- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Global Biofuel Alliance Sets up Three-Pronged Work Plan
Global Biofuel Alliance Sets up Three-Pronged Work Plan
13-05-2024

Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) has adopted a work plan focused on assessing country landscapes, drafting policy frameworks, and conducting biofuel workshops, petroleum and natural gas ministry officials said.
- These were adopted as immediate goals at a key meeting of the body held on the sidelines of the G20 deliberations in Brazil last month. And, the officials added that the GBA has decided to take stock of them in July.
About Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA):
- GBA Overview: GBA is a multi-stakeholder alliance comprising governments, international organizations, and industries. This initiative, initiated by India, brings together the largest consumers and producers of biofuels to drive their development and deployment.
- GBA Launch: GBA was launched on the sidelines of the 2023 G20 summit in New Delhi.
- GBA Mission: The initiative aims to position biofuels as a key component of the energy transition and contribute to jobs and economic growth.
-
GBA Significance:
- The alliance emphasizes strengthening markets, facilitating global biofuels trade, promoting concrete policy lesson-sharing, and providing technical support for national biofuels programs worldwide.
- GBA intends to accelerate the global uptake of biofuels by facilitating capacity-building exercises, promoting technology advancements, and intensifying the utilization of sustainable biofuels through stakeholder participation.
- GBA will also act as a central repository of knowledge and an expert hub in the field of biofuels.
- As of now, 24 countries and 12 international organizations have agreed to join the alliance.
What is Biofuel?
- Biofuel Introduction: Biofuel is a fuel produced rapidly from biomass, unlike the slow natural processes involved in forming fossil fuels such as oil.
-
Generations of Biofuel:
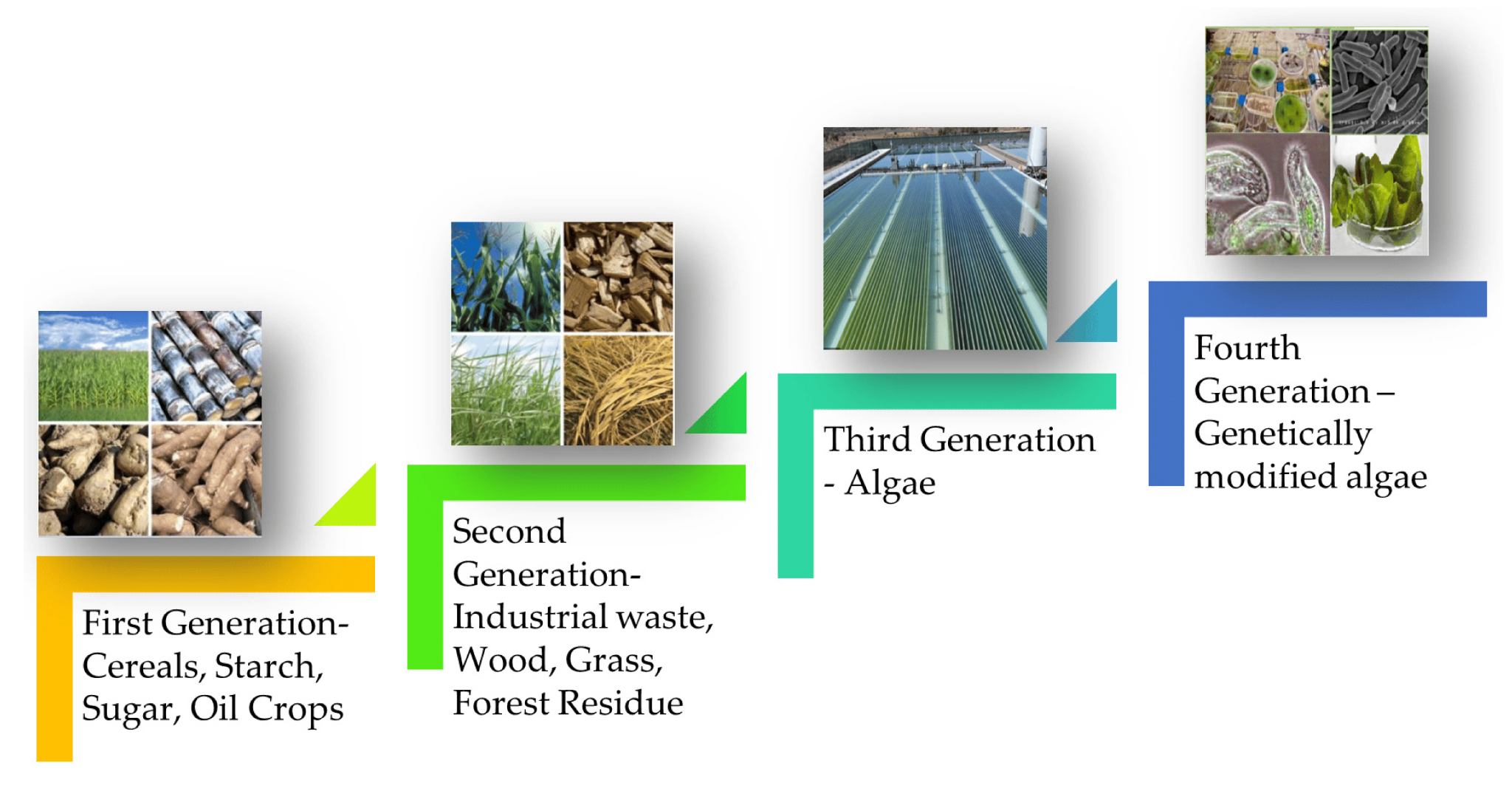
- First Generation: Made from sugar, starch, vegetable oil, or animal fats using conventional technology. Includes bioalcohols, biodiesel, vegetable oil, bioethers, and biogas.
- Second Generation: Produced from non-food crops such as cellulosic biofuels and waste biomass. Includes advanced biofuels like biohydrogen and biomethanol.
- Third Generation: Produced from microorganisms such as algae.
- Fourth Generation: Fourth-generation biofuels are produced from genetically engineered feedstock from algae. These biofuels focus on developing sustainable energy and capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.