- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Israel Used GPS Spoofing Against Iran ||ENSURE IAS
Israel Used GPS Spoofing Against Iran ||ENSURE IAS
20-04-2024
Israel reportedly used GPS spoofing to disrupt Iran's missile targeting teams by manipulating Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation signals.
What is GPS Spoofing?
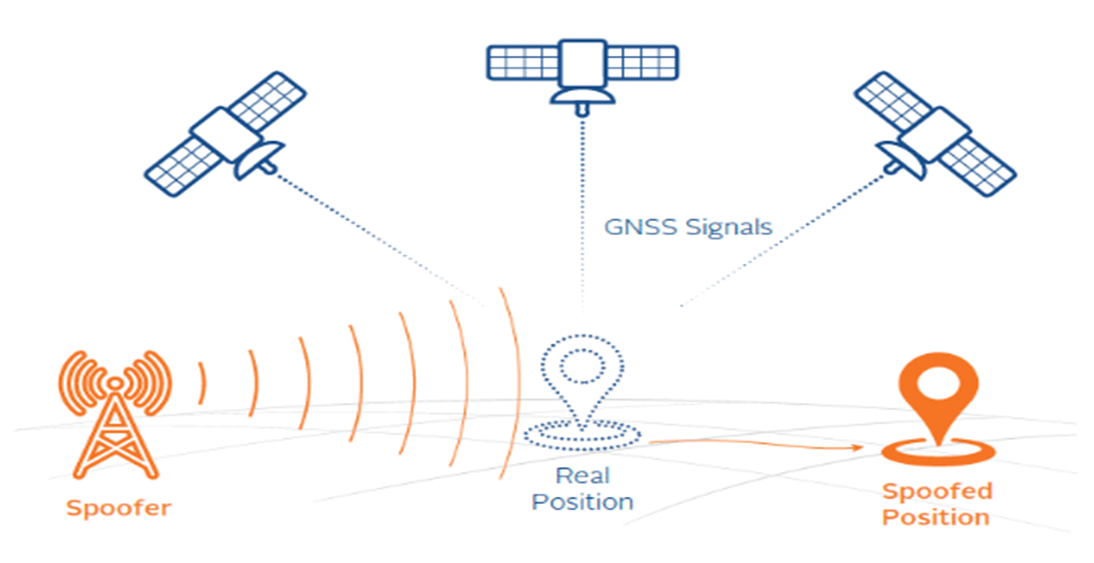
- GPS Spoofing (or GPS Simulation):
- GPS spoofing involves manipulating a GPS receiver by transmitting a false GPS signal.
- This misleads the recipient, causing it to believe that it is located somewhere where it is not, resulting in inaccurate location data.
- Cyberattack:
- GPS spoofing undermines the reliability of GPS data critical to various applications.
- Evolution of Spoofing:
- Initially a theoretical threat, GPS spoofing has now become a practical concern due to accessible software and hardware capable of transmitting fake GPS signals.
- Spoofing vs. Jamming:
- Spoofing is different from jamming. Jamming involves disrupting GPS signals, while spoofing involves manipulating them.
- Aircraft commonly face jamming problems, but this type of spoofing has never been reported before.
Working of GPS Spoofing:
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities:
- GPS spoofing takes advantage of the weak signal strength of GPS satellites.
- GPS Functioning:
- The Global Positioning System sends signals from satellites to GPS receivers on Earth.
- Receivers calculate their position based on the time taken for these signals to arrive.
- Overwhelming Weak Signals:
- The weak signal strength of GPS satellites makes them susceptible to being overwhelmed by fake signals, leading to inaccurate location data.
Impacts of GPS Spoofing:
- Navigation Concerns:
- GPS spoofing can have devastating effects, especially in navigation-dependent scenarios.
- Industry Implications:
- GPS spoofing has the potential to impact industries such as logistics, supply chain, telecommunications, energy and defense on a large scale.
Navigation:
- Navigation refers to the study of monitoring and controlling the movement of a ship or vehicle from one place to another.
FAQs:
Q: How does GPS work?
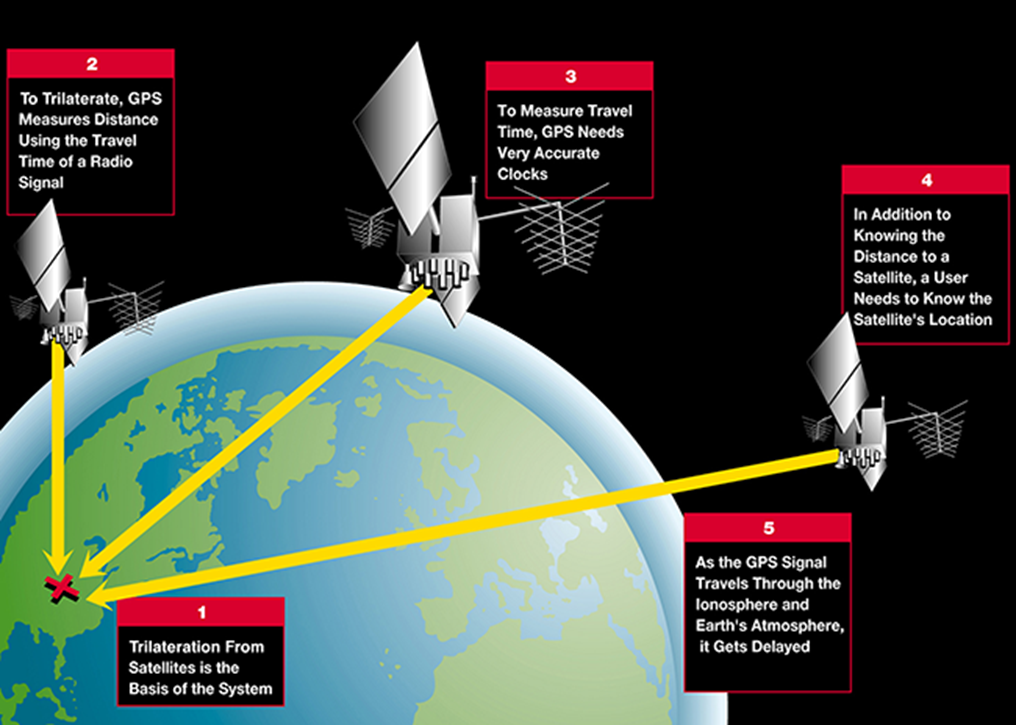
- GPS uses satellites to determine location through a technique called trilateration.
- The GPS satellites carry atomic clocks that provide accurate time, which is then broadcast in codes that a receiver can use to determine the time the signal was sent.
- The receiver uses the time difference between the time of signal reception and the broadcast time to calculate the distance from the satellite.
- The GPS satellites circle the Earth twice a day, each transmitting a unique signal and orbital parameters. A GPS receiver must be locked on to the signal of at least three satellites to calculate a 2D position (latitude and longitude) and track movement. With four or more satellites in view, the receiver can determine the user's 3D position (latitude, longitude and altitude).
GPS works in any weather conditions, anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day, with no subscription fees or setup charges. The U.S. Department of Defense (USDOD) originally put the satellites into orbit for military use, but they were made available for civilian use in the 1980s.
GPS has many applications, including:
- Road transportation
- Fleet management
- Public transport monitoring
- Taxi services
- Dispatch services
- Logistics and delivery services
- Private car users
- Internet of things
- Banking
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
India’s EV Mission: Progress Delayed, Not Denied
India’s EV Mission: Progress Delayed, Not Denied


