- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Economic Growth Trends
Economic Growth Trends
Context:
- The CRISIL Report indicates that the Indian economy might grow more slowly in 2024-25.
What is CRISIL?
- CRISIL i.e. Credit Rating Information Services of India Limited is a leading analytical company based in India.
- They provide ratings to companies and government bodies which helps people make smart financial decisions such as investment.
What has been the growth trend of the Indian economy?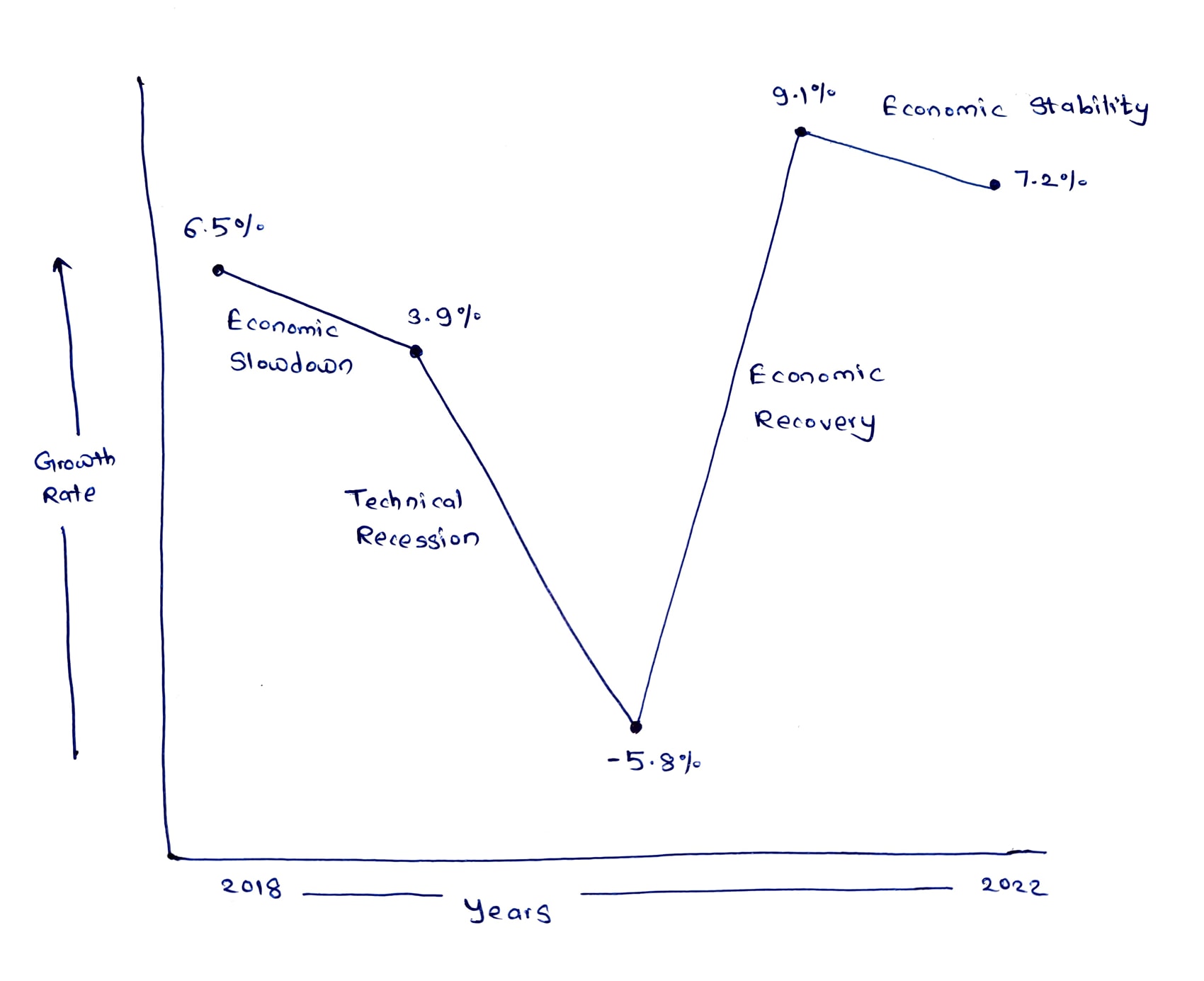
- World Bank Data shows the following trend:
|
Year |
Growth Rate |
|
2018 |
6.5% |
|
2019 |
3.9% |
|
2020 |
-5.8% |
|
2021 |
9.1% |
|
2022 |
7.2% |
- The above graph shows that the Indian Economy has gone through the following phases:
|
Period |
Phase |
Explanation |
Reasons |
|
2018-19 |
Economic Slowdown |
A period of reduced economic activity with a decline in growth rates, employment and consumer spending. |
Global economic slowdown which impacted demand for Indian exports and overall economic activity. Also, the effects of Demonetisation and GST implementation led to a slowdown in domestic consumption. |
|
2019-20 |
Technical Recession |
A period of 2 back-to-back quarters of negative economic growth, indicating a short-term contraction in the economy. |
COVID-19 led to lockdowns resulting in reduced economic activities. |
|
2020-21 |
Economic Recovery |
A phase where the economy starts to grow again with increasing economic activity, employment and overall improvement. |
Government measures such as an economic package in the form of Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan pushed self-reliant growth. Also, India's strong domestic market helped it grow steadily. |
|
2021-22 |
Economic Stability |
A state where an economy experiences consistent growth without many ups and downs |
Foreign Direct Investment also contributed to the stability (around $80 Billion in 2022) Government investments in infrastructure projects like roads, railways and digital connectivity improved logistics and boosted growth. |
- Hence, it can be said that the Indian Economy has seen a V-shaped recovery i.e. a quick and strong bounce back of an economy after a sharp decline.
What are the major challenges for the Indian Economy at present?
- Unemployment: High unemployment among the youth, especially among the graduates - around 42%. (According to State of Working India Report 2023)
- Income Disparity: The top 10% of the population gets 57% of national income. (According to UNDP)
- Inflationary Pressures: Rapid economic recovery can sometimes lead to increased demand for goods and services, potentially causing inflation.
- Sustainability: Economic recoveries often focus on rapid growth, sometimes at the expense of environmental sustainability. Industries may prioritize short-term gains over long-term environmental impact, leading to pollution, resource depletion and climate change.