Militancy, Insurgency and Terrorism:
|
Aspect |
Militancy |
Insurgency |
Terrorism |
|
Objective |
Political, Social, ideological or territorial aims |
Overthrowing the existing State or Government |
Instilling psychological fear for political, ideological or religious goal |
|
Targets |
Military Personnels |
Military Personnels + Administrative Personnels + Some Civilians |
Specifically Civilians |
Emergence of militancy in Kashmir: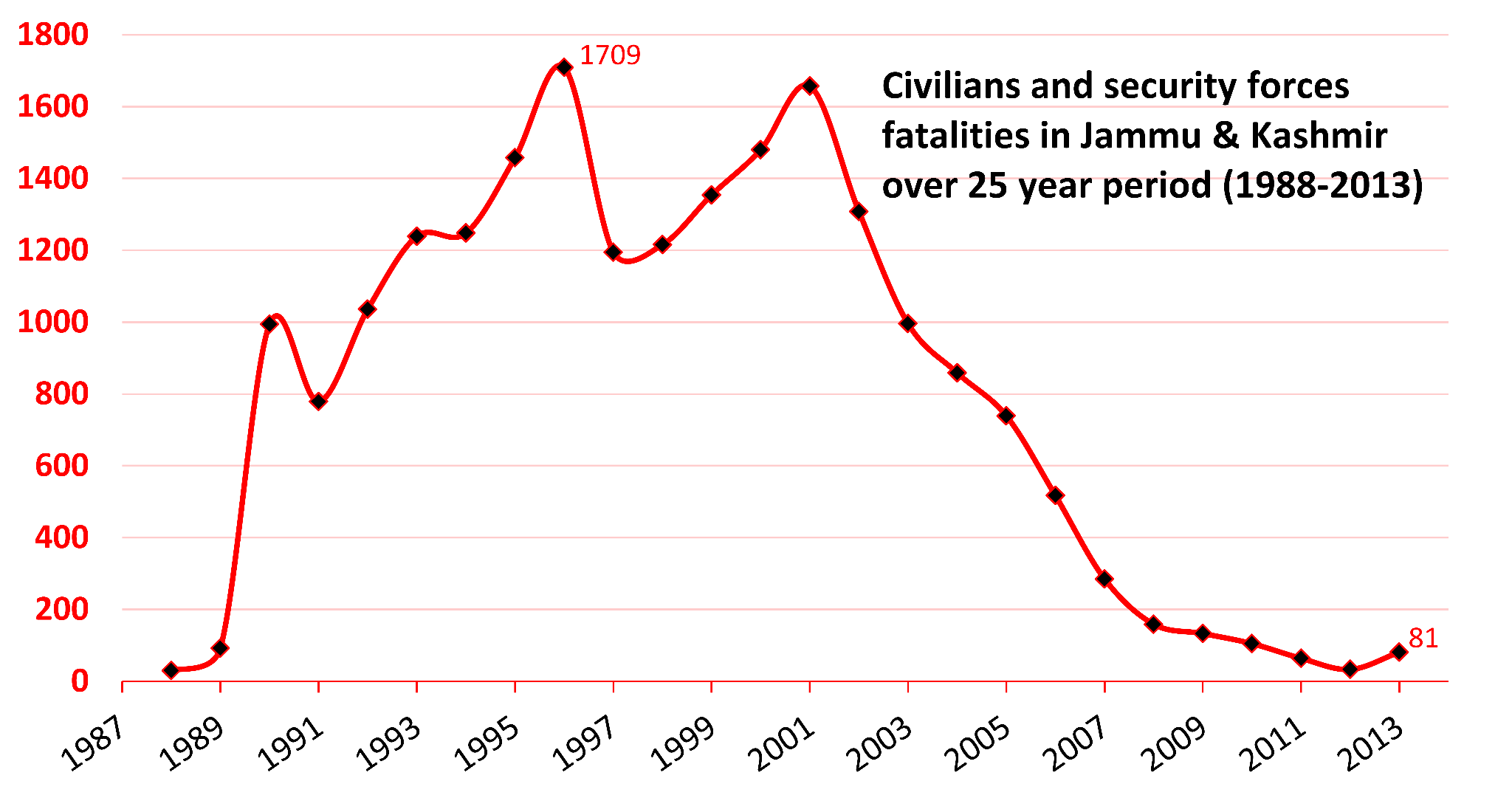
- Radical Separatism: Some groups want Kashmir to be separate, which has led to strong beliefs in favor of independence. There's a long-standing conflict over what status Kashmir should have, causing ongoing tensions.
- Political Unrest: After the rigged elections in 1989, people became upset with the weak democracy and loss of autonomy, sparking unrest.
- Human Rights Violations: Both militants and the army have been involved in violating people's rights, causing more tension and conflict.
- Religious and Ethnic Issues: Events like the exodus of Kashmiri Pandits and the Anantnag land transfer to Hindus in 2008 have worsened divisions based on religion and ethnicity.
- External Support: Groups outside Kashmir, like ISI, have supported terrorism, making the situation more complicated and violent.
- Economic Problems: Lack of jobs and uneven development have made some people feel left out, contributing to the rise of militancy.
Prominent Militant Groups:
- Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT): Known for attacks, notably the 2008 Mumbai attacks and the Uri attack.
- Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM): Responsible for the 2019 Pulwama attack, escalating India-Pakistan tensions.
- Harkat-ul-Mujahideen (HuM): Known for hijacking of Indian Airlines Flight 814 in December 1999, leading to a hostage crisis.
- The Resistance Force (TRF) and Kashmir Tigers: Claiming a secular approach, it's these are considered to be a new front or a rebranding of existing militant groups in Kashmir.
Local Militant Recruitment in Kashmir:
|
Year |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
|
Recruitment |
53 |
66 |
88 |
126 |
218 |
126 |
167 |
- Note: 2018 was an unusual year with sudden rise in local militant recruitment.
Problems in Kashmir |
Solutions |
|
Radical Separatism: Some groups want Kashmir to be independent. Political Unrest: Before 1989, Kashmir was relatively stable. However, the manipulations in the 1989 State Assembly Elections led to the widespread unrest among many kashmiris. As a response, they chose the path of militancy. Human Rights Violations: Both militants and the army have been involved in violating people's rights, causing more tension and conflict.
|
Community Engagement and Integration: Embracing an inclusive approach that respects the Kashmiri aspirations, fosters dialogue and ensures their say in decisions. Initiatives like "Operation Sadbhavana," the revocation of Article 370 and the establishment of District Development Councils aim at local autonomy and community involvement. Positive Narratives: Promote unity, diversity, and cultural richness via media, education, and cultural programs. |
|
External Support: Groups outside Kashmir, like Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), have supported terrorism, making the situation more complicated and violent. |
Security Measures: Enhanced security measures include troop deployment, increased surveillance, and better intelligence-sharing mechanisms, including checkpoints and bunkers. Counterinsurgency Operations like Operation All Out focus on addressing insurgent activities. Use of Technology: Implementing advanced surveillance technology to monitor and secure the region. |
|
Economic Problems: Lack of jobs and development in Kashmir have made some people feel left out, contributing to the rise of militancy. |
Economic Development: Empower Kashmiri youth with skills, jobs, and integrate them into the mainstream. Programs like the "Udaan" initiative aim to provide skill development and job opportunities for Kashmiri youth. Use of Technology: Using technology for developmental purposes such as infrastructure, healthcare, education, and economic growth. |
|
Exodus of Kashmiri Pandits (1989–1995): Many Kashmiri Pandits were forced to leave their homes in the Kashmir Valley because of violence and threats from militant groups. Anantnag Land Transfer Issue (2008): Government transferred a piece of land in Anantnag to the Amarnath Shrine Board (Hindu group) which caused tensions and disagreements among various groups in Kashmir. |
Countering Narratives Using AI: Utilizing artificial intelligence to counter and address conflicting narratives and misinformation. De-Radicalization of Youth: Educate, train, and instill peace among young individuals who may have been influenced by extremist ideologies. Initiatives like Sahi Rasta by the Indian army focus on countering radicalization. Realization of Soft Border Concept: Initiatives like the Srinagar-Muzaffarabad bus service aim to create softer borders to encourage interaction. |



