- Courses
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
KAKRAPAR ATOMIC POWER PROJECT
KAKRAPAR ATOMIC POWER PROJECT
Context
Recently, the 4th module of the Kakrapar Atomic Power Project (KAPP-4) in Gujarat, boasting a capacity of 700 MWe, initiated a controlled fission chain reaction, achieving criticality.
initiated a controlled fission chain reaction, achieving criticality.
KAPP-4: Key points
Built by |
Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) |
Fuel |
Pressurised heavy water reactors (PHWRs), including those at KAPP, utilise natural uranium for fuel. |
Coolant |
In the context of nuclear reactors, a coolant is a substance circulated to remove or transfer heat, with water being the most commonly used coolant. |
Moderator |
A moderator, such as ordinary water, heavy water, or graphite, is employed in reactors to slow down high-velocity neutrons, thereby increasing the likelihood of fission. |
About Criticality and Nuclear Fission:
Process |
In the nuclear fission process, a neutron colliding with an atom, like Uranium-235, causes it to split, releasing substantial heat convertible into energy. |
Fissile choice |
The choice of Uranium-235 for nuclear power is due to its favourable splitting characteristics. |
Regulatory approval |
Regulatory approval from India's Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) was obtained for the criticality test, ensuring safe implementation. |
Significance of this achievement: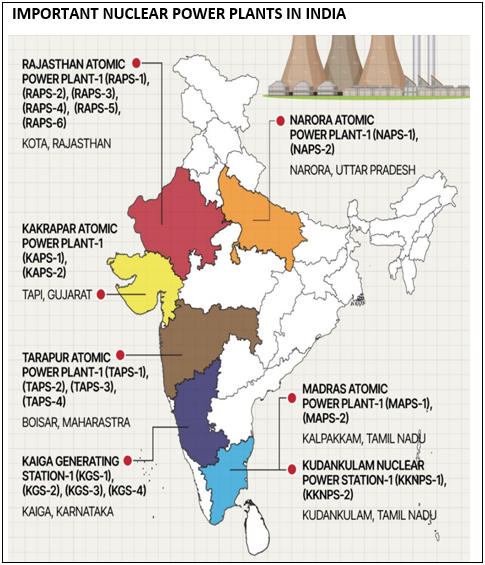
This milestone signifies a crucial advancement in the nuclear power plant's operational readiness. Enabling efficient and continuous electricity production through nuclear energy.
India's nuclear power program operates in three stages:
1. First Stage: Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs)
- Focuses on using natural uranium as fuel and heavy water as a moderator and coolant.
- Establishes a self-sustaining nuclear fuel cycle with the goal of developing indigenous nuclear technology.
2. Second Stage: Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs)
- Involves the use of fast breeder reactors to produce more fissile material (like plutonium-239) than consumed.
- Aims to achieve a closed nuclear fuel cycle, where FBRs produce fuel for themselves and other reactors.
3. Third Stage: Thorium-Based Reactors
- Envisions utilising thorium as a primary nuclear fuel.
- Seeks to develop advanced reactors capable of using thorium to generate power, promoting sustainability and minimising nuclear waste.



