- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
GENOME INDIA PROJECT
GENOME INDIA PROJECT
11-03-2024
The government's Genome India initiative achieved a significant milestone when researchers completed sequencing of 10,000 healthy genomes from different regions of the country.
- The Genome India Project, funded and coordinated by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
What is the Genome India Project?
- Started in 2020: Initiated by DBT on January 3.
- Leadership: Led by the Centre for Brain Research at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, with 20 other institutions.
- Goal: Involves studying 10,000 people's DNA to understand diseases better and create predictive tests.
- Population Diversity: India's many different people help scientists learn about various genetic traits and diseases.
Significance of Genome India Project:
- Local Mutation Awareness: Helps to understand genetic mutations affecting 4.5% of the population.
- Growing Life Sciences Sector: India's biology field is rapidly growing and will be worth over US$130 billion in 2024, influencing the country's future.
What is Genome Sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is a method to read the genetic information in DNA. It helps the scientists to understand the order of bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T) in the DNA of living things, like bacteria, plants, and animals.
Steps of Genome Sequencing: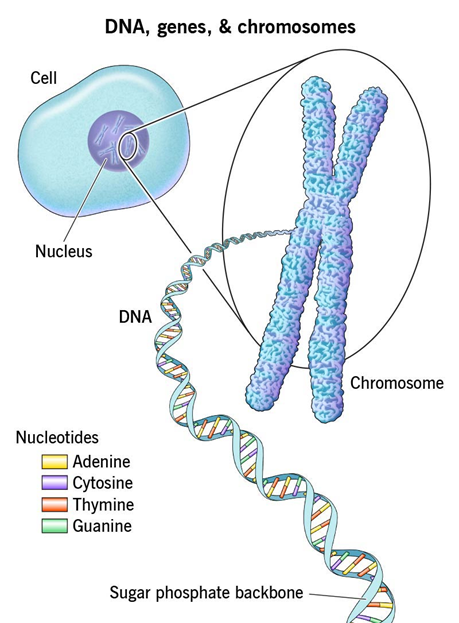
- Collecting DNA: Scientists take a sample, usually blood, to get DNA.
- Breaking it Down: They break the DNA into smaller pieces.
- Adding Tags: Each piece gets a special tag with a fluorescent marker to help identify it.
- Reading the Pieces: Using a machine called a DNA sequences, they read the order of the DNA pieces.
- Putting it All Together: Computers help put the DNA pieces back in the right order to understand the genetic sequence.
DNA, Genes, and Genome:
|
Applications of Genome Sequencing:
- Biomedical Research: Helps understand diseases, find mutations, and discover treatments.
- Pharmacogenomics: Predicts how people will respond to drugs for personalized treatments.
- Agricultural Genomics: Identifies genes for better crops and improves breeding.
- Evolutionary Biology: Studies genetic differences and relationships between species.
- Conservation Biology: Helps protect species by studying genetic diversity and planning conservation efforts.
Note
- First human genome sequenced in 2003, took 13 years and $3 billion. India announced its first complete human genome in 2009.
- Now, it takes about 5 days to sequence a genome with quality checks.



