- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Genetically Engineered Insects
Genetically Engineered Insects
14-11-2023
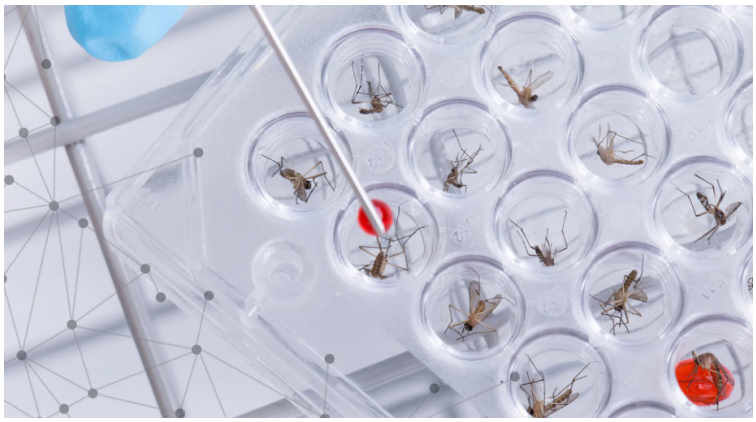
Why in News?
India aims to boost Bioeconomy's contribution to GDP from 2.6% to 5% by 2030, as per the Department of Biotechnology's 'Bioeconomy Report 2022'.
- The DBT's April 2023 'Guidelines for Genetically Engineered (GE) Insects' offer procedural guidelines for those attempting to create GE insects with issues.
Key Highlights of the Bioeconomy Report 2022
- India's bioeconomy is expected to reach a value of USD 150 billion by 2025 and surpass USD 300 billion by 2030.
- The sector saw a significant 14.1% growth, reaching USD 80 billion in 2021, up from USD 70.2 billion in 2020.
- The bioeconomy generated USD 219 million daily, indicating its substantial economic impact.
- In 2021, the biotech sector saw the daily establishment of three startups, resulting in a total of 1,128 startups for the year.
- The industry has committed over USD 1 billion to research and development, demonstrating a strong commitment to innovation and advancement.
- India demonstrated its resilience and capacity by administering 4 million Covid-19 vaccine doses and conducting 3 million daily tests during the global pandemic.
- Over the past decade, the number of biotech startups has grown significantly, from 50 to over 5,300, with projections of doubling by 2025.
- The Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) has established 74 bio-incubation centers in 21 states/UTs, providing a supportive environment for bio-entrepreneurs.
- India has the second-highest number of USFDA-approved manufacturing plants outside the US, demonstrating its global standing in the biotech industry.
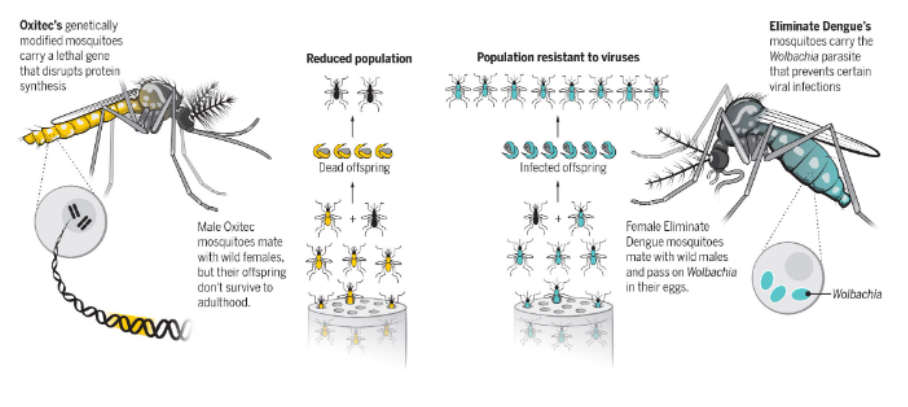
Genetically Engineered (GE) Insects
-
About:
- GE insects are organisms modified through genetic engineering techniques to introduce desired traits or characteristics.
- This involves altering the insect's DNA in a non-natural manner, often to provide specific advantages or tackle specific issues.
-
Application:
- Effective management of vectors is crucial for maintaining human and livestock health.
- The management of major crop insect pests is a crucial aspect of agricultural operations.
- The goal is to enhance human health and the environment by minimizing the use of chemicals.
- The production of proteins for healthcare purposes is a crucial aspect of modern medical science.
- Genetic improvement is the process of improving beneficial insects such as predators, parasitoids, pollinators like honey bees, and productive insects like silkworm and lac insect.
-
Issues with Genetically Engineered (GE) Insects Guidelines:
- The guidelines in India lack specificity on the approval purposes of GE insects, focusing on health, agriculture, and environment, but do not align with the broader bioeconomy commitment.
- The guidelines are restricted to research and do not address confined trials or deployment, raising concerns about community exposure without individual choice.
- The definition of 'beneficial' in GE insects is ambiguous, affecting investment and progress, similar to ambiguities in other gene-editing guidelines.
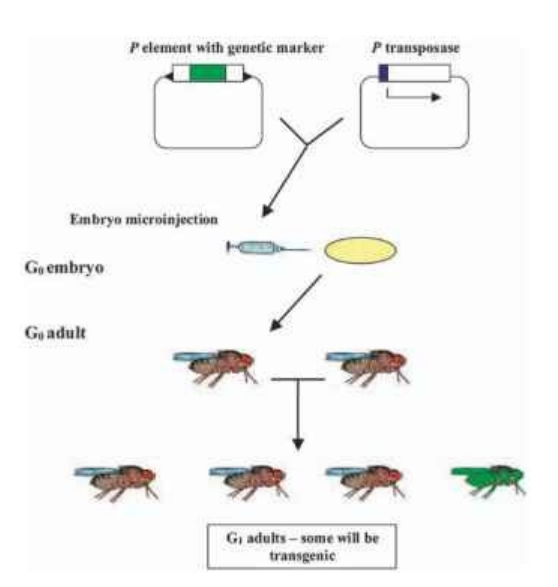
Challenges Related to Genetically Engineered (GE) Insects
-
Ecological Impact:
- Genetically modified insects pose a significant ecological risk, potentially disrupting ecosystems by affecting non-target species or altering existing population balance.
-
Unintended Consequences:
- Genetic engineering is a complex process that can lead to unexpected effects on insect behavior, lifespan, and interactions with other organisms due to changes in targeted genes.
- Modified insects pose a risk of spreading modified genes beyond their intended population, potentially causing unintended consequences if they breed with wild populations.
-
Ethical Concerns:
- Some individuals express concern about the ethical implications of altering the genetic makeup of living organisms, especially when it involves their release into the environment.
-
Regulatory Challenges:
- Creating regulatory frameworks for genetically engineered insects is challenging, necessitating careful testing, monitoring, and oversight to guarantee safety and effectiveness.
-
Long-Term Stability:
- The stability of engineered traits over generations is crucial, as genetic modifications must remain effective and not degrade or be influenced by natural selection pressures.
-
Costs and Scalability:
- The ongoing challenge of ensuring cost-effectiveness and scalability for large-scale applications like disease vector control is posed by the high costs associated with developing and implementing genetically engineered insect technologies.
Way Forward
- Clear policies are essential for achieving bio-economy goals and addressing issues for sector growth and contribution to the national economy.
- The success of genetically modified insects’ hinges on a multidisciplinary approach involving scientists, policymakers, ethicists, and the public to mitigate potential risks.
- The responsible handling of these complexities requires continuous research and open dialogue.


