- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Korean 'Artificial Sun' Sets Record At A Temperature 7 Times Hotter Than The Sun's Core.
Korean 'Artificial Sun' Sets Record At A Temperature 7 Times Hotter Than The Sun's Core.
25-05-2024
- South Korean scientists achieved a breakthrough in nuclear fusion research.
- Their reactor, Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR), successfully sustained plasma at a record-breaking temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius for 48 seconds.
- This is a significant leap as it's seven times hotter than the Sun's core.
- The previous record, also held by KSTAR, was 31 seconds achieved in 2021.
International Collaboration:
- The Tokamak (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) is a collaborative project launched in 1985 by 35 nations, including India.
- Located in France, ITER aims to demonstrate the potential of nuclear fusion as a large-scale and carbon-free energy source.
- KSTAR serves as a prototype for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) project in France, a global collaboration for developing fusion technology.
Significance:
- Nuclear fusion promises a clean and virtually limitless energy source by replicating the process that powers stars.
- This achievement marks a major step towards developing commercially viable fusion reactors.
- While challenges remain, this record demonstrates significant progress in harnessing fusion energy.
What is a Fusion reactor?
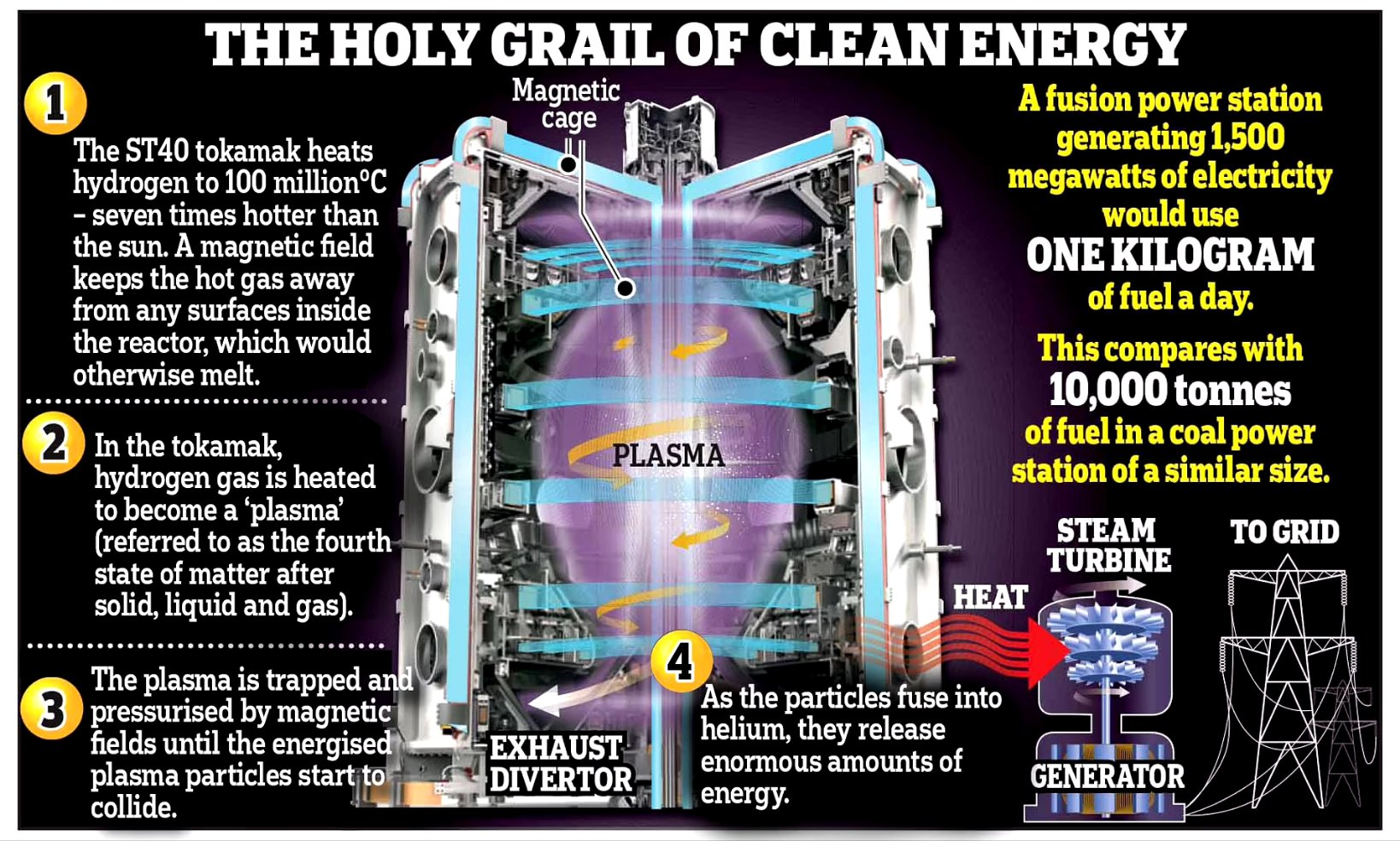
- Fusion reactors are devices designed to harness the energy released during nuclear fusion reactions.
- Nuclear fusion is the process where 2 lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy in the process.
- This is the same process that powers the sun and stars.
Types of fusion reactors:
There are 2 main types of fusion reactors currently being developed:
-
Magnetic confinement reactors: These use powerful magnetic fields to confine the plasma and keep it away from the reactor walls. The most common type of magnetic confinement reactor is the tokamak.
-
Inertial confinement reactors: These use high-energy lasers or particle beams to compress and heat a small pellet of fuel, causing it to explode and ignite fusion reactions.
Challenges and future prospects:
- Fusion power has the potential to be a safe, clean, and virtually limitless source of energy.
- However, there are still many challenges to overcome before fusion reactors can become a reality.
- These challenges include achieving sustained fusion reactions, developing materials that can withstand the extreme conditions inside a fusion reactor, and finding ways to make fusion power economically viable.
Despite the challenges, there has been significant progress in fusion research in recent years, and many scientists believe that fusion power could be a major source of energy in the future.
Must Check: UPSC Coaching Institute In Delhi


