- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Global Gender Gap Report 2024
Global Gender Gap Report 2024
19-06-2024
The Indian cabinet's recent composition highlights a significant gender disparity, with only two women out of 30 ministers. This mirrors the country's wide gender gap, as indicated by the Global Gender Gap Report 2024. In the analysis, India ranked poorly among South Asian economies, falling behind countries like Bangladesh and Nepal.
Key Points:
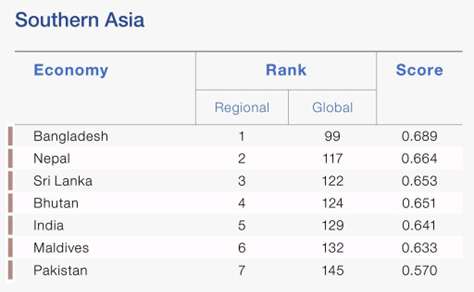
- India has been ranked 129th out of 146 economies in the Global Gender Gap Report 2024, released by the World Economic Forum.
- The country has one of the largest gender gaps in the world, with a score of 63.7% in terms of gender parity.
- India fares worse than its South Asian neighbours, including Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Bhutan.
- The country's ranking has been dragged down due to widening education and political disparities.
Political Empowerment:
- India has only 2 women ministers out of 30 in the newly formed cabinet, a significant drop from the previous government's 10 women ministers.
- The country ranks 65th in the 'Political Empowerment' parameter, but has a low representation of women in ministerial positions (6.9%) and parliament (17.2%).
- India scores well on the head-of-state indicator (40.7%), but lags behind in other political empowerment indicators.
Economic Participation and Opportunity:
- India ranks 142nd in 'Economic Participation and Opportunity', with a significant gap in estimated earned income (28.6%), legislative, senior officials, and management roles (14.4%), labour-force participation rate (45.9%), and professional and technical workers (49.4%).
- The country's economic parity peaked at 46% in 2012, but has since declined.
Educational Attainment:
- India ranks 112th in 'Educational Attainment', with a significant gap in literacy rates between men and women (17.2 percentage points).
- While women's enrollment in primary, secondary, and tertiary education is high, the gap has only modestly increased.
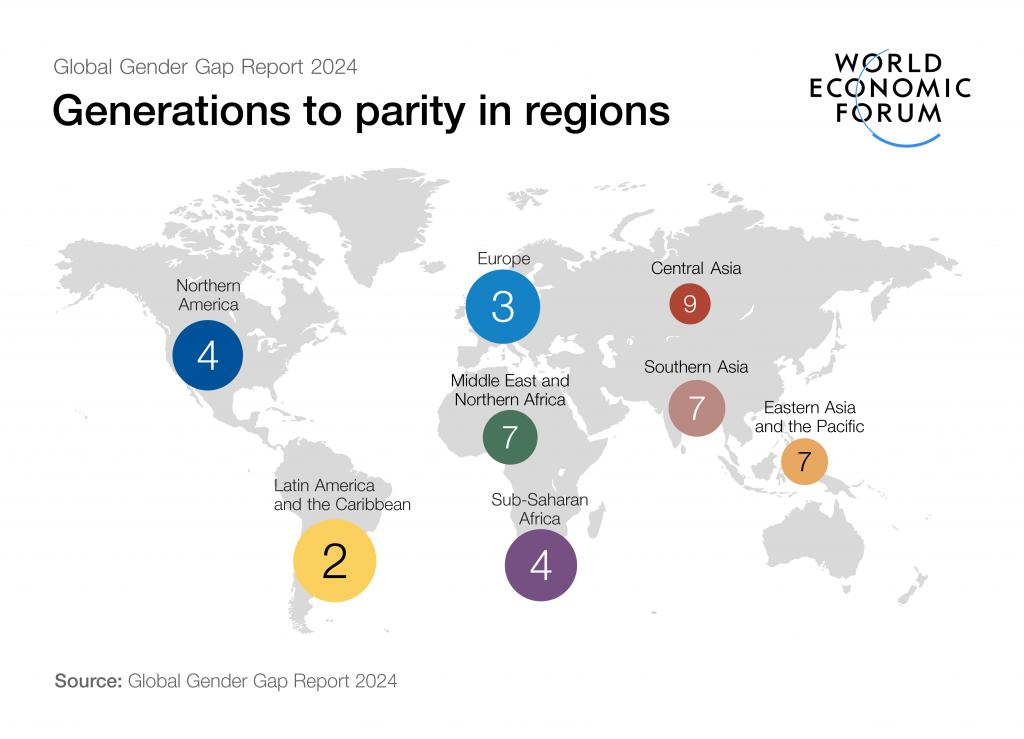
Regional Performance:
- Southern Asia, which includes India, ranks 7th out of 8 regions in terms of gender parity, with a score of 63.7%.
- The region has improved its gender gap score by 3.9 percentage points since 2006, but still lags behind other regions.
- Bangladesh is the only country in the region to rank in the top 100, with a rank of 99.
Top-Ranked Countries:
- Iceland retained its position as the most gender-equal country for the 14th consecutive year, scoring 91.2% in the gender gap assessment.
- Other Nordic countries, including Norway, Finland, and Sweden, also feature in the top five.
Global Trends:
- The world has closed 68.5% of the gender gap, with Europe having the least disparity across parameters.
- Labour-force participation rates for women have rebounded to 65.7% globally, after dipping during the pandemic.
- Latin America and the Caribbean have made significant progress, recording their highest economic parity score to date (65.7%) and the second-highest regional political empowerment score (34%).
What is Gender Parity:
- Gender parity refers to relative equality in terms of numbers and proportions of women, men, girls, and boys.
- It is often calculated as the ratio of female-to-male values for a specific indicator.
Conclusion:
- India needs to bridge the gender gap in various areas, including education, economic participation, and political empowerment, to improve its ranking.
- The country's low representation of women in politics and economy is a major concern, and efforts are needed to increase their participation and representation.
- The Global Gender Gap Report 2024 serves as a wake-up call for India and other countries to take concrete steps towards achieving gender parity.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi