- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
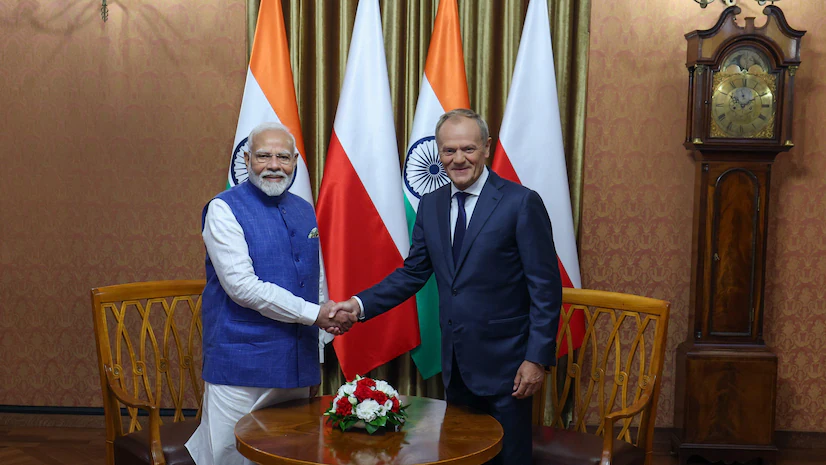
India-Poland Joint Statement: Strategic Partnership
India-Poland Joint Statement: Strategic Partnership
24-08-2024

Historical Context
- Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Poland on August 21-22, 2024, at the invitation of Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk.
- The visit marked the 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Poland.
- This was the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister to Poland in 45 years, since Morarji Desai's visit in 1979.
Elevation to Strategic Partnership
- During the visit, the two leaders elevated their bilateral relationship to a "Strategic Partnership."
- Aimed at deepening cooperation across various domains and enhancing global stability.
Agenda and Meetings
- Meetings:
- PM Modi met with Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk and President Andrzej Duda.
- Discussions covered trade, investment, science, technology, defense, security, cultural cooperation, and people-to-people ties.
- Address to the Indian Diaspora:
- PM Modi addressed the Indian community in Warsaw, highlighting strong bilateral ties and the role of the diaspora.
- Announced the Jamsaheb Memorial Youth Exchange Program, inviting 20 Polish youth to India annually.
Key Points from Address to Diaspora
- Bilateral Ties: Emphasized shared democratic values.
- Diaspora Role: Acknowledged the diaspora's contribution to bilateral relations and Operation Ganga.
- Historical Acknowledgment: Recalled Poland’s assistance during the Gujarat earthquake and India's future aspirations.
- Areas of Collaboration: Highlighted potential collaborations in technology, clean energy, and green growth.
Outcomes of Meetings
- Strategic Partnership: Upgraded India-Poland relations to a “Strategic Partnership.”
- Sectoral Opportunities: Identified collaboration opportunities in food processing, urban infrastructure, water management, electric vehicles, green hydrogen, renewable energy, AI, and mining.
- Cultural Ties: Emphasized the historical bond between the two countries.
Role in Russia-Ukraine Conflict
- Statement by Tusk: Prime Minister Tusk suggested that India could play a crucial role in resolving the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- PM Modi’s Stance: PM Modi’s commitment to seeking a peaceful resolution was acknowledged.
Engagements with Polish Scholars and Business Leaders
- Scholars: PM Modi met with Polish scholars and Indologists, appreciating their contributions to cultural ties.
- Business Leaders: Engaged with Polish business leaders to discuss investment opportunities in India and collaboration in sectors such as IT, hygiene products, and emerging technologies.
Promotion of Kabaddi
- PM Modi met with the Kabaddi Federation of Poland, commending efforts to popularize Kabaddi in Europe and emphasizing the role of sports in promoting cultural exchange.
Historical Background
- Diplomatic Relations:
- Established in 1954.
- Embassies opened in Warsaw and New Delhi in 1957.
- World War II Refugee Assistance:
- Over 6,000 Polish women and children were sheltered in India during World War II.
- Maharaja Jam Saheb Digvijaysinhji Ranjitsinhji of Nawanagar played a crucial role in providing sanctuary to these refugees.
Action Plan (2024-2028) for the Implementation of the India-Poland Strategic Partnership
- Political Dialogue and Security Cooperation:
- Regular contacts between foreign ministers.
- Annual political dialogue at the level of deputy ministers.
- Regular consultations on defense cooperation.
- Trade and Investment:
- Cooperation in high-tech, agriculture, energy, climate, infrastructure, defense, healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and mining.
- JCEC meetings at least twice every five years.
- Climate, Energy, Mining, Science, and Technology:
- Expand cooperation in sustainable technological solutions, cleaner energy approaches, and mining collaboration.
- Work on a cooperation agreement for space exploration.
- Transport and Connectivity:
- Explore cooperation in developing transport infrastructure and enhance flight connections.
- Terrorism:
- Condemnation of terrorism and efforts to designate individuals affiliated with UN Security Council 1267 sanctions committee-listed groups as terrorists.
- Cyber Security:
- Strengthen interactions and exchanges in ICT-related fields.
- Health:
- Strengthen collaboration in health by sharing information and enhancing contacts among health experts.
- People-to-People Ties and Cultural Cooperation:
- Implement the Agreement on Social Security.
- Strengthen cooperation between cultural institutions, artists, scholars, and think tanks.
- Promote cooperation in higher education and establish partnerships between academic institutions.
- Expand tourist flows and hold cultural festivals.
- India-EU Relations:
- Support the early conclusion of India-EU trade and investment negotiations.
- Operationalize the India-EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC).
- Implement the India-EU Connectivity Partnership.
Way Forward
- Regularly monitor the implementation of the Action Plan through annual political consultations.
- Review and potentially extend the Action Plan for another five-year period by the respective foreign affairs ministers.
Conclusion
The India-Poland Joint Statement of August 22, 2024, marks a significant milestone in bilateral relations, elevating them to a "Strategic Partnership." This partnership is set to enhance cooperation across multiple sectors, bolster economic ties, and address global challenges together. Both nations have committed to deepening their collaboration through a comprehensive five-year action plan, signaling a new era of mutual growth and stability.