- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Fintech companies leading India's startup ecosystem
Fintech companies leading India's startup ecosystem
19-07-2024
- Fintech companies remain a popular choice for entrepreneurs in the start-up ecosystem. According to data from Tracxn, fintechs have secured over 15% of the total equity funding into start-ups in FY24 so far.
About Fintechs
- Fintech is a combination of ‘financial’ and ‘technology,’ refers to businesses that use technology to improve or automate financial services and processes.
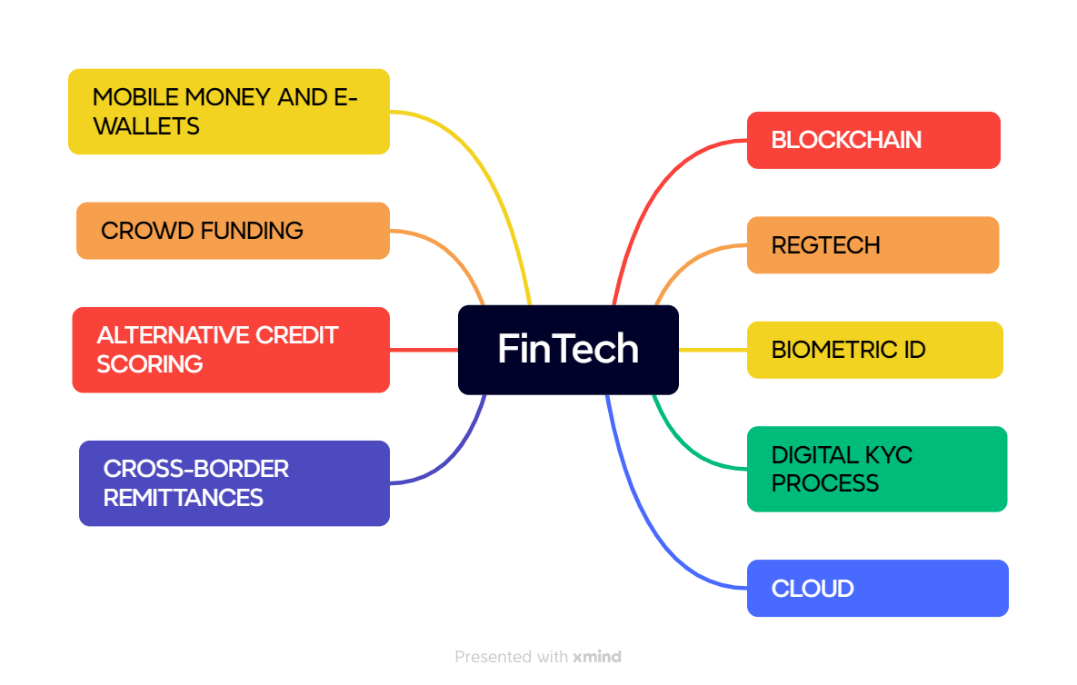
Types
- Digital Payments: These provide digital payment solutions such as mobile wallets, online payment gateways, and peer-to-peer (P2P) payments. Examples include PhonePe and Paytm.
- Alternative Lending: Known as marketplace lending or Peer-2-Peer (P2P lending).
- Peer-to-peer lending is a form of direct lending of money to individuals or businesses without an official financial institution participating as an intermediary in the deal.
- P2P lending is generally done through online platforms that match lenders with the potential borrowers, with investors seeking high-yield investments.
- Examples include Lending Club, Prosper, PayPal Working Capital, and GoFundMe.
- Insurance: These offer digital insurance solutions such as health insurance, life insurance, and car insurance. Examples include Digit Insurance and Policybazaar.
- InvestmentTech: These provide digital investment solutions such as stock trading, mutual funds, and cryptocurrency trading.
- Examples include Zerodha and Groww.
- Other Types: These include crop loan risk management (e.g., Satsure), online fraud detection (e.g., Tutelar), debt management (Debt Nirvana), and Banking-as-a-Service platforms (e.g., FidPay).
State of the Fintech Industry in India
- FinTech Ecosystem: India is a global leader in fintech, ranking 3rd globally after the US and UK, with a combined valuation of over USD 155 billion.
- Nearly a 3rd of the soonicorn universe (soon to be unicorns) consists of fintechs.
- According to Startup India (Ministry of Commerce and Industry), the market size of India’s fintech industry is projected to reach USD 150 billion by 2025.
- High Adoption Rate: The Economic Survey 2022-23 reported that fintech companies in India experienced an 87% adoption rate across various user bases, compared to the global average of 64%.
- Driving Digital Payments: Fintech companies in India account for 70% of digital payment transactions, doubling their share in FY22 compared to FY19.
- Financial Inclusion: More than 10 million people and small businesses gained access to savings accounts, insurance, investment options, and credit facilities through mobile-based services and digital platforms.
- Democratising Lending Process: Peer-to-peer lending platforms are democratizing lending by providing individuals and small businesses access to funds without traditional financial institutions.
- Rise in Public Investment: Investment platforms and robo-advisors are making investments in stocks, mutual funds, and other financial instruments more accessible.
- A robo-advisor is a type of automated financial advisor that provides algorithm-driven wealth management services with little to no human intervention.
Government Initiatives Driving the Growth of FinTech
-
Digital Identity Infrastructure (JAM Trinity)
- Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): This financial inclusion program has provided bank accounts to over 450 million people.
- It creates a large customer base for FinTech companies to offer new financial products like remittances, credit, insurance, and pensions directly through these accounts.
- Aadhaar: A World Bank study reveals that Aadhaar has enabled over 570 million previously unbanked adults in India to open bank accounts.
- The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AePS) allows users to conduct financial transactions using their Aadhaar number and biometric authentication (fingerprint or iris scan).
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): UPI transaction volume has increased by 49% year-on-year.
- The number of integrated banks has grown from 414 in April 2023 to 581 in April 2024, boosting UPI transaction growth.
- Regulatory Support and Innovation: In 2017, the RBI recognized P2P lending platforms as Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), which authorized the sector and expanded credit access for individuals and small businesses.
- Regulatory Sandbox (RS) and Fintech Repository: The Regulatory Sandbox (established by the RBI in 2017) allows FinTech companies to live test their products or solutions before regulatory approval, saving time and costs.
- The Fintech Repository (launched in 2021) serves as a centralized information hub for fintech companies, promoting transparency and regulatory compliance.
- Self-Regulatory Organizations (SRO) Framework: Introduced by the RBI in 2023, this framework promotes responsible growth and industry-led self-regulation.
- SROs act as guardians within the industry, establishing and enforcing a code of conduct, grievance redressal mechanisms, and consumer protection standards.
Potential Growth Areas for the Fintech Sector in India
- SME Lending: Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) face challenges accessing traditional credit channels.
- Fintech solutions using alternative data sources and AI-powered credit scoring can streamline lending processes and make credit more accessible for SMEs.
- Supply Chain Financing: Traditional supply chain financing methods are often complicated and lack transparency.
- Blockchain-based fintech solutions can streamline payments, improve traceability, and enhance working capital management for businesses within the supply chain.
- Supply chain finance is a financing solution in which suppliers can receive early payment on their invoices.
- It reduces the risk of supply chain disruption and enables both buyers and suppliers to optimize their working capital.
- Agritech: Fintech solutions can provide crop loan risk management, micro-insurance for farmers, and digital marketplaces for agricultural products, supporting and empowering rural communities.
- Regulatory Landscape and Long-Term Stability: The RBI's framework for managing "user harm" within the fintech sector may create a cautious investment climate in the short term.
- However, clear and well-defined regulations will enhance consumer protection, build trust, attract long-term investors, and promote sustainable growth.
Steering Committee Recommendations Related to Fintech
- The Steering Committee led by Subhash Chandra Garg on Fintech Related Issues, submitted its report to the Finance Minister in 2019. It aimed to make Fintech regulations more flexible and promote entrepreneurship.
Recommendations
- Expanding Fintech Services: Encourage the use of Fintech to strengthen cybersecurity, fraud control, and money laundering prevention.
- Explore virtual banking and the dematerialisation of financial instruments (converting physical certificates to electronic form).
- Policy Actions for Promotion: Government and public sector institutions should use AI for back-end automation.
- Collaborate with MSMEs to implement blockchain solutions in trade finance.
- Financial Inclusion: Develop a credit registry for farmers using AI/ML-based credit scoring to facilitate easier loan access.
- Use Fintech to manage claims and premium payments in agricultural crop insurance schemes.
- Create a common digital platform for small savings products, micro-pension schemes, and government pensions to enable digital subscriptions.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Form an advisory council on Fintech with industry experts for each financial sector regulator.
- Establish an inter-regulatory technical group for better coordination between regulatory bodies.
- Set up an inter-ministerial group to explore potential applications of Fintech-enabling technologies.
- Collaborate with other countries to share knowledge on Fintech risks and benefits.
- Data Protection: Establish a task force within the Ministry of Finance to address data protection challenges specific to the financial sector.
What are Startups?
Significance of Startups
What is a Unicorn?
Startups in India
Economic Survey 2021-22 Highlights
Government Initiatives
|
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus