- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Hansa-3 (NG): India's Indigenous Trainer Aircraft
Hansa-3 (NG): India's Indigenous Trainer Aircraft
07-04-2025
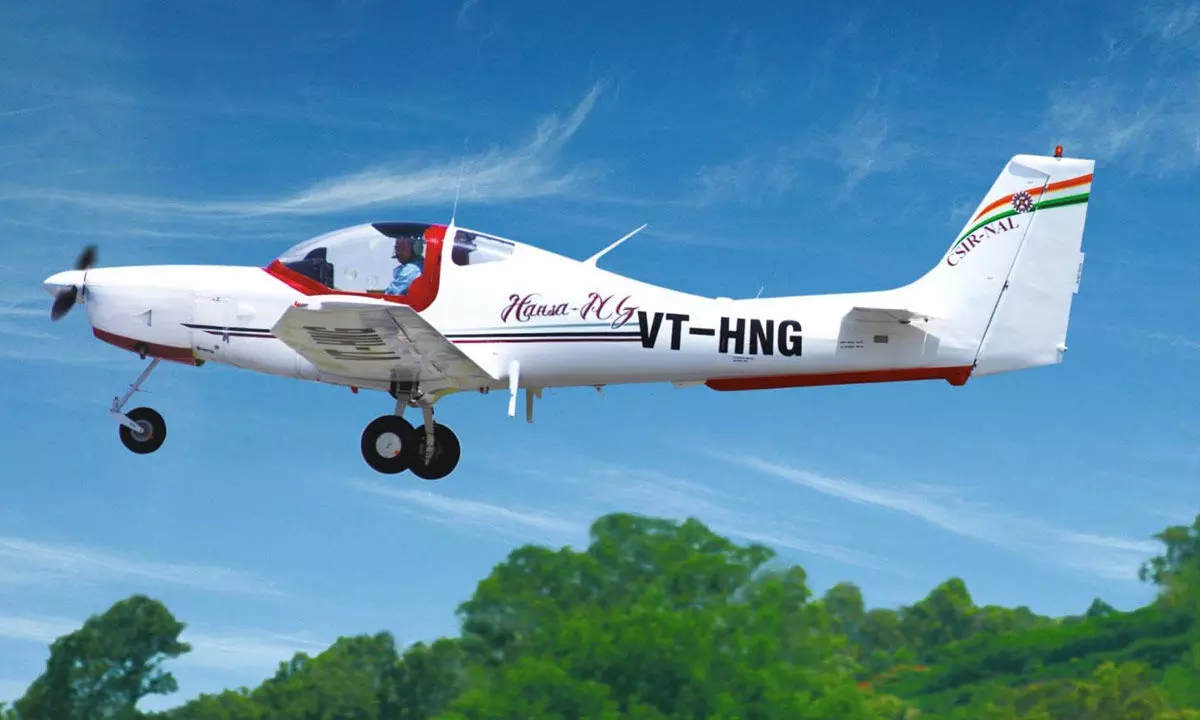

- The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), in collaboration with the National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), has signed a technology transfer deal with a private firm to manufacture the HANSA-3 trainer aircraft in India.
- This marks a historic achievement as the HANSA-3 is the first aircraft to be fully designed and developed indigenously in India and will be manufactured based on this local technology.
Key Features of HANSA-3 (NG)
- Engine: The aircraft is powered by the Rotax 912 iSc3 Sports engine, which is known for its fuel efficiency, contributing to lower operational costs and environmental sustainability.
- Performance:
- Range: The aircraft has a range of 620 nautical miles, making it suitable for various training requirements.
- Endurance: It boasts an impressive 7 hours of endurance, ensuring long-duration training sessions.
- Speed: The aircraft achieves a maximum cruise speed of 98 Knots Calibrated Airspeed (KCAS), suitable for its role as a trainer.
Significance of HANSA-3 (NG)
- Flying Training Ecosystem: The HANSA-3 contributes to the creation of a world-class flying training ecosystem in India, enhancing the quality and capacity of aviation training.
- Strengthening India's Aviation Industry: By manufacturing this trainer aircraft locally, India takes a significant step toward self-reliance in its aviation sector, boosting both the industry and the economy.
- Indigenous Technology:
The HANSA-3 aircraft is a testament to India's growing capabilities in aerospace technology, marking a new chapter in the development of indigenous aviation solutions.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |