- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary - 20th March 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary - 20th March 2025
Development vs. Environmental Rights
In the landmark Auroville Foundation v. Navroz Kersap Mody case, the Supreme Court of India emphasized the need to harmonize industrial development with environmental protection.
The Ongoing Debate:
- Golden Balance: Economic and industrial progress must not come at the cost of the environment—both should go hand-in-hand.
- Environmental Rights: The right to a clean and healthy environment is a fundamental right under Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution.
- Right to Development: Recognized under Articles 14, 19, and 21, supporting industrial growth and economic advancement.
- Sustainable Development: Economic growth must be environmentally sustainable, safeguarding the future.
Internationalisation of Rupee: RBI and Bank of Mauritius sign MoU
The RBI and Bank of Mauritius have signed an MoU to promote local currencies in cross-border trade, pushing for the internationalisation of the Indian Rupee (INR).
What is Internationalisation of the Rupee?
It means enhancing the global acceptance of INR in trade, investment, and foreign exchange reserves.
Why is it Important?
- Reduces forex dependency, especially on the US Dollar.
- Minimizes foreign exchange risks.
- Strengthens India’s global financial standing.
- Boosts trade competitiveness.
Key Steps Taken:
- Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements with countries like Japan, Sri Lanka, Bhutan.
- Promotion of Masala Bonds (Rupee-denominated bonds issued abroad).
Future of Free Speech Index 2025: India Ranks 24th

A global report by The Future of Free Speech ranks India 24th out of 33 countries in terms of free speech support.
Key Highlights:
- Top Performers: Norway, Denmark, Sweden, along with Hungary and Venezuela showed the strongest support for free speech.
- Declining Trends: Countries like Japan, Israel, and the U.S. have seen a drop-in free speech support since 2021.
- Modern Challenges: Rise of social media, AI tools, and traditional media has reshaped the free speech discourse.
Revival of Kamba Ramayana

- The Ministry of Culture has initiated efforts to revive the 'Kamba Ramayana', a classical Tamil rendition of the epic Ramayana.
- This move aims to honour regional literary traditions, promote vernacular classics, and reconnect modern audiences with timeless spiritual and cultural wisdom.
About Kamba Ramayana (The Ramavataram)
- The Kamba Ramayana, also known as "Ramavataram", is a Tamil epic poem that offers a regional and poetic adaptation of Valmiki’s Sanskrit Ramayana.
- Composed by Tamil poet Kamban during the 12th–13th century CE, it is regarded as one of the greatest masterpieces of Tamil literature.
- While rooted in Valmiki’s original narrative, Kamban infused the story with local idioms, Dravidian ethos, and a deep spiritual-philosophical tone.
- The work consists of over 10,000 verses, composed in virutham and santham meters, showcasing the elegance of classical Tamil poetry.
- It was traditionally recited in temples and cultural gatherings, serving as a medium of devotional education and moral instruction for Tamil-speaking communities.
About Poet Kamban
- Kamban (also spelled Kambar) was a celebrated Tamil poet and scholar, believed to have lived in Thanjavur, in the heart of the Chola Kingdom.
- His literary contributions have earned him the title “Kavi Chakravarthy” (Emperor of Poets) in Tamil literature.
- Kamban’s poetic style is known for its depth of emotion, philosophical richness, and devotional fervour, blending Bhakti (devotion) with intellectual eloquence.
- He is said to have had the patronage of the Chola court, and his compositions were inspired by Shaiva and Vaishnava traditions, particularly the Bhakti movement which was thriving in South India during that period.
Significance of Kamba Ramayana in Tamil Culture
- The epic holds immense religious, cultural, and linguistic importance in Tamil Nadu and across the Tamil diaspora.
- It is considered not merely a translation but a creative reinterpretation of the Ramayana, reflecting regional sentiments, Tamil social values, and local narrative traditions.
- The characterization of Rama, Sita, and Ravana in the Kamba Ramayana is portrayed with nuanced emotional depth and moral complexity, distinguishing it from the Valmiki version in several narrative aspects.
Objective of the Revival Effort
The Ministry of Culture’s revival initiative aims to:
-
- Promote regional epics and classical literature across linguistic boundaries.
- Digitize, publish, and disseminate annotated versions of the Kamba Ramayana.
- Support research, translations, and cultural performances that showcase its literary richness.
- Encourage youth engagement with classical texts through educational and cultural platforms.
Broader Context: Reviving Classical Indian Texts
- This initiative aligns with India's broader cultural vision to celebrate linguistic diversity and heritage literature.
- Similar efforts are being undertaken to revive regional epics, folk traditions, and classical manuscripts in Sanskrit, P
VARUNA 2025:
- The 23rd edition of the bilateral naval exercise VARUNA, a maritime cooperation between India and France, is being held from 19 to 22 March 2025.
- Since its inception in 2001, the VARUNA exercise has grown into a significant platform for enhancing naval interoperability, operational coordination, and strategic partnership between the two nations.
- Over the years, Exercise VARUNA has evolved into a cornerstone of Indo-French maritime collaboration, reflecting the shared commitment to a free, open, and secure Indo-Pacific region.
Highlights of VARUNA 2025
This year's edition is marked by multi-domain operational drills across surface, sub-surface, and aerial platforms, aimed at refining tactical expertise and bolstering maritime readiness.
- Aircraft Carrier Operations: The INS Vikrant and French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle will jointly participate, along with their carrier-based fighter aircraft, showcasing combined sea-air combat capabilities.
- Advanced Air Defence and Fighter Drills: Exercises will include mock air-to-air combat between the French Rafale-M and Indian MiG-29K, enhancing air superiority tactics and mutual understanding of aerial combat dynamics.
- Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW): Intensive ASW drills, supported by an Indian Scorpene-class submarine, will focus on enhancing underwater domain awareness and detection capabilities.
- Surface Warfare Operations: Coordinated manoeuvres and engagements involving destroyers and frigates from both navies will demonstrate tactical proficiency in maritime combat scenarios.
- Replenishment-at-Sea and Logistical Coordination: Exercises on mid-sea replenishment operations will boost logistical interoperability, a vital component of sustained joint naval deployments.
- Maritime Patrol and Surveillance: Maritime patrol aircraft from both countries will be deployed to improve situational awareness and reconnaissance capabilities in the operational theatre.
National Innovation Challenge for Drone Application and Research (NIDAR)
- The National Innovation Challenge for Drone Application and Research (NIDAR) was launched by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Drone Federation of India under the SwaYaan initiative.
- Purpose: Promote innovation in collaborative autonomous drones for Disaster Management and Precision Agriculture.
About SwaYaan:
- Approved by MeitY in 2022.
- Focuses on developing skills and technology in Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS).
FireSat Project: AI-based Wildfire Detection from Space
The first FirSat satellite has been launched into Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
About FireSat:
- Developed by Google Research, Earth Fire Alliance, Moore Foundation, and Muon Space.
- Will deploy 50 satellites providing AI-enabled, high-resolution wildfire alerts every 20 minutes.
- Can detect wildfires as small as a classroom and estimate fire intensity.
Betwa River
The Betwa River is facing challenges in maintaining its natural flow due to human activities.
Key Facts:
- Also called Vetravati in Sanskrit.
- Tributary of Yamuna, originating near Bhopal (Jhirri Village) and joining Yamuna near Hamirpur.
- Flows through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
Historical Significance:
- Mentioned in Mahabharata, and Chedi Kingdom's capital Suktamati stood on its banks.
- Governed by Betwa River Board Act, 1976.
- Linked to the Ken-Betwa River Link Project (2021).
Kerala HC on Cinema & Violence: Expression vs Regulation
The Kerala High Court, in Women in Cinema Collective v State of Kerala, debated regulation of violence in cinema while protecting freedom of expression.
Key Points:
- Justice K. Hema Committee was formed to probe gender inequality in Malayalam cinema.
- Balancing censorship and freedom of speech is critical.
Judicial Landmarks:
- K.A. Abbas v Union of India: Allowed pre-censorship for public morality.
- S. Rangarajan v Jagjivan Ram: Advocated reasonable restrictions.
- Ramesh v Union of India: Protected films from censorship due to protests.
- F.A. Picture Intl. v CBFC: Supported artistic freedom.
Societal Impacts of Glorified Violence in Films:
- Toxic Masculinity: Kabir Singh, Animal portray aggression as strength.
- Gender Stereotypes: Dabangg sidelines women.
- Psychological Influence: Pushpa, Gangs of Wasseypur glorify violent lifestyles.
- Social Disharmony: KGF promotes brute force as success.
India's Quantum Leap: Thematic Hubs Made Operational Under National Quantum Mission
- In a significant step towards advancing quantum technology in India, the central government has made "Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs)" operational as part of the National Quantum Mission (NQM).
- These hubs are envisioned to serve as the driving force behind India's quantum revolution by promoting cutting-edge research, fostering innovation, and building a robust quantum ecosystem.
Thematic Hubs: Building Blocks of India's Quantum Ecosystem
- As part of this initiative, four Thematic Hubs (T-Hubs) have been established, each focused on a specific technology vertical within the broader domain of Quantum Technology (QT).
- These hubs will not only spearhead technology development but also focus on human resource development, entrepreneurship promotion, industry collaboration, and international partnerships to position India at the forefront of global quantum research.
- The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kanpur has been entrusted with the role of management coordinating centre for these hubs, ensuring smooth coordination and strategic implementation across the mission’s components.
Key Technology Verticals of the Thematic Hubs
- Quantum Computing
- Lead Institute: Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru
- Quantum computers operate using quantum bits (qubits), which differ significantly from conventional bits used in classical computers.
- While a regular bit can exist only in a state of 0 or 1, a qubit can exist in both states simultaneously, thanks to the principle of quantum superposition.
- This unique feature provides quantum computers with immense processing power, enabling them to solve complex problems far beyond the capabilities of traditional systems.
- Quantum Communication
- Lead Institute: IIT Madras
- Quantum communication involves encoding information in quantum states, usually of photons (light particles), and transmitting them securely over distances.
- This technology offers unprecedented levels of data security, making it crucial for secure communication systems such as satellite-based quantum communication.
- Quantum Sensing and Metrology
- Lead Institute: IIT Bombay
- Quantum sensing utilizes quantum systems to enable ultra-precise measurements at atomic and subatomic levels.
- Quantum metrology, a subfield, focuses on enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of measurements for various physical conditions, including magnetic fields, time, and gravity.
- These technologies have vast applications in fields like healthcare, navigation, and geological surveys.
- Quantum Materials and Devices
- Lead Institute: IIT Delhi
- This vertical focuses on studying the structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of nanoscale systems across a range of advanced materials.
- The goal is to develop quantum devices and components that can be integrated into quantum computers, sensors, and communication tools, forming the foundational hardware for quantum applications.
|
National Quantum Mission (NQM) The establishment of these T-Hubs forms a key part of the broader vision of the National Quantum Mission (NQM), launched to accelerate India's capabilities in quantum science and technology.
|
Indore to Launch India's First PPP-Based Green Waste Processing Plant
- In a pioneering step towards sustainable urban waste management, India’s first Green Waste Processing Plant under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model is all set to be launched in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- This initiative has been undertaken as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban, aiming to transform the way cities manage biodegradable waste.
- The upcoming facility is designed to convert green waste into valuable eco-friendly resources, thereby promoting resource recovery and sustainable urban living.
- The plant will play a key role in addressing the growing challenge of organic waste disposal in urban centers.
Key Highlights of the Indore Green Waste Processing Plant
- The facility will handle green waste materials such as wood, tree branches, leaves, and flowers, which are often left untreated or improperly disposed of in many cities.
- The project will also serve as a revenue-generating model for the Indore Municipal Corporation (IMC) by turning waste into marketable products like compost and bio-resources.
- Under the framework of the Swachh Bharat Mission, the IMC will provide land for the plant and ensure the transportation of green waste to the facility.
- The operational responsibilities will rest with Astronomical Industries Private Limited, a private firm that will oversee the installation, operation, and maintenance of the plant, making this a classic case of a PPP-based infrastructure solution.
India’s Efforts in Green Waste Management: Key Initiatives
India has been actively working on strengthening its green waste and biodegradable waste management systems through various policies and missions:
- Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
- These rules mandate that biodegradable waste must be processed and treated preferably within the premises through methods such as composting or bio-methanation.
- The aim is to reduce landfill dependency and promote decentralized waste processing.
- National Bioenergy Programme
- This central government initiative supports the development of bioenergy projects across the country, including those that convert green and organic waste into energy.
- It aims to boost renewable energy production and improve waste utilization efficiency.
- Waste to Wealth Mission
- Launched under the Prime Minister’s Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC), this mission aims to strengthen India’s waste management ecosystem.
- The focus is on scientific solutions and innovation to turn waste into valuable resources, supporting the goals of a circular economy.
|
About Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) The green waste processing plant in Indore is a part of the broader national framework of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) — one of India’s flagship cleanliness campaigns launched to promote sanitation and solid waste management across urban and rural areas. Two Key Components of SBM:
|
NASA Astronauts Return to Earth After 286 Days in Space
- After an unexpectedly extended mission, NASA astronauts have returned to Earth after spending 286 days aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
- Their prolonged stay became necessary due to technical glitches in Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft, which was originally meant to bring them back sooner.
What Went Wrong with the Starliner?
- The CST-100 Starliner, designed by Boeing, suffered from helium leaks and a malfunctioning thruster, which posed safety concerns during re-entry.
- These technical issues delayed the crew’s return, extending their mission far beyond its original timeline.
Longest Stay in Space: A Global Benchmark
While this mission was unusually long, the record for the longest single human stay in space is still held by Soviet cosmonaut Valeri Polyakov, who spent 438 continuous days aboard the Mir space station.
Opportunities from the Extended Space Mission
Despite the challenges, the unplanned long-duration stay offered several scientific and strategic benefits:
- Medical Research: The mission provided rare opportunities to study the effects of extended space exposure on the human body, especially in an unplanned scenario.
- Technology Testing: It allowed NASA to evaluate the endurance and reliability of life-support systems, onboard equipment, and spacecraft functionality beyond standard mission timelines.
- Deep-Space Mission Preparation: Valuable insights from this extended stay will help prepare for future lunar and Mars missions, where astronauts will be in space for long durations.
Health Challenges Faced During Long-Term Space Missions
Prolonged space travel brings with it a host of physiological and psychological challenges. NASA continues to document and study these effects for better preparation.
- Space Radiation: Constant exposure to cosmic rays and solar radiation raises the risk of cancer and other radiation-related illnesses.
- Microgravity Effects:
- Extended exposure to microgravity leads to muscle atrophy and bone density loss.
- Upon return to Earth, astronauts often experience balance and coordination issues due to gravity re-adaptation.
- NASA reports 1% to 1.5% weight-bearing bone loss per month in space conditions.
- Psychological Impact:
Isolation, confinement, and distance from Earth can affect mental well-being, team dynamics, and interpersonal relationships aboard the space station.
|
Understanding the International Space Station (ISS) The ISS is a habitable artificial satellite orbiting Earth at altitudes ranging from 370–460 km. It serves as a collaborative scientific platform for space research.
|
India Develops World’s First Pink Bollworm-Resistant GM Cotton
In a major breakthrough for agricultural biotechnology, the CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) has developed the world’s first genetically modified (GM) cotton variety resistant to Pink Bollworm (PBW) — a pest that has caused extensive damage to cotton crops in India.
Understanding Bt Cotton and How It Works
Bt cotton is a genetically modified variety developed by incorporating a gene from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) to combat pest infestation.
Bt Cotton Mechanism:
- Gene Insertion: A specific gene from Bt bacterium is inserted into the cotton plant's DNA, enabling it to produce a protein called Cry protein.
- Toxin Production: When bollworm larvae feed on Bt cotton, they ingest the Cry protein which disrupts their digestive system, eventually killing them.
- Targeted Pest Control: The Cry protein targets specific pests like bollworms while remaining safe for humans and beneficial insects. It also reduces the need for chemical pesticide sprays.
Bt Cotton in India
- Approved in 2002 by the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- Bt cotton has been used extensively to fight pests such as American bollworm and spotted bollworm, using varieties like Bollgard 1 and Bollgard 2.
The Pink Bollworm Challenge
Despite the success of earlier GM cotton varieties, Pink Bollworm (PBW) has evolved resistance to Cry 1Ac protein, limiting the effectiveness of existing solutions.
PBW: A Persistent Threat
- PBW (Gulabi Sundhi) undergoes multiple life stages—egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- The larval stage causes maximum damage by burrowing into cotton bolls and destroying seeds and fibers.
Agricultural Impact:
- States like Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana have suffered up to 30% yield losses due to PBW infestations.
CSIR-NBRI’s Novel Solution: Enhanced GM Cotton
To address this escalating threat, CSIR-NBRI has developed a new genetically engineered insecticidal gene, providing superior resistance to PBW, surpassing the performance of Bollgard 2.
Key Features of the New GM Cotton:
- High efficacy against Pink Bollworm
- Additional protection from pests like cotton leafworm and fall armyworm
- Aims to restore productivity and reduce farmer dependence on chemical pesticides
UNCTAD’s World of Debt Report 2024
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has released its much-anticipated ‘A World of Debt Report 2024’, highlighting the growing global debt burden and its disproportionate impact on developing countries.
While public debt can be a powerful tool to fuel development and fund essential infrastructure and welfare, the report warns that the rapid rise in debt levels, particularly in the Global South, now threatens global financial stability.
Understanding Public Debt
- Public debt, also known as sovereign debt, refers to the total financial liabilities incurred by a government when its expenditure exceeds its revenue.
- To bridge this gap, governments borrow from domestic and international sources, resulting in accumulated debt over time.
- While borrowing is often essential for developmental investments, unsustainable debt levels can become a heavy burden on economies.
Key Highlights from the ‘A World of Debt Report 2024’
- Global Debt Explosion: The total global public debt reached a staggering $97 trillion by the end of 2023, reflecting an alarming rise in borrowing worldwide.
- Faster Debt Accumulation in Developing Nations: Debt levels in developing countries have been rising at twice the pace of developed countries. This trend signals growing financial vulnerabilities in the Global South.
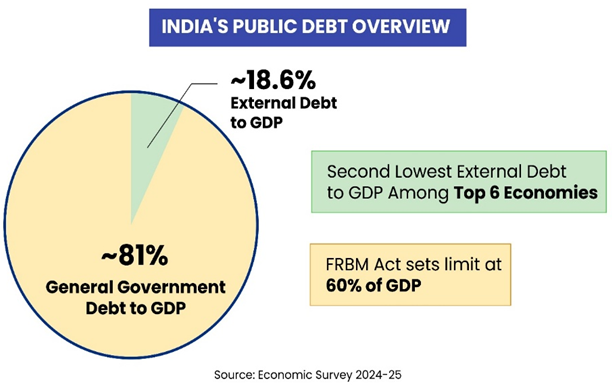
- India's Debt Position: India’s public debt stood at $2.9 trillion, reflecting a significant portion of the developing world’s debt share.
- Debt Servicing Pressure: In 54 developing countries, interest payments now exceed expenditure on critical social sectors such as education, health, and welfare services.
- Interest Rate Disparities: The report underscores how developing nations are compelled to pay 2 to 12 times higher interest rates compared to their developed counterparts—reflecting deep-rooted inequalities in the global financial architecture.
Rising Debt: What Challenges Lie Ahead?
The report draws attention to a series of interlinked challenges stemming from the growing debt burden, especially for low- and middle-income economies:
- Debt Overhang: When a nation’s debt burden becomes excessive, it can dampen economic growth by diverting funds from productive investments to debt servicing, discouraging private investment and consumption.
- Liquidity Crisis: The withdrawal of approximately $50 billion in private capital from developing economies has further tightened liquidity, deepening fiscal distress.
- Costly Debt Restructuring Mechanisms: With a creditor landscape dominated by Western-led institutions (private, multilateral, and bilateral), debt restructuring becomes complex, slow, and expensive, often delaying economic recovery.
UNCTAD’s Policy Recommendations: A Global Call to Action
To tackle the debt crisis effectively, the report proposes comprehensive reforms and global cooperation to ensure inclusive financial governance:
- Establish Coordinated Debt Restructuring Mechanisms:
A well-structured, fair, and transparent framework is needed to streamline the complex and fragmented debt restructuring process, especially for highly indebted developing countries. - Expand Contingency Financing Options:
There is an urgent need to develop pre-emptive financing mechanisms and safety nets to help vulnerable economies manage shocks and prevent full-blown debt crises. - Strengthen Representation of Developing Countries:
Inclusive reforms in global financial governance structures are essential to give developing nations a stronger voice in international financial decision-making bodies and create equitable access to capital.
Also Read
NCERT Books For UPSC UPSC Monthly Magazine Best IAS Coaching in Delhi




