- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Framework to handle challenges of crypto assets
Framework to handle challenges of crypto assets
06-09-2023

Latest Context:
Recently, the finance minister said that the government is working on a framework to handle challenges related to crypto assets.
What are crypto assets?
- Crypto assets are a category of digital or virtual assets that use cryptographic techniques to secure and verify transactions on a blockchain.
- These assets have gained significant popularity and attention since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, but the term "crypto assets" includes a wide range of digital tokens and cryptocurrencies beyond just Bitcoin.
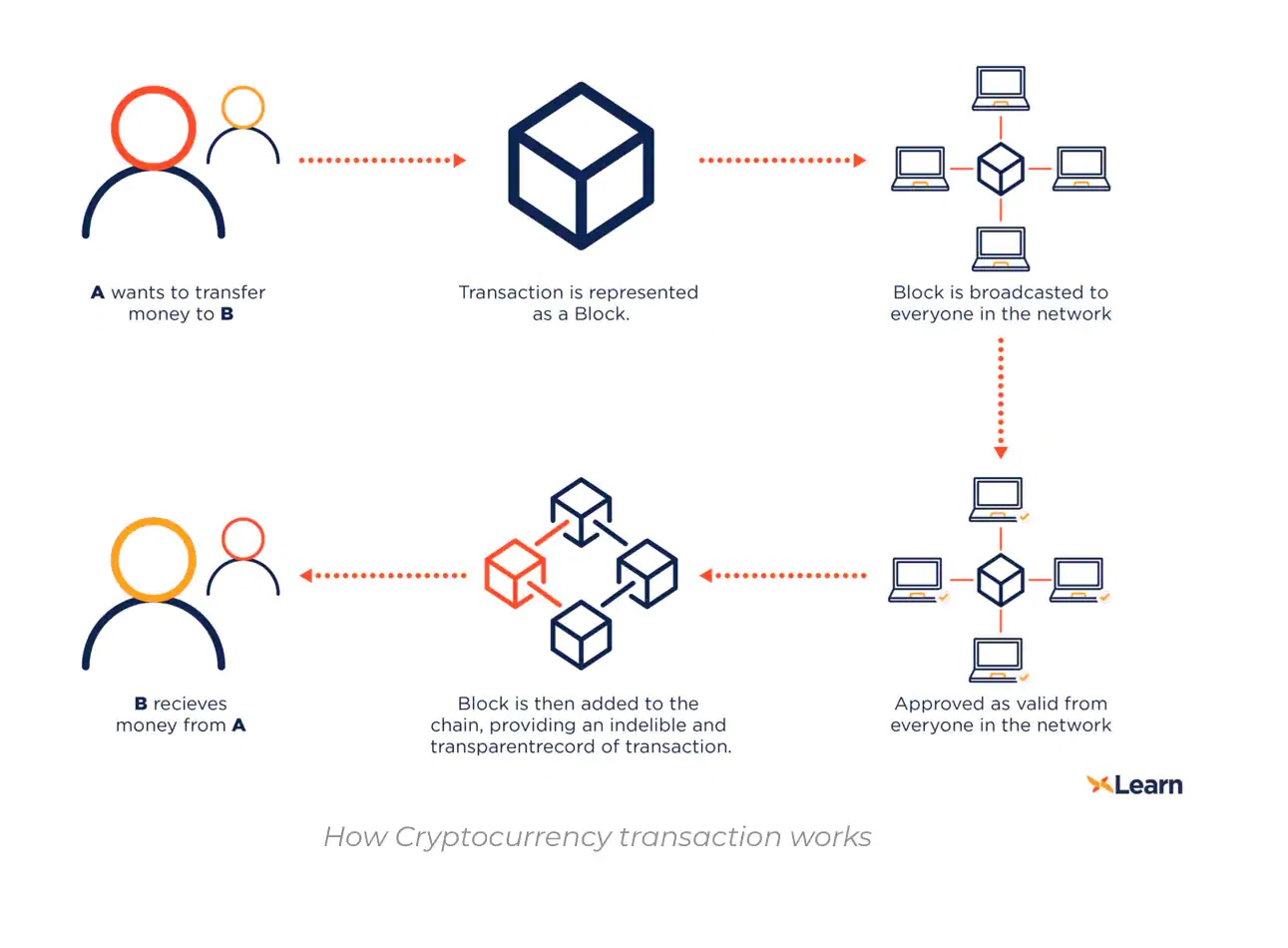
Some key characteristics and types of crypto assets are:
- Digital and Decentralized: Crypto assets exist purely in digital form and do not have a physical counterpart like traditional currencies (e.g., dollars, euros). They operate on decentralized blockchain networks, which means they are not controlled by any central authority, such as a government or central bank.
- Cryptography: The use of cryptographic techniques ensures the security and integrity of transactions on the blockchain. Private and public keys are used to authenticate and protect user identities and assets.
- Distributed Ledger: Transactions involving crypto assets are recorded on a public ledger, known as the blockchain. This ledger is maintained by a network of nodes (computers) participating in the blockchain network.
Crypto assets include a wide range of tokens with different uses, including:
- Cryptocurrencies: These are digital currencies designed for peer-to-peer transactions and as stores of value. Bitcoin (BTC) is the most well-known cryptocurrency.
- Utility Tokens: These tokens provide access to specific services or products within a blockchain ecosystem. For example, Ethereum's Ether (ETH) is used to pay for computational services on the Ethereum network.
- Security Tokens: These represent ownership in a real-world asset, such as shares in a company or real estate, and often comply with securities regulations.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of a specific item, such as digital art, collectibles, or in-game assets.
- Stablecoins: These are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging their price to a fiat currency (e.g., US dollar) or other assets. Tether (USDT) and USDC are examples of stablecoins.
What are the challenges raised by crypto assets?
- Regulatory Uncertainty: One of the most significant challenges in the crypto space is the lack of clear and consistent regulatory frameworks across different countries. Governments and regulatory bodies are still struggling with how to classify and regulate crypto assets.
- Volatility: Crypto assets are known for their price volatility. While this volatility can present trading opportunities, it also poses risks to investors. Extreme price fluctuations can result in substantial financial losses.
- Security Concerns: Security breaches and hacks have hit the crypto industry, resulting in the theft of billions of dollars worth of cryptocurrencies. These incidents highlight the importance of secure storage solutions, such as hardware wallets, and the need for robust cybersecurity practices.
- Scams and Frauds: The relative anonymity of cryptocurrency transactions has made it a breeding ground for scams and fraudulent schemes. Ponzi schemes, fake initial coin offerings (ICOs), and phishing attacks are just a few examples of the scams that have defrauded investors.
- Lack of Consumer Protection: Unlike traditional financial systems, cryptocurrencies often lack the same level of consumer protection, such as insurance on deposits. If a user loses their private keys or falls victim to a scam, recovering lost funds can be extremely challenging.
- Market Manipulation: The crypto market is susceptible to market manipulation due to its relatively low liquidity compared to traditional financial markets. Pump-and-dump schemes, spoofing, and other manipulative trading practices can artificially inflate or deflate the prices of cryptocurrencies.
- Legal and Tax Compliance: Taxation of crypto assets varies by jurisdiction, and tracking transactions for tax reporting purposes can be complex.
- Technological Limitations: While blockchain technology offers many advantages, it also faces limitations, such as scalability issues and slow transaction processing times in some networks. These limitations can hinder the adoption of crypto assets for everyday transactions.
- User Education: Many users are unfamiliar with the technical aspects and risks associated with crypto assets. Lack of understanding can lead to poor decision-making, such as improper storage of private keys or investments in high-risk projects.
- Geopolitical Concerns: The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies can pose challenges for governments in terms of monitoring and regulating financial activities. Some countries have expressed concerns about the potential use of cryptocurrencies for illegal activities, including money laundering and tax evasion.
Conclusion:
Despite these challenges, crypto assets continue to evolve and gain acceptance in various sectors. As the industry matures, efforts are being made to address these issues through improved regulation, enhanced security measures, and advancements in blockchain technology.



