- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India leads as top origin country and destination for Hindu migrants
India leads as top origin country and destination for Hindu migrants
04-09-2024
Recently, the Pew Research Center released a report titled "The Religious Composition of the World’s Migrants," based on data from the United Nations and 270 censuses and surveys. This report examines the global patterns of religious migration and provides insights into how religion influences both emigration and immigration trends.
Key Findings:
Global Migration Statistics
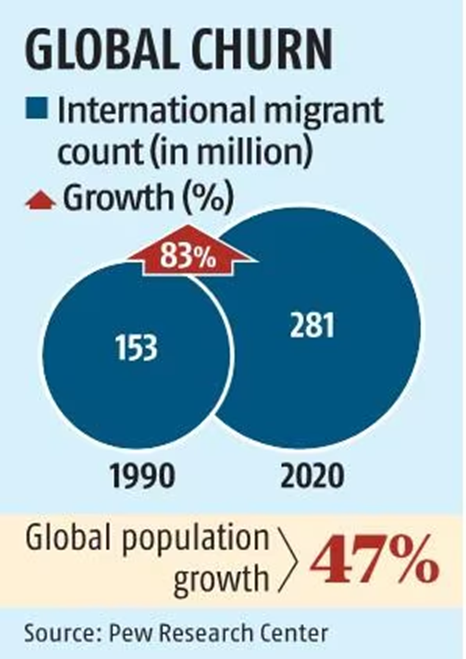
- Total International Migrants: Over 280 million people (3.6% of the world’s population) were international migrants in 2020.
- Migration Increase: From 1990 to 2020, the number of international migrants increased by 83%, significantly outpacing global population growth of 47%.
- Average Distance Traveled: Migrants travel an average distance of 2,200 miles.
Religious Composition of Migrants
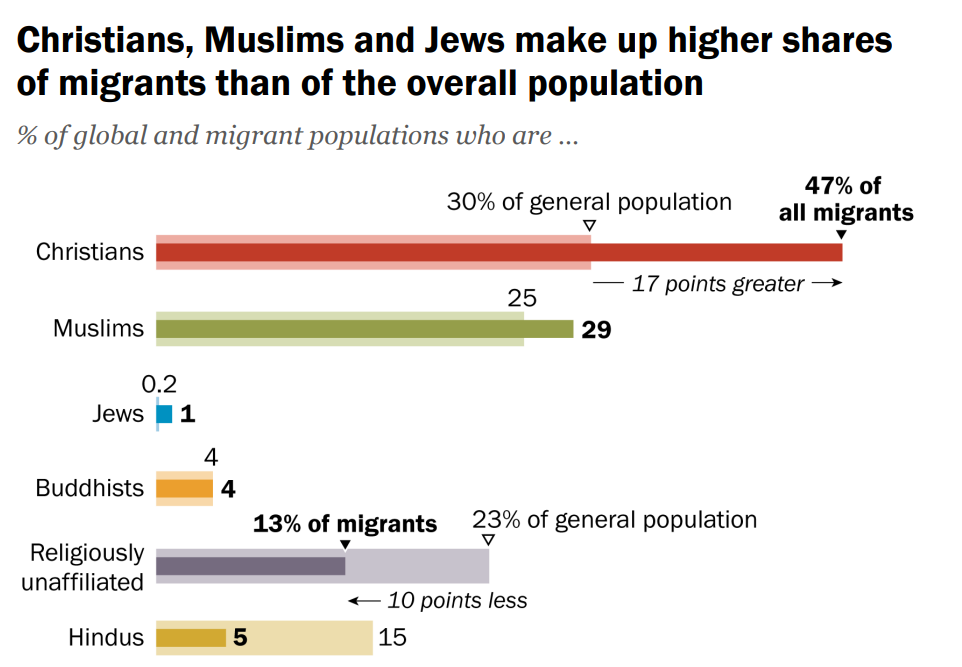
- Christians: Represent the largest share of global migrants at 47%.
- Hindus: Comprise 5% of all international migrants. Hindus tend to travel longer distances, averaging 3,100 miles.
Trends by Religion and Region
-
Hindu Migration Trends:
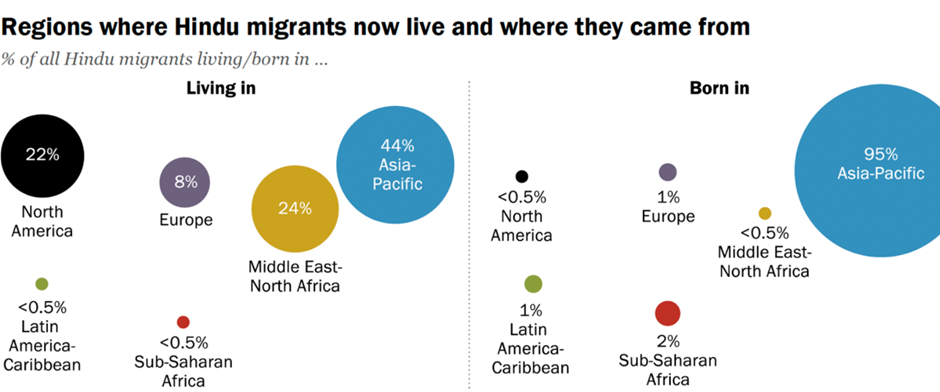
- Emigration & Immigration: India is both a top source and destination for Hindu migrants.
- Global Distribution: Hindu migrants are predominantly from the Asia-Pacific region, with significant numbers from India, Bangladesh, and Nepal.
- Destinations: The largest share of Hindu migrants resides in the Asia-Pacific region (44%), followed by the Middle East-North Africa (24%) and North America (22%).
-
Christian Migration Trends:
- Global Share: Christians make up 47% of the global migrant population.
-
Muslim Migration Trends:
- Indian Muslim Migrants: Represent 33% of all Indian-born migrants, with significant populations in UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Oman.
- Global Trends: India is the second-largest source of Muslim migrants.
-
GCC Countries:
- Growth: Migrant population in GCC countries grew by 277% since 1990.
- Religious Breakdown: 75% of GCC migrants are Muslims, while Hindus and Christians make up 11% and 14%, respectively.
- Indian Migrants: GCC countries host 9.9 million Indian migrants.
Migration Patterns and Religion:
- Religious Alignment: Migrants often move to countries where their religion aligns with the local population, influenced by cultural and religious familiarity.
Hindu Migration Patterns
- Underrepresentation: Hindus make up a smaller share (5%) of international migrants compared to their global population proportion (15%).
- Longest Distance: Hindu migrants travel the longest distances, averaging 3,100 miles, the farthest among Asian religious groups.
- Regional Destinations: Major destinations include the Asia-Pacific region, Middle East-North Africa, and North America.
- Source Countries: Primarily from India (57% of Hindu migrants), with significant numbers from Bangladesh and Nepal.
Notable Migration Routes:
- India to US: 1.8 million Hindus migrate from India to the US for employment and education.
- Bangladesh to India: 1.6 million Hindus migrate from Bangladesh to India due to historical and socio-economic reasons.
Impact of Diaspora on Home-Country Growth
- Remittances: In 2022, migrants from emerging and developing countries sent USD 430 billion in remittances, three times more than financial aid received.
- GDP Contribution: Remittances constitute a significant portion of GDP in countries like Tajikistan (37%), Nepal (30%), and others.
- Diaspora Investments: Includes investments in home-country businesses and government bonds, enhancing financial capital.
- Knowledge Transfer: Diasporas contribute to productivity and development by transferring skills and knowledge.
- Business and Governance: Diaspora members assist with navigating global markets and improving local business practices, such as Indian executives facilitating outsourcing to India.
Conclusion
Migration and diaspora communities play a crucial role in boosting home-country economies through remittances, investments, and knowledge transfer. To maximize these benefits, governments should foster strong diaspora networks, reduce investment barriers, and support diaspora-driven initiatives to enhance capital inflow and sustainable development.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




