- Courses
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
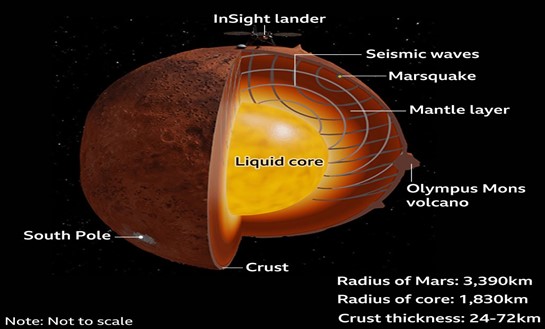
Marsquake
Marsquake
25-10-2023
Context
Recently, scientists have revealed the source of the most powerful marsquake in history.
Key Findings Related to Marsquake
- A Marsquake, or Martian earthquake, is a seismic event occurring on Mars. In 2022, a significant marsquake with a magnitude of 4.7 was recorded.
- Similar seismic indications from previous quakes triggered by meteoroids led to the initial suspicion of a meteoroid impact.
- The European Space Agency, the Chinese National Space Administration, the UAE Space Agency, and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) worked together on a ground-breaking effort to look for a crater on Mars.
- Since there was no impact crater discovered during the search, it was determined that increased seismic activity was the cause of the earthquake, which was caused by internal tectonic processes.
- The reason was identified as the accumulated strains in the crust of Mars, which developed over billions of years as a result of varying rates of cooling and shrinkage in various locations.
- This finding will help determine safe landing spots and areas that astronauts should avoid in the future when exploring Mars.
Major Facts Related to Mars
- Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, takes its name from the Roman God of war. It is often referred to as the "Red Planet" due to its distinctive reddish appearance. This reddish colouration is primarily attributed to the presence of a significant amount of iron oxide, commonly known as rust, in its surface rocks and soil.
- Mars is almost half the size of Earth and has a diameter of 6,791 kilometres, making it the second smallest planet in our solar system after Mercury.
- It is home to the moons Phobos and Deimos.
- Because of its considerable distance from the sun, the planet experiences extreme cold, with equatorial temperatures reaching 20°C and polar parts reaching as low as -140°C.
- The tallest volcano in our solar system, Olympus Mons, is located on Mars and is about three times higher than Mount Everest.
- Due to its extended orbit around the Sun, a Martian year lasts about twice as long as an Earth Day, lasting 687 Earth days. A Martian day is 24 hours and 37 minutes, somewhat longer than an Earth Day.
- The plane of Mars' orbit around the Sun is skewed by 25 degrees on its axis of rotation. This is comparable to Earth's 23.4-degree axial tilt.
- Although the seasons on Mars are different from those on Earth, they stay longer.
Missions Sent to Mars
- India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan (2013).
- Tianwen-1: China's Mars Mission (2021).
- ExoMars rover (2021) (European Space Agency).
- UAE’s Hope Mars Mission (UAE’s first-ever interplanetary mission) (2021).
- Mars 2 and Mars 3 (1971) (Soviet Union).
Q. Consider the following statements: (UPSC-2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi