- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
GSI Finds 40 Million Year Old Fossils in South Garo Hills
GSI Finds 40 Million Year Old Fossils in South Garo Hills
06-05-2024

- Geological Survey of India (GSI) explorers have explored ancient fossils in Tolegre, South Garo Hills of Meghalaya. Estimated to be around 35-40 million years old.
- Discovered during the Core Geo Expedition's exploration earlier this year, the fossils were found in the remote Gongdap village near Tolegre.
- The Core Geo Expedition team expressed the rarity of the find, speculating it could be linked to the genera Rhodocetus or Amulocetus (now extinct), considered ancestors of modern whales.
- The GSI team is set to return to the site for further investigation, marking a significant milestone in paleontological research within India.
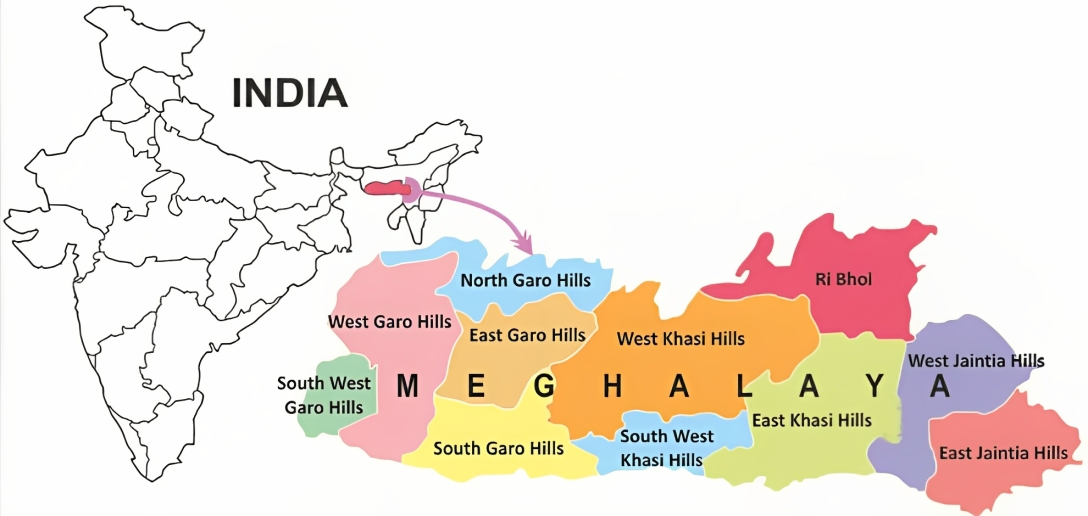
About Garo Hills: A Region of Natural Beauty and Cultural Heritage
Physical Geography:
- The Garo Hills, covering around 8,000 square kilometers, constitute the western part of Meghalaya State in India.
- Part of the Meghalaya subtropical forests, the Garo Hills lie near the Indo-Bangladesh border and form part of the Patkai hill range, which stretches across the Indo-Myanmar border.
- Remarkably, the Garo Hills are recognized as one of the wettest regions in the world.
- The region is drained by various tributaries of the mighty Brahmaputra River.
- Administratively, the Garo Hills comprise 5 districts: North Garo Hills, East Garo Hills, West Garo Hills, South Garo Hills, and South-West Garo Hills.
Garo People and Culture:
- The Garo tribe, known as Achik-mande in their native language, is the predominant ethnic group in the Garo Hills.
- Forming the second-largest tribe in Meghalaya, the Garos are one of the few remaining matrilineal tribes globally.
- Wangala, a harvest festival primarily observed.
- The Garo Hills feature 2 mountain ranges, the Arabella range and the Tura range, which create the Balpakram valley in between.
- The Balpakram area holds religious significance for the Garo community, as they believe it is where the spirits of the dead reside.
- The highest point in the Garo Hills is Nokrek Peak, reaching an elevation of 1412 meters. Covered in a lush forest.
- Nokrek National Park, located within the region, safeguards a diverse array of plant and animal species. In recognition of its ecological value, UNESCO designated the park as a biosphere reserve in 2009.
What is Geological Survey of India (GSI):
Establishment and Purpose:
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) was established in 1851, primarily with the objective of locating coal deposits for the development of India's railway network.
- As the second-oldest survey organization in India after the Survey of India (founded in 1767), GSI has a rich legacy of geological exploration and research.
Objective:
- GSI aims to provide objective, impartial, and up-to-date geological expertise and geoscientific information.
- The organization's focus is on supporting policy-making decisions, commercial needs, and socio-economic development through the provision of accurate and reliable geological data.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi