- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Gender Gap Report-2023 by World Economic Forum (WEF)
Gender Gap Report-2023 by World Economic Forum (WEF)
22-06-2023
-1688099859201.jpg)
Latest Context:
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the Gender Gap Report-2023 in which India has been ranked at 127 out of 146 countries in terms of gender equality.
About the Gender Gap Report of World Economic Forum
- It’s an annual publication of the World Economic Forum (WEF) that assesses the gender equality gap in various countries around the world.
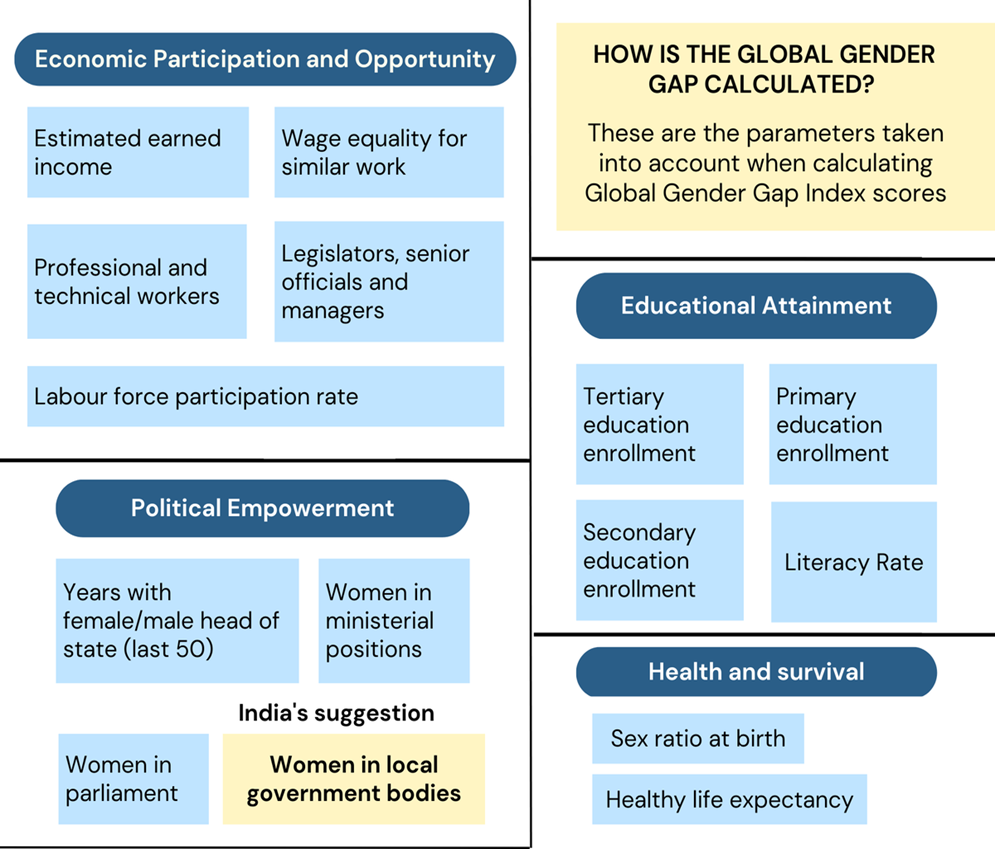
- The report measures gender gaps across four key areas: Economic Participation and Opportunity, Educational Attainment, Health and Survival, and Political Empowerment.
- The report ranks countries based on their overall gender gap index scores, where a higher score indicates greater gender parity.
- The Gender Gap Report provides valuable insights into the progress and challenges related to gender equality globally. It highlights the disparities that exist between men and women in different aspects of life and serves as a tool for policymakers and organizations to identify areas that require attention and improvement.
- The report takes into account a wide range of indicators and data sources to assess gender gaps. These include factors such as labour force participation, wage equality, educational enrolment rates, political representation, maternal mortality rates, and many more. By analysing these indicators, the report provides a comprehensive view of the gender gaps prevalent in societies.
- The Gender Gap Report not only presents an overall global ranking but also provides country-specific data and analysis. This enables governments and organizations to identify specific areas of strength and weakness within their countries and formulate policies and interventions accordingly.
S
ome Key Highlights of the report are:
- As per report, India showed an improvement of almost 1.4% points and jumped by 8 places from its earlier rank of 135 in 2022.
- If we go with the current rate of progress, it will take almost 131 years to reach full parity.
- Iceland with 91% gender parity has remained on top position. Norway with 88% got the second rank and Finland with 86% ranked on third.
- The report mentioned that India has attained better parity in the area of education enrolment but it has reached only 36.7% parity in the area of ‘Economic Participation and Opportunity’ and 25.3% parity in the area of ‘Political Empowerment’.
- Neighbouring countries of India like Bangladesh (59), China (107), Nepal (116), Sri Lanka (115) and Bhutan (103) performed better than India in the area of gender parity.
The Indian government has taken several initiatives to improve gender parity and promote gender equality in the country. Some of the key initiatives include:
- Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao (Save the Daughter, Educate the Daughter): This initiative aims to address the declining child sex ratio and promote the education and welfare of girls. It includes efforts to prevent female foeticide, improve access to education for girls, and enhance the status of women in society.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY): This scheme provides financial assistance to pregnant and lactating women to support their health and nutrition needs. It aims to reduce maternal and child mortality rates and ensure proper care and nutrition during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Mahila E-Haat: It is an online platform that enables women entrepreneurs to showcase and sell their products. This initiative promotes women's economic empowerment and helps them become financially independent.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana: This scheme encourages parents to save for the future education and marriage expenses of their girl child. It provides a safe and long-term investment option along with tax benefits.
- Maternity Benefit Program: Under this program, pregnant women and lactating mothers working in the organized sector are entitled to paid maternity leave of 26 weeks. This initiative aims to ensure the health and well-being of women during and after childbirth.
- Swadhar Greh: It is a scheme that provides temporary shelter, rehabilitation, and support services to women who are victims of violence or are in difficult circumstances. It aims to empower women and facilitate their re-integration into the society.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM): NRLM focuses on women's empowerment through self-help groups and provides them with financial support, skill development, and access to livelihood opportunities. It enables women to start and manage their own income-generating activities.
- Gender Budgeting: The Indian government has adopted gender budgeting as a strategy to mainstream gender concerns in policymaking. It ensures that adequate resources are allocated to programs and schemes aimed at promoting gender equality and women's empowerment.



