- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
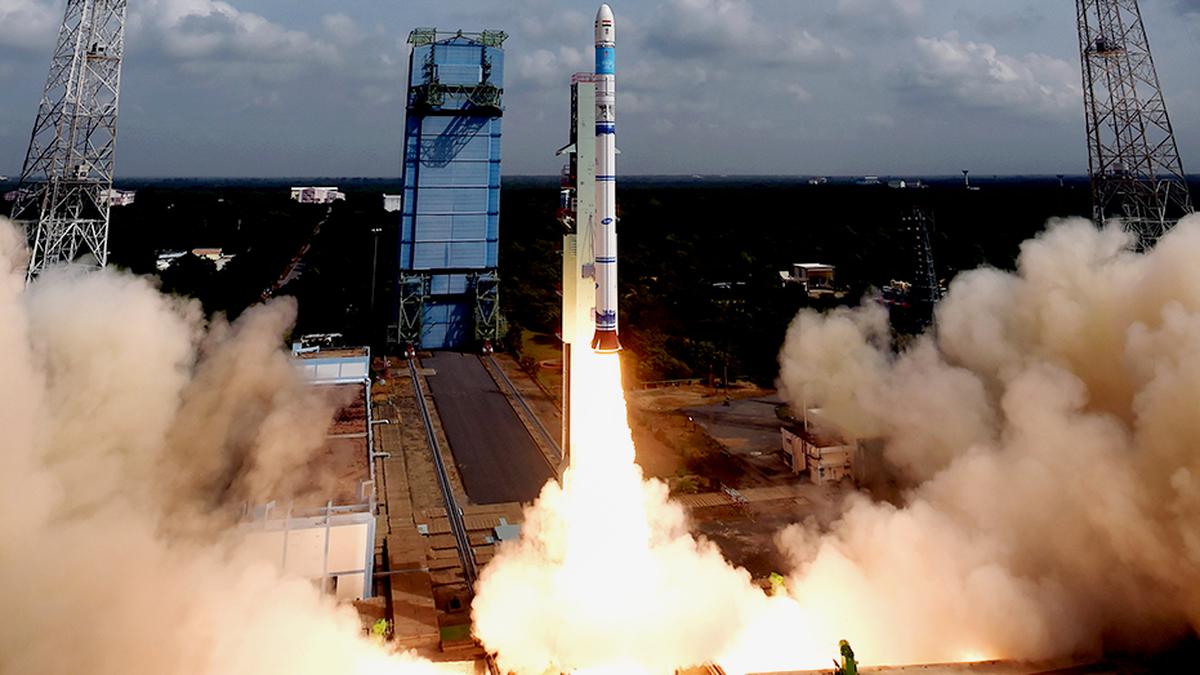
ISRO launches SpaDeX mission for space docking
ISRO launches SpaDeX mission for space docking

- On December 30, 2024, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the SpaDeX mission (Space Docking Experiment), marking a major achievement in India’s space exploration capabilities.
- This mission aims to demonstrate India’s space docking technology, a crucial step towards future interplanetary missions, space station construction, and large-scale payload transfers in space.
- The mission began with the launch of PSLV-C60, ISRO’s reliable workhorse rocket, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
- PSLV-C60: This refers to the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) used for the mission.
- It's a reliable workhorse rocket that has been used for numerous successful launches by ISRO.
- The rocket successfully placed two small satellites into lower Earth orbit (LEO), which will serve as the key components for demonstrating docking in space.
Key Highlights of the SpaDeX Mission:
- Launch Details: The PSLV-C60 rocket launched 2 small satellites into orbit, designed for the SpaDeX mission.
- The satellites are the SDX01 Chaser and SDX02 Target, which will test the capabilities for docking in space.
- Docking Date: According to S. Somanath, ISRO’s chairperson, the docking is planned for January 7, 2025.
- This mission sets the foundation for India’s future space initiatives, including the construction of a space station, the Chandrayaan-4 mission to the Moon, and the development of space infrastructure.
- Future Missions: ISRO is planning multiple high-profile missions for 2025, starting with the launch of the NVS-02 satellite on the GSLV rocket for India’s NavIC navigation constellation.
What is Space Docking and Why is It Crucial?

- Space docking refers to the process where two spacecraft connect while in orbit, allowing them to work together.
- Docking is essential for future missions that require the transfer of payloads, such as heavy modules for space stations, or even for interplanetary missions.
- This capability is important for long-duration space travel, where multiple spacecraft will need to cooperate in orbit to assemble and maintain space infrastructure or undertake complex tasks.
Global Significance:
- The successful completion of this docking experiment will make India the 4th country globally to possess docking technology, joining the ranks of the United States, Russia (formerly the USSR), and China.
- This will place India among the leaders in advanced space exploration technologies.
Mission Components and Docking Process
The SpaDeX mission involves two satellites:
- SDX01 (Chaser): The Chaser satellite is equipped with a high-resolution camera for visual tracking and docking assistance. It will reduce its distance from the Target satellite progressively.
- SDX02 (Target): The Target satellite carries a multispectral payload to monitor natural resources, vegetation, and space radiation. This satellite also contains a propulsion system to maintain the required distance between the two satellites during the docking process.
Docking Maneuver:
- After the two satellites are placed in a 475-km circular orbit, the mission will initiate the docking process.
- A 20-km distance will first be created between the Chaser and Target satellites.
- The propulsion system on the Target satellite will fire to counter the relative velocity, ensuring the two satellites maintain a fixed distance and prevent drift.
- Over the course of 7-8 days, the Chaser satellite will progressively reduce the distance to the Target:
- 5 km → 1.5 km → 500 meters → 225 meters → 15 meters → 3 meters, before making the final docking.
- Once the docking occurs, the two satellites will transfer electrical power and stay connected for a short period before undocking and continuing their separate missions.
Scientific and Technological Innovations in the SpaDeX Mission
The SpaDeX mission is not only about docking technology but also features multiple cutting-edge technologies and experiments that will support future space exploration.
Some key components include:
POEM (PS4 Orbital Experiment Module):
The POEM module serves as a platform to test and demonstrate 24 different technologies from ISRO, startups, and educational institutions. These technologies will span various applications including satellite servicing, space sustainability, and biological studies.
- CROPS (Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies): The CROPS experiment will focus on the germination of seeds and plant growth in microgravity, which is critical for future long-term space missions where food production in space will be necessary.
- The plants will grow up to the two-leaf stage for observation.
- Robotic Arms: The mission will test two types of robotic arms:
- Debris Capture Arm: This arm will attempt to capture space debris using a visual feed and object motion prediction.
- Moveable Robotic Arm: This robotic arm is being tested for potential use in future satellite servicing missions, such as repairing or refueling satellites in orbit.
Other Experiments:
- Amity University: A study of plant cells in microgravity will compare their behavior in space to that in Earth’s gravity.
- RV College of Engineering, Bengaluru: An experiment will study the growth curve of gut bacteria in space, exploring how microorganisms behave in microgravity.
- Synthetic Aperture Radar: Two synthetic aperture radar systems will be tested for earth observation applications, particularly for monitoring natural resources and vegetation.
- Green Propulsion System: The mission will demonstrate a green propulsion system as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional rocket propulsion methods, which typically rely on toxic propellants.
Importance of Space Docking for Future Missions
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): One of the key future projects for ISRO is the development of the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), India’s first space station.
- The space station will consist of five modules that will need to be docked in space.
- This will require the capability to assemble large structures in orbit, making docking technology essential.
- The first module of the space station is planned for launch in 2028.
- Chandrayaan-4 Mission: The Chandrayaan-4 mission, aimed at bringing back lunar samples to Earth, will require docking technology.
- The re-entry module, which is designed to withstand the intense heat of re-entry, will be launched separately from the sample transfer module.
- These two modules will need to dock in space before returning to Earth with the lunar samples.
- Heavy Payload Missions: Space docking also facilitates the transport of heavy payloads that cannot be launched in a single mission.
- Different spacecraft can dock in orbit to combine their resources and perform complex tasks that would otherwise be impossible with a single spacecraft.
- This will be particularly useful for interplanetary missions that require a combination of spacecraft modules for long-duration operations.
Global and National Impact
India’s Position in Space Exploration:
- The success of the SpaDeX mission enhances India’s standing as a leader in space exploration and allows the country to join the ranks of space powers like the US, Russia, and China.
- India’s growing space capabilities could open new avenues for international collaborations, especially in space station development, interplanetary exploration, and satellite servicing.
Technological Advancement:
- The mission also places India at the forefront of the space innovation ecosystem, integrating contributions from startups, academic institutions, and space agencies.
- The technology demonstrations will push the boundaries of space science and help address global challenges such as space debris management and sustainable space exploration.
Private Sector and Research Collaboration:
- The SpaDeX mission underscores the growing role of private companies and educational institutions in India’s space program.
- This collaboration will fuel further growth in the Indian space sector, with more startups and research bodies contributing to space technology development.
Conclusion
The SpaDeX mission is a pivotal milestone for ISRO and for India’s space ambitions. By demonstrating space docking technology, ISRO is not only preparing for complex future missions like the Chandrayaan-4 and Bharatiya Antariksh Station but also positioning India as a leader in global space exploration. The successful demonstration of docking will have far-reaching implications for satellite servicing, space infrastructure development, and interplanetary exploration.
|
Also Read |
|