- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Daily Current Affairs Summary 15th APRIL 2025
Daily Current Affairs Summary 15th APRIL 2025
Karnataka Government to Regulate Online Betting and Gaming
The Karnataka Government has set up a committee to draft legislation aimed at regulating online gambling and betting platforms. The goal is to curb fraudulent practices and promote a transparent, legal gaming environment.
Understanding Gambling
Gambling typically involves three essential elements:
- Consideration: Something of value is wagered.
- Chance: The outcome is influenced by luck.
- Reward: A prize or monetary gain is involved.
Why Regulation Is Needed
- Improved Monitoring and Enforcement
A complete ban on betting has not been effective. Legalising and regulating the sector can lead to better enforcement mechanisms. (Law Commission’s 276th Report) - Curbing Match-Fixing in Sports
Bringing sports betting under regulation could reduce unethical practices like match-fixing by players. (Justice Lodha Committee) - Preventing Black Money
According to FICCI, legalised betting could generate ₹12,000–₹19,000 crore in revenue and reduce the underground economy.
Challenges in Regulating Online Gambling
- Games of Skill vs. Games of Chance
- Sports betting is argued to be a game of skill, similar to horse racing, and thus should be permitted.
- In RMD Chamarbaugawala v. Union of India (1957), the Supreme Court held that activities requiring substantial skill are commercial in nature and protected under Article 19(1)(g) of the Constitution.
- Federal Structure and State Autonomy: Gambling is a State subject under the Constitution. If the Centre tries to regulate it, it could lead to a violation of the federal principle of power distribution.
- Tourism Considerations: While most states ban gambling for residents, some like Goa allow it as a tourist attraction, contributing to their local economy.
Current Regulatory Framework
- IT Rules 2021: These rules introduced a co-regulatory system, where self-regulatory bodies—recognized by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY)—determine if an online real-money game is fit for public access.
- Amendment Rules 2023
- Mandate registration and verification of online games.
- Ensure transparency in privacy policies and user agreements.
- State-Specific Laws
- Assam: Assam Gaming and Betting Act, 1970
- Goa: Goa, Daman and Diu Public Gambling Act, 1976
These laws differ across states, reflecting varied approaches based on regional needs and socio-economic factors.
Morag Axis: Strategic Security Corridor in Gaza
Israel has successfully taken control of a newly established security corridor called the Morag Axis, marking a significant move in the ongoing conflict in Gaza.
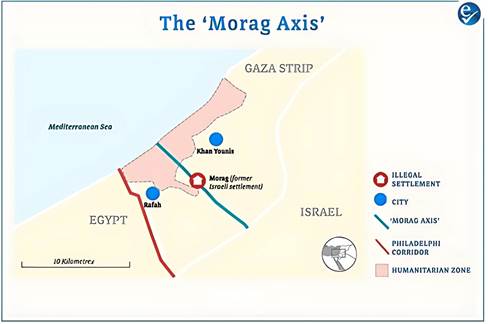
What is the Morag Axis?
- The Morag Axis primarily consists of agricultural land situated between Khan Younis and Rafah, stretching east to west across the Gaza Strip.
- The corridor is named after "Morag," a former illegal Israeli settlement that existed in the region from 1972 until 2005.
- This area is of strategic importance due to its location and potential use for military operations and territorial control.
Cyber Slavery: A Growing Transnational Crime
In a recent development, over 60 Indian nationals have been rescued from Myanmar, where they were victims of a disturbing new form of exploitation known as cyber slavery.
Understanding Cyber Slavery
- Cyber slavery is a modern form of organized crime, where individuals are exploited through digital means under coercive or deceptive conditions.
- It often involves trafficking skilled, tech-savvy youth across borders under the false promise of legitimate job opportunities.
Key Characteristics
- Transnational in Nature
- Victims are often transported across countries, making it a cross-border human trafficking issue.
- It is driven by organized criminal networks operating in multiple regions.
- Forms of Cyber Slavery
- Forced participation in cybercrimes, such as money laundering and cryptocurrency fraud.
- Involuntary involvement in online scams, including digital arrest scams and phishing schemes.
- Exploitation in the gig economy, where victims may be coerced into unpaid or low-paid digital labor.
Cyber slavery represents a serious threat not just to individual rights, but also to international security and digital integrity. The rescue of Indian nationals highlights the urgent need for international cooperation to combat this evolving crime.
Velvet Worms Rediscovered in India
Researchers from the Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and the Environment (ATREE) have recently rediscovered a velvet worm, a rare and ancient invertebrate belonging to the phylum Onychophora.
What Are Velvet Worms?
- Velvet worms, also known as Onychophorans, are often called "walking worms" or "peripatus" due to their unique movement and caterpillar-like appearance.
- Their skin is covered in tiny projections called papillae, giving it a soft, velvety texture.
- These worms are relatively small, typically measuring between 0.5 cm and 15 cm in length.
- They prefer moist habitats, such as forest floors, leaf litter, and areas under rocks, which help them retain body moisture.
- Velvet worms come in a variety of colors, including orange, red, brown, green, blue, and even gold, offering some camouflage in their environment.
Unique Features and Behavior
- Velvet worms are carnivorous predators.
- They have a fascinating hunting method: they shoot a sticky, adhesive slime from specialized glands to trap their prey, often insects like beetles.
- This slime can be projected up to 30 cm, making it an effective tool for immobilizing targets.
Global and Indian Distribution
- There are around 183 known species of velvet worms worldwide.
- In India, however, only one species has been documented, found in the state of Assam.
- Their rediscovery is significant, as it provides fresh insights into their evolutionary history and conservation status, especially in India.
Velvet worms are not only rare but also play an important role in the ecosystem as predators of small insects. Their rediscovery highlights the need for continued research and conservation of lesser-known species in India's biodiversity hotspots.
Types of Diabetes: Now Including Type 5
At the International Diabetes Federation’s (IDF) World Diabetes Congress, a new form of diabetes has been officially recognized — Type 5 Diabetes, also known as malnutrition-related diabetes.
Type 5 Diabetes (J-type Diabetes)
- Type 5 diabetes is closely linked to chronic undernutrition, especially during childhood or adolescence.
- It is most often seen in individuals with low body weight or low Body Mass Index (BMI).
- Unlike other types of diabetes, which are often associated with overnutrition or autoimmune factors, Type 5 stems from long-term malnutrition, affecting the body's ability to regulate blood sugar properly.
Other Recognized Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Caused by the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- As a result, the body cannot produce insulin, which is essential for controlling blood sugar levels.
- It usually develops in childhood or early adulthood.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or the body's inability to produce enough insulin.
- Often linked to obesity, overnutrition, and lack of physical activity.
- It is the most common form of diabetes and typically develops in adults, though it is increasingly seen in younger people.
Gestational Diabetes
- Occurs during pregnancy, when blood glucose levels rise due to hormonal changes and insulin resistance.
- It can lead to health complications for both the mother and the baby, and may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
GPS Spoofing: A Growing Threat to Navigation and Security
In a recent incident, Indian Air Force aircraft reportedly encountered GPS spoofing while flying through Myanmar's airspace, raising concerns over aviation and national security.
What is GPS Spoofing?
- Also known as GPS simulation, GPS spoofing involves sending fake GPS signals to a receiver.
- The goal is to deceive the device into believing it is in a false location.
- This manipulation causes the GPS system to display inaccurate or misleading location data.
How Does It Work?
- GPS spoofing takes advantage of the inherently weak signals sent by satellites.
- Attackers broadcast stronger, false signals that overpower genuine satellite transmissions.
- As a result, the GPS receiver locks onto the fake signals and shows incorrect positional information.
Why is it a Concern?
GPS spoofing poses a serious threat across various sectors:
- Defense: Can mislead military aircraft or drones, as seen in the Myanmar incident.
- Logistics and Supply Chains: Disrupts routing, tracking, and delivery systems.
- Telecommunications: Affects time synchronization used in data networks.
- Energy Sector: Can disrupt operations that depend on precise timing and location, such as power grids.
Pink Moon: April’s First Full Moon
On the night of April 12, skywatchers witnessed a beautiful celestial event — the Pink Moon, which marks the first full moon of April.
Why is it Called the "Pink Moon"?
- Despite its name, the Pink Moon doesn't actually appear pink in color.
- The term originates from a wildflower called Phlox subulata, which blooms around this time in North America.
- The flower's bright pink hue led early observers to associate the seasonal full moon with its arrival, hence the name.
A Micromoon in the Sky
- This full moon was also classified as a "micromoon", meaning it appeared slightly smaller and dimmer than a typical full moon.
- This happens because the moon was at apogee — the farthest point in its elliptical orbit from Earth.
- As a result, the moon's size and brightness were slightly reduced when seen from the ground.
Thangjing Hill: A Sacred Peak in Manipur
Recently, civil society organisations have issued warnings to the Meitei community regarding visits to Thangjing Hill, urging them to avoid climbing the sacred site due to emerging tensions in the region.
Location and Geography
- Thangjing Hill is located in the Churachandpur district of Manipur, to the west of Moirang town.
- The hill is part of a mountain range that marks the western boundary of the Imphal Valley.
- It holds both geographical and spiritual significance for the local population.
Cultural and Religious Importance
- The hill is considered a sacred site by the Manipuri people, especially those from the Moirang region.
- It is believed to be the abode of Thangching, the ancestral deity of Moirang.
- Each year, the Meitei community undertakes a pilgrimage to the summit of the hill in devotion to this revered deity.
Hydrological Features
- Several streams originate from the western slopes of Thangjing Hill.
- These streams eventually flow into the Leimatak River, which moves northward to join the Irang River.
- In the southern direction, the Tuila River rises and later merges with the Tuivai River, a significant watercourse in the Churachandpur district.
Major Harvest Festivals Across India
As spring arrives, various regions across India come alive with traditional harvest festivals, which also mark the beginning of the New Year in many cultures. These festivals are a way of expressing gratitude for a bountiful harvest and celebrating the seasonal change.
Major Harvest Festivals in India
Baisakhi – Punjab
- Celebrated with great enthusiasm, Baisakhi marks the harvesting of Rabi crops, especially wheat.
- It also holds historical and religious significance for Sikhs, as it commemorates the formation of the Khalsa Panth.
- Traditional dances like Bhangra and Gidda are performed in vibrant community gatherings.
Vishu – Kerala and Tamil Nadu
- Vishu symbolizes the spring equinox, a time when day and night are of equal length.
- The festival includes rituals like Vishukkani (auspicious first sight) and fireworks, and is seen as the beginning of a prosperous year.
Poila Boishakh – West Bengal
- Known as the Bengali New Year, Poila Boishakh is a time for business communities to start fresh account books, called Haal Khaata.
- It is marked by cultural programs, traditional food, and new clothing.
Other Prominent Harvest and New Year Festivals
- Bohag Bihu / Rongali Bihu (Assam): Celebrates the Assamese New Year and the start of the sowing season.
- Puthandu (Tamil Nadu): Tamil New Year, marked by feasting, family gatherings, and religious rituals.
- Makar Sankranti (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana): Observes the sun’s transition into Capricorn, celebrated with kite flying and sweet dishes.
- Lohri (Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir): Traditionally celebrates the harvest of sugarcane and winter crops, marked by bonfires and folk songs.
- Pongal (Tamil Nadu): A four-day-long festival thanking the Sun God and farm animals, with rice boiled in milk as a symbolic dish.
New Self-Regulatory Body Introduces Standards for Influencer Marketing in India
- In a significant step towards regulating the growing influencer marketing industry, key industry players have launched the India Influencer Governing Council (IIGC).
- This self-regulatory body includes members from major tech firms such as Meta and Google.
What Has Been Introduced?
- The IIGC has rolled out a Code of Standards for influencers to promote ethical and responsible content creation.
- Additionally, a system of weekly influencer ratings has been introduced to improve transparency and accountability across digital platforms.
- This move comes at a time when the influencer marketing industry in India is projected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated ₹3,375 crore by 2026.
Why Regulation Is Necessary
1. Preventing Consumer Misinformation and Fraud
- Influencers often promote products or services that lack proper verification, including health supplements, financial investments, or cryptocurrency schemes.
- Clear regulations can ensure that all claims are evidence-based, thereby protecting consumer interests.
2. Protecting Vulnerable Audiences
- Many influencers target young, impressionable audiences, sometimes promoting age-inappropriate products like alcohol or online gambling.
- Regulation can help impose age-based restrictions, safeguarding minors and other at-risk groups.
3. Ensuring Fair Market Competition
- Influencer-led promotions often bypass traditional advertising norms, which are subject to stricter rules and checks.
- Introducing standards creates a level playing field, ensuring fairness and ethical business practices.
4. Addressing Mental Health and Unrealistic Standards
- Many influencers set unrealistic beauty or lifestyle expectations through heavily filtered or edited content.
- Guidelines can help mitigate harmful content by mandating disclosures, warnings, or limits on visual manipulation.
5. Closing Platform Accountability Gaps
- Social media platforms have often escaped responsibility for the content shared by influencers.
- Regulations can compel platforms to monitor, review, and remove violative content, increasing overall ecosystem safety.
Code of Standards for Influencers (India Influencer Governing Council)
To ensure ethical practices and transparency in the influencer marketing industry, the India Influencer Governing Council (IIGC) has introduced the following Code of Standards for influencers:
1. Paid Partnerships
- Disclosure Requirement: Influencers must clearly disclose any material partnership or paid collaboration with brands.
- Transparency is essential to ensure that the audience is aware of the influencer's commercial relationships.
2. AI Influencers
- Adherence to Human Influencer Rules: Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven influencers must follow the same standards as human influencers.
- Non-Human Disclaimer: AI influencers must clearly mention their non-human nature to avoid misleading audiences.
3. Brand Relations
- Authenticity in Endorsements: Influencers cannot promote products they don’t genuinely support.
- Conflicting Endorsements: Influencers are prohibited from endorsing competing brands simultaneously to maintain credibility and trust.
4. Defluence
- Honest Criticism: Influencers are allowed to provide honest critiques of brands.
- Responsibility: All criticisms must be truthful, constructive, and responsible to avoid spreading misinformation.
5. Child-Safe Content
- Appropriateness for Children: Content targeted at younger audiences must be safe, positive, and age-appropriate.
- Influencers must ensure their content does not expose children to harmful or inappropriate material.
6. Consumer Complaint Forum: A dedicated forum has been established under the IIGC to address consumer complaints related to influencer content, ensuring a transparent and accountable system for resolving issues.
Concerns Over the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023: Impact on the RTI Framework
Over 120 Members of Parliament (MPs) have raised concerns about Section 44(3) of the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023. They argue that this section weakens the Right to Information (RTI) Act, 2005, and have called for its repeal.
Key Provisions of Section 44(3) of the DPDP Act
- Section 44(3) of the DPDP Act, 2023 amends Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act, 2005.
- It prohibits the disclosure of personal information unless it is explicitly in the public interest.
- Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act previously allowed the exemption of personal information from disclosure, but only when the information was not considered to be in the public interest.
Concerns Raised by MPs
1. Public Accountability
- The blanket exemption and vague definition of "personal information" in the DPDP Act provide significant discretion to public authorities.
- This impacts citizens’ ability to scrutinize public officials, demand clarity on government policies, and hold institutions accountable.
2. Constitutional Balance Between Privacy and Transparency
- Privacy and transparency are both fundamental rights, but they need to be balanced carefully.
- Key references:
- Justice A.P. Shah Committee (2012): Warned that data protection should not override access rights under the RTI Act.
- K.S. Puttaswamy vs. Union of India (2017): The Supreme Court ruled that privacy and transparency should be balanced proportionally, ensuring any restrictions are justified and necessary.
- Girish Ramchandra Deshpande vs. Central Information Commissioner & Ors.: The Supreme Court emphasized privacy but stated that public interest could justify the disclosure of certain information.
Recommendations for Reconciliation
1. Justice BN Srikrishna Committee (2018)
- Recommended narrowly tailored exemptions for non-disclosure, allowing it only in cases of grave harm, such as:
- Identity theft
- Discrimination
2. Suo-motu Disclosure
- The promotion of public entities to disclose information that is of public interest as per Section 4 of the RTI Act.
- This would enhance transparency and reduce the negative impact of excessive secrecy.
India Tests Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System Capable of Disabling Drones, Missiles, and Aircraft
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully conducted a trial of its Mk-II(A) LASER-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system at the National Open-Air Range (NOAR) in Kurnool district, Andhra Pradesh.
- With this achievement, India becomes the fourth country in the world, after the US, China, and Russia, to possess advanced LASER weapon capabilities.
About the Mk-II(A) Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System
- Developed By: The system has been indigenously developed by the DRDO’s Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS), located in Hyderabad.
- Working Mechanism:
- The Mk-II(A) DEW system detects a target using either radar or an inbuilt Electro Optic (EO) system.
- Once a target is identified, it uses a 30-kilowatt high-energy LASER beam to cut through the target, leading to its structural failure.
- Key Characteristics:
- The system is designed for lightning-fast engagement with high precision.
- It can deliver lethal effects to a target in just a few seconds.
Significance of the Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) System
- Revolutionizing Warfare Economics:
- DEWs can significantly reduce the dependence on expensive ammunition, offering a more cost-effective solution in modern warfare.
- It also lowers the risk of collateral damage, making military operations more precise and targeted.
- Counter-Electronic Capabilities:
- The High-Power Microwave (HPM) weapons integrated within the system can disable electronic systems, radars, and communications without causing physical destruction.
- Dual Application for Offensive and Defensive Warfare:
- The system can be used in a range of military scenarios, including:
- Tactical air defense
- Anti-ballistic missile defense
- Anti-satellite (A-SAT) defense
- Low-power lasers can also be employed for crowd control and pirate deterrence.
- The system can be used in a range of military scenarios, including:
What Are Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs)?
- Principle: DEWs use concentrated energy derived from electromagnetic or particle technology, rather than traditional kinetic energy, to degrade or destroy targets.
- Types of Directed Energy Weapons:
- High-Energy Lasers (HELs)
- High-Power Microwave Weapons (HPMs)
- Millimeter-Wave Weapons
- Particle Beam Weapons
Union Commerce Minister Highlights the Lack of Deep-Tech Innovation in Indian Startups
- The Union Commerce Minister recently acknowledged the impressive growth of consumer-driven startups in India, such as food delivery and Q-commerce apps.
- However, the minister also highlighted a significant gap in the emergence of deep-tech innovations within Indian startups.
Understanding Deep-Tech Startups
Deep-tech startups focus on high-risk, long-term ventures that leverage advanced technologies like AI/ML, blockchain, and more. These startups aim to create innovative solutions for complex, real-world problems. Notable examples include Skyroot Aerospace and Sarvam AI.
Current Status of the Startup Ecosystem in India
- Unicorns: India is home to over 100 unicorns, positioning itself as the third-largest startup hub globally.
- Global Innovation Index: India ranks 39th in the 2024 Global Innovation Index, reflecting the country's progress in fostering innovation.
- Deep-Tech Startups: There are approximately 4,000 deep-tech startups in India, which collectively attracted $1.6 billion in 2024—a significant 178% year-over-year increase.
- Tier II and III Cities: Nearly 50% of Indian startups originate from Tier II and Tier III cities, expanding the startup ecosystem beyond the major metropolitan areas.
Government Policies and Initiatives for Startups
India has introduced several policies and schemes to support the startup ecosystem:
- Draft National Deep-Tech Startup Policy (2023): A comprehensive policy aimed at fostering deep-tech startups.
- Startup India Seed Fund: A fund to support early-stage startups in India.
- IndiaAI Mission and Fund of Funds for Deep-Tech: A Rs 10,000 crore initiative to boost deep-tech startups.
- BHASKAR (Bharat Startup Knowledge Access Registry): An initiative to provide knowledge access and promote startup growth.
Challenges Facing the Indian Startup Ecosystem
Despite the positive growth, several issues are hindering the full potential of the startup ecosystem:
- Funding Challenges:
- The availability of both government and private capital is limited, which stifles startups working on complex problems.
- From 2014 to 2024, India’s total tech investment is estimated at $160 billion, significantly lower than China’s $845 billion.
- India’s venture capital (VC) landscape tends to prioritize quick returns, making it harder for deep-tech startups to secure patient capital.
- Education and Research Infrastructure:
- India faces a lag in developing its ecosystem due to subpar educational infrastructure.
- Key issues include a lack of quality research, weak industry-academia linkages, and a shortage of skilled workers, contributing to brain drain.
- Governance Issues:
- Policy uncertainty and regulatory challenges hinder the ease of doing business in India.
- Startups face difficulties in accessing credit, dealing with taxation, navigating import barriers on raw materials, and overcoming bureaucratic hurdles like approvals, red tape, and corruption.
Way Forward: Proposed Solutions
To address these challenges and foster innovation, several steps are needed:
- Policy Reforms:
- Provide grants and create regulatory sandboxes to test prototypes and allow startups to refine their solutions.
- Offer logistical support to help startups commercialize their innovations.
- Promote deep-tech-focused skill development programs to bridge the talent gap.
- Investment Promotion:
- Set up dedicated deep-tech innovation funds to support startups in the sector.
- Create co-investment programs in partnership with venture capitalists to attract long-term investments.
- Education Reform:
- Strengthen academia-startup collaborations to foster quality research and innovation.
- Build strong industry-academia bridges to ensure a continuous flow of skilled talent into the startup ecosystem.



