- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
India - UAE Relations: Dawn of A New Era
India - UAE Relations: Dawn of A New Era
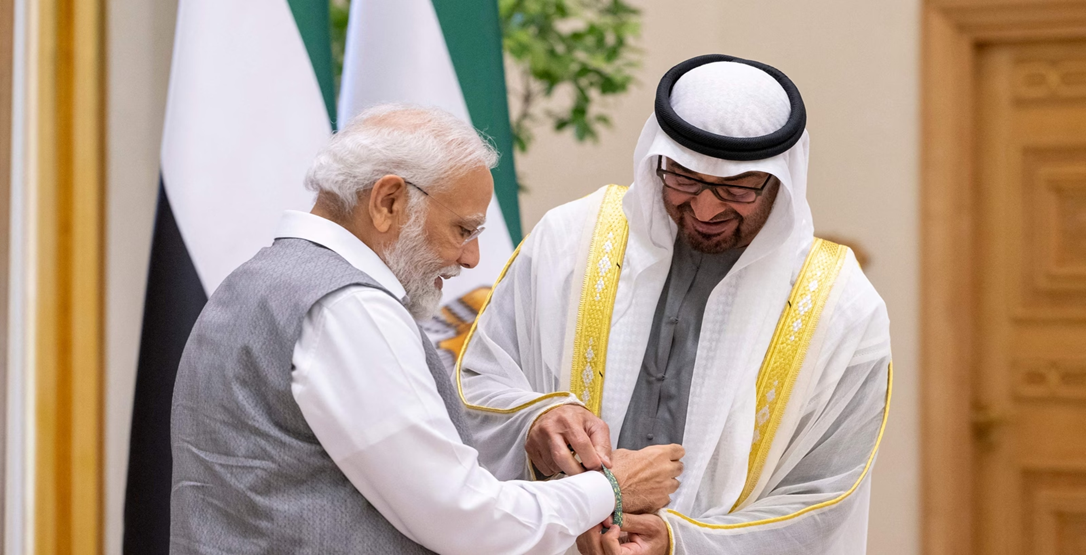

India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) recently held high-level talks to strengthen their relationship and enhance their Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. The Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi visited India, where several key agreements were signed to boost cooperation, especially in energy.
Key Agreements Signed During the Visit
Civil Nuclear Cooperation:
- MoU: India and UAE signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for civil nuclear cooperation.
- Parties Involved: The agreement involves the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) and the Emirates Nuclear Energy Company (ENEC).
- Barakah Plant: This MoU covers the operation and maintenance of the Barakah Nuclear Power Plant, the Arab world’s first nuclear power plant located in Abu Dhabi.
Energy:
- LNG Supply: An MoU was signed for the long-term supply of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) between the two countries.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR): An MoU was signed with India Strategic Petroleum Reserve Limited (ISPRL) for petroleum supply. SPRs ensure a stable crude oil supply during disruptions.
Food Parks:
- An MoU was signed with the Government of Gujarat for developing food parks in India, part of the I2U2 grouping’s initiative.
Why is the UAE Important for India?
Strategic Political Partnership:
- The partnership reflects growing political and strategic alignment, including a new ‘strategic security dialogue’.
Bilateral Trade:
- The UAE is India’s third-largest trading partner. The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) signed in 2022 has boosted trade, increasing from USD 72.9 billion to USD 84.5 billion year-on-year.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- UAE is India’s fourth-largest investor. FDI from UAE surged to USD 3.35 billion in FY23 from USD 1.03 billion in the previous year.
Energy Security:
- UAE is a crucial oil supplier and plays a key role in India's Strategic Petroleum Reserve, essential for India’s energy security.
Finance:
- India’s RuPay card and Unified Payments Interface (UPI) have been introduced in the UAE. Both countries are also working on a Local Currency Settlement System for transactions in Indian Rupee and AED (UAE Dirham).
Space Exploration:
- ISRO and the UAE Space Agency signed an MoU for cooperation in space exploration.
Defence and Security Cooperation:
- Enhanced cooperation includes counter-terrorism, intelligence sharing, and joint military exercises like Exercise Desert Cyclone. UAE shows interest in Indian defence products like BrahMos missiles and Tejas fighter jets.
Multilateral Engagements:
- The I2U2 grouping (India-Israel-UAE-US) and UAE’s role in the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) highlight its strategic significance.
Regional Stability:
- UAE's involvement in the Abraham Accords and its role in regional stability are important for India, which relies heavily on Gulf nations for energy.
Cultural and Diaspora Links:
- The large Indian diaspora in the UAE (about 3.5 million) strengthens cultural ties. Initiatives like the first Hindu temple in Abu Dhabi reflect shared values.
Cooperation During COVID-19:
- India and UAE collaborated by providing medical supplies and vaccines to each other, strengthening their partnership.
Challenges in India-UAE Relations
- Limited Diversification of Trade Categories: Trade remains concentrated in a few sectors like gems, jewellery, and petroleum, limiting broader economic benefits.
- Rising Import Costs: Imports from the UAE increased by 19% year-on-year, affecting India’s trade balance and surplus.
- Non-Tariff Barriers: Indian exports face hurdles such as the Halal certification requirement, affecting processed food exports.
- Human Rights Concerns: Issues related to the Kafala system, which controls migrant workers' employment and status, are a concern.
- Diplomatic Balancing Act: Navigating regional conflicts, such as tensions between Israel and Hamas or Iran and Arab nations, adds complexity to relations.
- Financial Support to Pakistan: UAE’s financial assistance to Pakistan raises concerns about potential misuse for anti-India activities.
Way Forward
- Promote Trade Diversification: Explore emerging sectors like technology, renewable energy, and pharmaceuticals to diversify trade.
- Strengthen Economic Ties: Seek joint ventures and partnerships to enhance economic collaboration and manage high import costs.
- Enhance Dialogue on Human Rights: Address concerns related to the Kafala system and advocate for improvements in migrant workers' rights.
- Focus on Areas of Common Interests: Engage in proactive diplomacy to align on shared interests and manage geopolitical tensions effectively.
Conclusion
The relationship between India and the UAE has evolved significantly, marked by a series of strategic agreements and collaborations across various sectors. Both countries benefit from their deepening ties, particularly in trade, energy, and defence. However, challenges such as trade imbalances, human rights issues, and geopolitical tensions need careful management. By focusing on diversifying trade, enhancing economic partnerships, addressing human rights concerns, and navigating regional conflicts, India and the UAE can strengthen their bilateral relations and maximize mutual benefits.