- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India Aims to Double Share of Manufacturing in GDP to 23% by 2047
India Aims to Double Share of Manufacturing in GDP to 23% by 2047
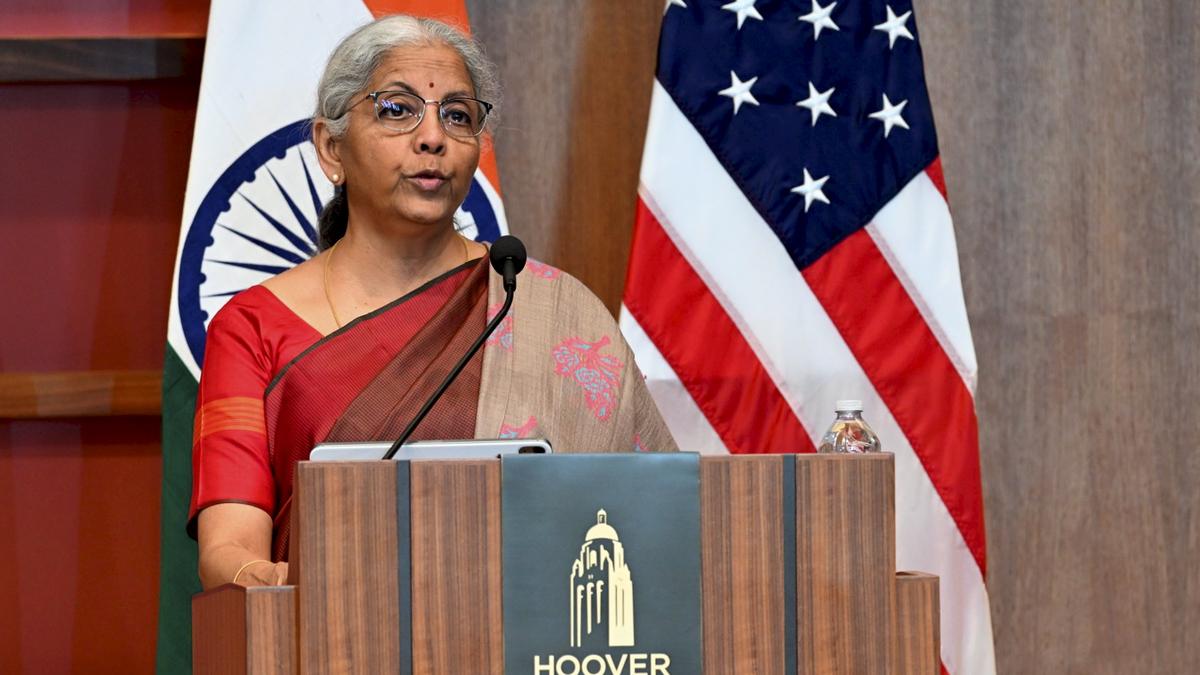

- In April 2025, FM Sitharaman announced that India wants to increase the contribution of the manufacturing sector in its economy (GDP) from 12% now to 23% by the year 2047.
- Why 2047?
- Because it marks 100 years of independence, and India wants to become a developed country (Viksit Bharat) by then.
Why Is This Important?
- India's economy today is mostly based on services (like IT, finance, tourism) — they make up about 64% of the GDP, but these do not create enough jobs, especially for low- and semi-skilled workers.
- Problems with current structure:
- Not enough jobs for India's large youth population (demographic dividend)
- Too much import of important goods like electronics and energy equipment
- Low participation in global manufacturing supply chains (like China or Vietnam)
Services vs. Manufacturing: Why Balance is Needed
|
Services Sector |
Manufacturing Sector |
|
64% of GDP |
~12% of GDP |
|
High-skill & urban jobs |
Labour-intensive, rural jobs |
|
Rapid growth |
Needed for job creation & exports |
Despite booming services (esp. IT, gig economy), manufacturing is essential for inclusive, sustainable, job-rich growth.
What Is the Government Planning to Do?
The government wants to:
- Create more jobs through manufacturing
- Reduce imports by producing more locally
- Export more and become part of global supply chains
- Focus on 14 high-potential sectors like electronics, pharma, semiconductors, EV batteries, etc.
Focus Areas: Which Sectors?
A. 14 Priority Sectors (via PLI Scheme)
|
Sector |
Key Details/Impact |
|
1. Electronics (LSEM) |
Mobile production ↑ 5.8 cr → 33 cr (2014–24), FDI ↑ 254%, exports ↑ |
|
2. Pharmaceuticals |
3rd largest by volume, 50% production exported |
|
3. Medical Devices |
Domestic CT/MRI production through tech transfer |
|
4. Automobiles |
₹25,938 cr outlay; EV focus; ₹67,690 cr expected investment |
|
5. Auto Components |
Linked to auto scheme; encourages advanced tech adoption |
|
6. Solar PV Modules |
₹24,000 cr outlay (Phases 1+2), target: 65 GW, import ↓, jobs ↑ |
|
7. Telecom & Networking |
60% import substitution, 5G/4G exports ↑ |
|
8. Drones & Components |
Turnover ↑ 7x; MSMEs/startups driving growth |
|
9. Food Processing |
Enhances exports, domestic value addition |
|
10. Textiles |
Focus on MMF & technical textiles; labour-intensive |
|
11. IT Hardware |
Local laptops, tablets, servers manufacturing encouraged |
|
12. White Goods (ACs, LEDs) |
Promotes energy efficiency; component ecosystem |
|
13. Specialty Steel |
Reduces import dependency, high-grade production |
|
14. Advanced Chemistry Cells (ACC) |
EV battery & grid storage boost |
B. Sunrise Sectors (New industries with high growth potential)
- Semiconductors
- Battery storage technologies
- Medical devices
- Renewable energy components
C. Labour-Intensive Industries
- Textiles
- Leather
- Crucial for rural employment and MSME sector
Government Strategy: Initiatives
A. PLI Scheme (Production Linked Incentive) :
|
Parameter |
Details |
|
Launched |
2020 |
|
Purpose |
Boost domestic manufacturing & exports |
|
Budget Outlay |
₹1.97 lakh crore (~US$24 billion) |
|
Investments (Till Aug 2024) |
₹1.46 lakh crore |
|
Production & Sales |
₹12.5 lakh crore |
|
Exports |
₹4 lakh crore |
|
Jobs Created |
~9.5 lakh (direct + indirect) |
B. Other Government Policies
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan (Self-reliant India)
- Make in India
- Start-Up India
- National Policy on Electronics
- National Manufacturing Policy (revamp expected)
India’s Industrial Revolution 4.0 (Industry 4.0)
- India is shifting from traditional manufacturing to smart, tech-driven manufacturing.
- Features:
- Automation & Robotics
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data & Analytics
Benefits:
- Improved efficiency and innovation
- Higher quality and lower costs
- Better integration into global tech supply chains
Key Terms Explained (Prelims Focus) :
|
Term |
Explanation |
|
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) |
The total value of all goods and services produced in a country within a specific time period. Measures the size and health of an economy. |
|
Sunrise Sectors |
New and emerging industries with high growth potential, like semiconductors, renewable energy, and battery technology. |
|
Industry 4.0 |
The 4th industrial revolution focused on smart manufacturing using technologies like automation, AI, IoT, and data analytics. |
|
Labour-Intensive Sectors |
Industries that require a large workforce to operate, such as textiles, garments, and leather. Crucial for job creation. |
|
Gig Economy |
A labor market based on short-term contracts or freelance work rather than permanent jobs (e.g., food delivery, ride-sharing). |
|
Import Dependency |
Reliance on foreign countries for essential goods or raw materials. High import dependency can make a country vulnerable to global disruptions. |
|
Global Supply Chains |
International networks through which goods and services pass from suppliers to customers. Efficiency here boosts trade and competitiveness. |