- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Government invited applications under Modified Semi con India Programme
Government invited applications under Modified Semi con India Programme
31-08-2023
Latest Context:
Recently, the government has decided to invite new applications for setting up Semiconductor manufacturing parks under the ‘Modified Semicon India Programme’.
About Modified Semi-con India Programme
- It was launched in 2021 by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) for the development of a sustainable semiconductor ecosystem in India.
- Objective of this program is to provide attractive incentive support to companies that are engaged in Silicon Semiconductor Fabs, Display Fabs, Semiconductor Design etc.
- Under this program, the support will be provided for 6 years.
- India Semiconductor Mission, within Digital India Corporation (MeitY) is the nodal agency for
implementing the programme.

What are Semiconductors?
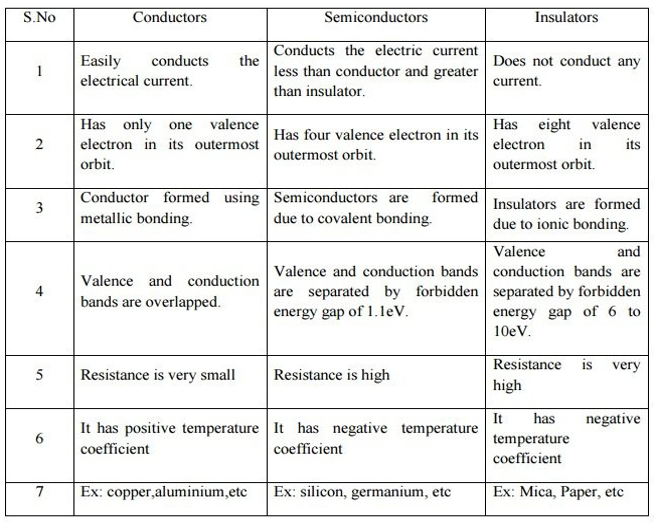
- Semiconductors are a class of materials that have electrical conductivity between that of conductors (like metals) and insulators (like non-metallic materials).
- These materials have a unique property that allows them to conduct electricity under certain conditions.
- It is estimated that, India’s semiconductor market will value around $64 billion by 2026, showing 3-times growth from 2019.
- As per India Electronics and Semiconductor Association (IESA), semiconductor consumption in India is growing at a rate of 15%.
- Presently, Taiwan is the world leader in manufacturing microchips with producing over 60% of the world's semiconductors and over 90% of the most advanced ones.
Significance of semiconductor industry for India
- Economic Growth: The semiconductor industry is a crucial driver of economic growth. By promoting domestic semiconductor manufacturing and design capabilities, India can create new job opportunities, attract investments, and contribute to the country's GDP growth.
- Reducing Import Dependency: India has been heavily reliant on semiconductor imports to meet the demands of its electronics and technology sectors. Developing a robust domestic semiconductor industry would help reduce import dependency and enhance the country's self-sufficiency in critical technologies.
- Strengthening Electronics Manufacturing: The semiconductor industry is the backbone of electronics manufacturing. By increasing its semiconductor capabilities, India can establish a stronger foundation for electronics manufacturing and attract more electronics companies to set up their manufacturing plants in the country.
- Promoting Innovation and Research: Investment in the semiconductor industry encourages research and innovation in cutting-edge technologies. This, in turn, promote a culture of innovation, leading to the development of new products and solutions that can benefit various sectors of the economy.
- Supporting Strategic Industries: Many strategic industries such as defence, space, and telecommunications heavily rely on semiconductor technologies. Building a robust semiconductor industry ensures access to critical technologies and enhances India's capabilities in these strategic sectors.
- Enabling Emerging Technologies: Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, and autonomous vehicles are heavily dependent on semiconductor technologies. Developing a strong semiconductor industry will position India to leverage these technologies for socio-economic growth.
- Export Opportunities: A strong semiconductor industry opens up opportunities for India to export semiconductor components, chips, and devices to global markets, generating foreign exchange earnings.
Some of the key uses of semiconductors are as follows:
- Transistors: Transistors are fundamental semiconductor devices used in electronic circuits for amplification, switching, and signal processing. They form the backbone of modern electronics and are found in nearly all electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, televisions, and audio equipment.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Integrated circuits, commonly known as chips, are complex assemblies of multiple semiconductor components (transistors, resistors, capacitors) integrated into a single package. ICs are the building blocks of modern electronic systems, and they are used in microprocessors, memory chips, and various specialized application-specific circuits.
- Diodes: Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction only. They are used in rectifiers, voltage regulators, and signal demodulation in communication systems.
- Solar Cells: Semiconductor-based solar cells are used to convert sunlight into electricity. They are widely used in solar panels to generate renewable energy.
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when current passes through them. They are used for lighting purposes, display panels, indicators, and other applications.
- Microcontrollers and Microprocessors: These are specialized integrated circuits that contain a Central Processing Unit (CPU) along with memory and input/output peripherals.
- Memory Devices: Semiconductors are used in various memory technologies, including dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), static random-access memory (SRAM), and flash memory, which store data in electronic devices.
- Power Electronics: Semiconductors are used in power electronic devices such as power transistors, insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), and thyristors. These devices are critical in controlling and converting electrical power efficiently in applications like power supplies, motor drives, and electric vehicle inverters.
- Sensors: Semiconductors are used in various sensor technologies, including temperature sensors, pressure sensors, humidity sensors, and gas sensors, to measure and monitor physical properties in electronic systems and industrial applications.
- Radio Frequency (RF) Devices: Semiconductors are crucial in RF circuits used in wireless communication systems, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and satellite communications.
Conclusion:
To realize the significance of the semiconductor industry for India, the government, industry stakeholders, and academia need to collaborate to create an ecosystem that encourages research and innovation, provides supportive policies and incentives, and to promote an environment conducive to the growth of the semiconductor sector.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



