- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons | 26 September
International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons | 26 September

The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons, observed annually on September 26, serves as a critical reminder of the world’s ongoing struggle against one of the most dangerous threats to humanity—nuclear weapons.
Background and Resolutions:
- Established: The Day was declared by the General Assembly in December 2013 (resolution 68/32), following a high-level meeting on nuclear disarmament on September 26, 2013.
- Annual Commemoration: Since 2014, the Day has been observed annually, promoting activities to enhance awareness regarding nuclear disarmament.
- UN Resolutions: Subsequent resolutions have called for negotiations on comprehensive conventions to prohibit nuclear weapons' possession, development, and use.
Historical Context:
- 1946: The UN General Assembly's first resolution focused on nuclear disarmament, leading to the formation of the Atomic Energy Commission (dissolved in 1952) to propose control over nuclear energy and weapons.
- 1959: The General Assembly endorsed the broader goal of general and complete disarmament.
- 1978: The first Special Session of the General Assembly devoted to disarmament highlighted nuclear disarmament as a primary objective.
Key Reasons Why This Day is Significant:
- UN General Assembly Resolution: The day was officially established through a UN General Assembly resolution, emphasizing the need for increased public awareness about the threats posed by nuclear weapons.
- Promotion of Global Disarmament: It serves as a call to action for countries to actively engage in nuclear disarmament, underscoring the urgency of eliminating nuclear arsenals worldwide.
- Alignment with the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT): The observance of this day reinforces the objectives of the NPT, which seeks to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and promote total disarmament.
- Historical Significance: The day builds on decades of disarmament efforts, from the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki to the Cold War nuclear arms race, reminding us that the goal of disarmament remains incomplete.
- Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zones: It highlights the establishment of nuclear-weapon-free zones in regions like Latin America and the Pacific, showcasing successful steps toward a nuclear-free world.
- Humanitarian Impact: The day emphasizes the severe human and environmental impacts of nuclear weapons, urging nations to recognize the global threat these weapons represent.
- Resistance from Nuclear Powers: Despite global calls for disarmament, nuclear-armed states continue to modernize and maintain their arsenals, posing a significant challenge to disarmament initiatives.
Key Facts on Nuclear Weapons:
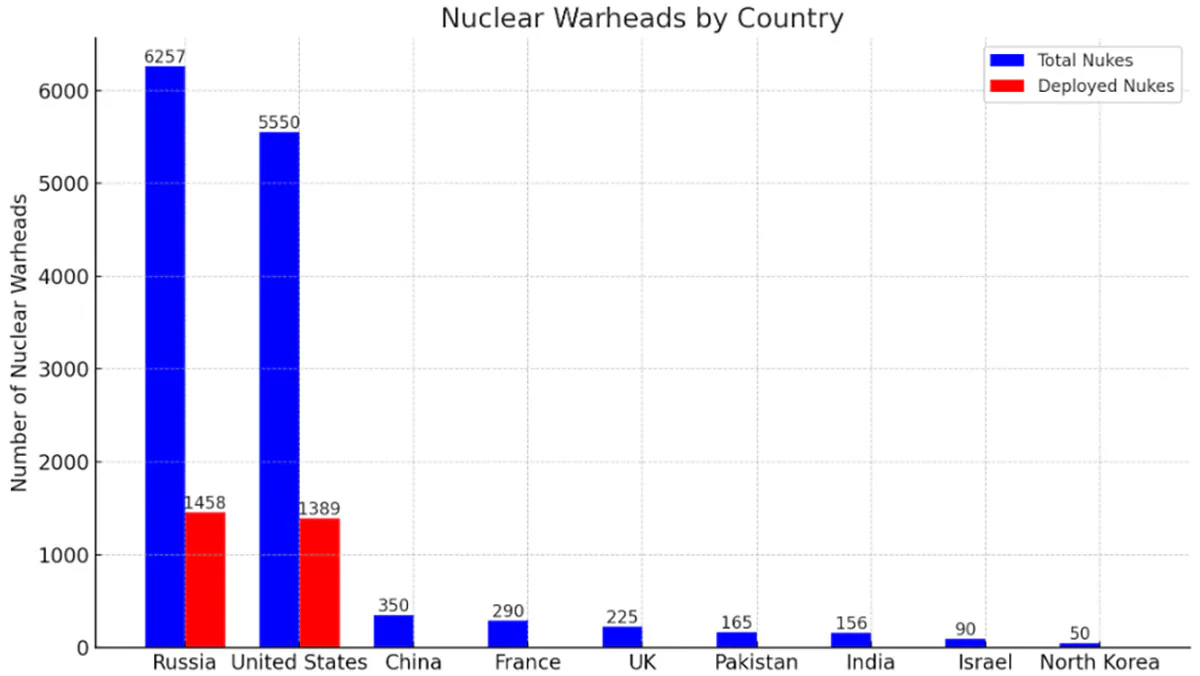
Statistics:
- Global Nuclear Stockpile: Approximately 13,080 nuclear warheads exist globally, a stark reminder of the ongoing threat.
- Russia: Holds around 6,257 warheads, with 1,458 actively deployed.
- United States: Possesses about 5,550 warheads, with 1,389 operational.
- Possessor States: More than half the world's population lives in countries with nuclear arsenals or alliances (e.g., NATO).
- Decline in Numbers: Although deployed nuclear weapons have decreased since the Cold War, no nuclear weapons have been dismantled under treaty obligations.
- Absence of Negotiations: Currently, no significant nuclear disarmament negotiations are taking place.
Notable Events in Nuclear Disarmament History:
|
Year |
Notable Event |
|
1945 |
The atomic bombs destroyed Hiroshima and Nagasaki, killing an estimated 213,000 people immediately. |
|
1946 |
The General Assembly identified nuclear disarmament as a leading goal of the United Nations in its first resolution. |
|
1959 |
The General Assembly included nuclear disarmament in the comprehensive goal of general and complete disarmament. |
|
1963 |
The Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests (Partial Test Ban Treaty) was opened for signature, prompted by the Cuban Missile Crisis. |
|
1978 |
The General Assembly held its first Special Session Devoted to Disarmament, prioritizing nuclear disarmament and prevention of nuclear war. |
|
1985 |
The South Pacific became the second nuclear-weapon-free zone (Treaty of Rarotonga). |
|
1991 |
South Africa voluntarily renounced its nuclear weapons program. |
|
1992 |
Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine renounced nuclear weapons via the Lisbon Protocol to the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START I). |
|
1995 |
The NPT Review and Extension Conference adopted decisions on the indefinite extension of the Treaty and related principles and objectives. |
|
1995 |
Southeast Asia became the third nuclear-weapon-free zone (Bangkok Treaty). |
|
1996 |
Africa became the 4th nuclear-weapon-free zone (Pelindaba Treaty). |
|
1996 |
The International Court of Justice provided an advisory opinion on the legality of the threat or use of nuclear weapons. |
|
1996 |
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty opened for signature. |
|
2006 |
Central Asia became the 5th nuclear-weapon-free zone (Treaty on a Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone in Central Asia). |
|
2013 |
The General Assembly held its first high-level meeting on nuclear disarmament and declared September 26 as the International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons. |
|
2017 |
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons was adopted, the first legally binding instrument for nuclear disarmament in 20 years. |
|
2020 |
The fiftieth anniversary of the entry into force of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). |
|
2021 |
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons entered into force on January 22. |
|
2021 |
The New START treaty was extended until February 4, 2026. |
|
2022 |
States parties to the TPNW adopted the “Vienna Declaration” at the First Meeting of the States parties. |
|
2023 |
The Russian Federation announced it would suspend participation in the New START treaty. |
|
2023 |
The first session of the Preparatory Committee for the 2026 Review Conference of the NPT took place. |
|
2023 |
The Russian Federation announced withdrawal from the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty on November 2. |
|
2024 |
The second session of the Preparatory Committee for the 2026 Review Conference of the NPT took place in Geneva. |
Conclusion
The International Day for the Total Elimination of Nuclear Weapons is a crucial observance aimed at reinforcing global commitments to nuclear disarmament. It emphasizes the urgent need for collective action to address the existential threat posed by nuclear weapons and to strive for a peaceful, secure world free from these arms.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




