- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Do cryptos have any rationale?
Do cryptos have any rationale?
Recently, former President Donald Trump expressed support for Bitcoin at a crypto gathering, even suggesting it could become a strategic reserve if he returns to office. This is surprising, given that cryptocurrencies lack the stability of gold or cash.
- Amid dissatisfaction with traditional financial systems, there is a growing interest in cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology for financial autonomy and innovation.
- However, the long-term viability and sustainability of these technologies remain uncertain.
What is Cryptocurrency and How Does it Work?
- Cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security.
- Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Litecoin.
- Functionality:
- Transactions are recorded on a public digital ledger called the blockchain.
- The blockchain is maintained by a decentralized network of computers that verify and add transactions.
- Users need a digital wallet to store their public and private keys for transactions.
- Cryptocurrencies can be acquired through "mining," which involves solving complex mathematical problems to validate and record transactions.
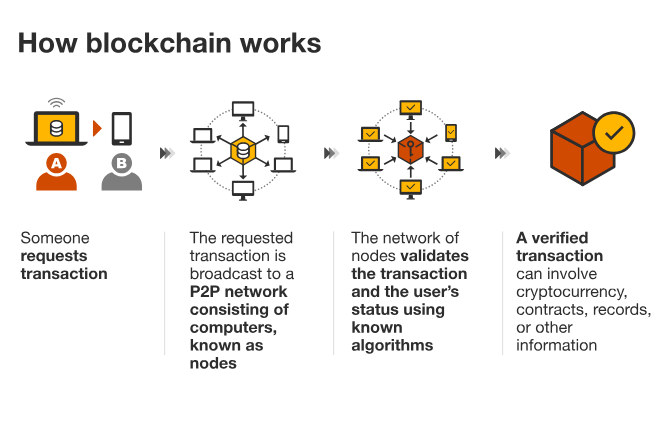
What is Blockchain Technology?
- Definition: Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers.
- Mechanism:
- Each block contains a set of transactions.
- New transactions are added to every participant's ledger, ensuring security and transparency.
- Applications Beyond Cryptocurrency:
- Financial Institutions: Used for secure and transparent transaction processing, reducing fraud and operational costs.
- Education: Potential for managing student records and academic achievements.
- Scholarship Systems: Could incentivize academic excellence and maintain records efficiently.
What is the Legal Status of Cryptocurrency in India?
- Regulation:
-
Cryptocurrency is unregulated but not banned. The government does not recognize it as legal tender and aims to limit its use in illegal activities.
- Taxation: Transfers of virtual currencies/cryptocurrencies are subject to a 30% tax as per the Union Budget 2022-23.
-
- Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC):
- India has introduced its own CBDC, the Digital Rupee (e-RUPI), in collaboration with NPCI and other stakeholders.
- CBDCs are legal tenders issued and backed by central banks, differing from decentralized cryptocurrencies.
Pros and Cons of Cryptocurrency:
- Pros:
- Security and Transparency: Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in transactions, reducing fraud.
- Innovation and Tokenization: Enables tokenization of assets and innovation in financial instruments.
- Reshaping Finance: Potential to transform global finance, offering new paradigms for value storage and transfer.
- Financial Autonomy: Provides alternatives to traditional banking, especially beneficial in unstable economies.
- Cons:
- Speculative Nature: High volatility and speculative trading undermine stability and reliability as a medium of exchange.
- Regulatory Challenges: Uncertain regulatory environment and concerns over illegal activities can hinder adoption and integration.
- Limited Acceptance: Low acceptance by merchants and high transaction costs limit practical utility and integration with traditional systems.
- High Costs and Inefficiency: Cryptocurrencies can have high transaction fees and slower processing times compared to conventional payment methods.
Conclusion:
India's rapid adoption of cryptocurrency highlights the nation's shift towards digitalization. However, the absence of a regulatory framework presents significant challenges, including potential risks of fraud, money laundering, and financial crimes. To foster a secure and functional cryptocurrency ecosystem, there is an urgent need for robust regulatory oversight and measures to integrate these technologies into the mainstream financial system while addressing their inherent risks.