- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
MCA exempted RRBs from CCIs merger control regime
MCA exempted RRBs from CCIs merger control regime
21-07-2023
Latest Context:
Recently, the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) exempted Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) from Competition Commission of India’s (CCI) ‘merger related investigation’.
More about the news:
- This exemption from merger related investigation will be available for 5 years.
- Basically, the Competition Commission of India (CCI) has the responsibility to examine whether mergers or consolidation will lessen competition in the market or affect consumer interests.
About the Competition Commission of India (CCI)
- CCI is a statutory body (established by an act).
- It was established under the Competition Act of 2002, with the primary objective of promoting fair competition and ensuring the protection of consumers interests in India.
- The CCI is responsible for enforcing competition laws and preventing anti-competitive practices in the Indian market.
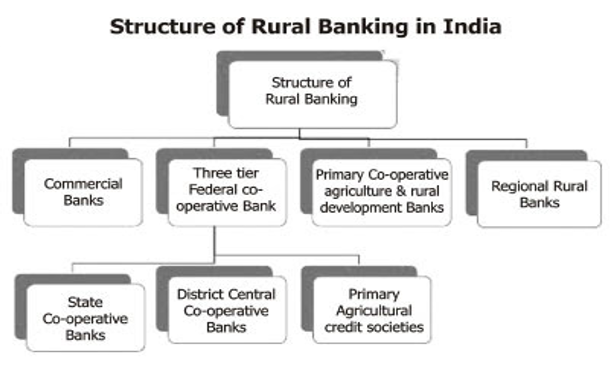
About the Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- RRBs are financial institutions that were established to fulfil the banking needs of rural areas.
- They were created with the aim of promoting rural agriculture, trade, commerce, and other productive activities by providing credit and other banking facilities to the rural population.
- They were established in 1975 on the recommendation of the Narsimhan Working Group.
- RRBs are jointly owned by the Government of India, the concerned State Government, and the Sponsor Bank. The Sponsor Bank is usually a private commercial bank (like HDFC, ICICI etc) or a public sector bank (like SBI or PNB etc).
- RRBs operate on a three-tier structure. At the top level, there is the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), which provides overall policy directions and refinancing facilities to RRBs. Under NABARD, there are State-level Rural Banks, and under them, there are Regional Rural Banks.
- RRBs are required to meet specific priority sector lending targets set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Priority sector lending includes lending to agriculture, micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), education, housing, and other specified sectors that benefit the economically weaker sections of society.
- The decision to exempt RRBs from the ‘merger related investigation’ is signalling towards the further consolidation of RRBs.
Background of the Consolidation of RRBs in India
- Consolidation of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) refers to the process of merging multiple RRBs to form a larger, stronger entity.
- The objective of this consolidation is to improve the financial situation, operational efficiency, and overall performance of RRBs.
- First Phase (2005): The first phase of consolidation of RRBs took place in 2005, where there were 196 RRBs. The Indian government decided to merge RRBs operating within the same state. The objective was to create larger RRBs with a stronger capital base and wider operational reach.
- Second Phase (2009): The second phase of consolidation occurred in 2009. The primary aim was to improve the financial health of the banks and to create regional rural banks that could provide better banking services to the rural population.
- Third Phase (2012-2013): In the third phase of consolidation, the government and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) undertook efforts to attach selected RRBs with strong sponsor banks. This move was aimed at enhancing the operational efficiency and financial stability of RRBs.
- Fourth Phase (2019): The fourth phase of consolidation occurred in 2019, where the government announced the merger of several RRBs to form strong RRBs. Currently, there are almost 43 RRBs.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi