- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT- First Ladder
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Creation of 5 New Districts in Ladakh
Creation of 5 New Districts in Ladakh
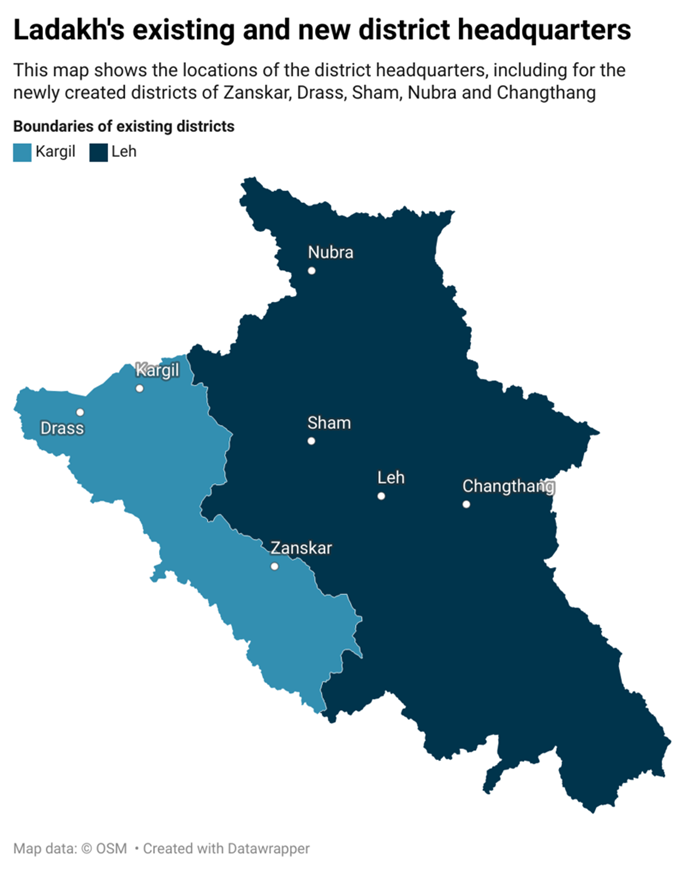
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has granted "in-principle approval" for the creation of five new districts in Ladakh, increasing the Union Territory's (UT) total to seven. This decision aims to enhance governance and development by addressing administrative challenges in the region's vast and rugged terrain.
New Districts in Ladakh and Their Purpose
New Districts:
- Zanskar
- Drass
- Sham
- Nubra
- Changthang
Significance:
- Current Structure: Ladakh previously had only 2 districts—Leh and Kargil. The new districts are expected to improve administrative efficiency and service delivery in remote and difficult-to-access areas.
- Geopolitical Importance: Ladakh’s strategic location makes it crucial for both civilian and military infrastructure development. The new districts aim to support and streamline these efforts.
- Development Initiatives: Ladakh is part of the Prime Minister’s Development Package (PMDP), which provides substantial funding and infrastructure projects. The creation of new districts is intended to further these developmental goals.
Next Steps:
- Formation of Committee: The Ladakh administration is to form a committee to evaluate the new districts' headquarters, boundaries, structure, and staffing.
- Report Submission: This committee must submit a detailed report within three months for the Union Home Ministry's review and further action.
Political and Public Reactions:
- Concerns: There are questions about whether the new districts will have elected Autonomous Hill Development Councils, similar to Leh and Kargil, to ensure effective local governance.
- Responses: The move has generally been welcomed, though some activists and former politicians are advocating for increased political representation and functional autonomy to ensure effective governance.
How New Districts are Created in India
Process:
- State Governments: District creation, alteration, or abolition is typically managed by state governments through executive orders or legislative action.
- Role of the Centre: The central government is involved in changes related to district names but does not directly create or alter districts.
- District Trends: As of 2024, India has 718 districts, up from 593 in 2011. The increase reflects efforts to improve administrative efficiency.
Background on Ladakh's UT Status and DemandsCurrent Status:
Primary Demands:
Government Response:
Context:
|
Constitutional Provisions Related to Formation of States in India
Article 3 of the Indian Constitution:
- Formation of States: Parliament can create new states, alter existing state boundaries, or change state names.
- Conditions: A bill for such changes must be recommended by the President and referred to the concerned state legislature for views.
Additional Considerations:
- Union Territories: Parliament has the authority to create or modify Union Territories without state legislature references.
Historical Context:
- Increased Number of Districts: As of 2024, the number of districts has increased to 718, reflecting state-level administrative changes.
Sixth Schedule Overview
About:
- Special Provisions: The 6th Schedule provides for the administration of tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram under Article 244(2) of the Constitution.
Objectives:
- Protection: Safeguard tribal land and resources and prevent exploitation.
- Autonomous Administration: Establish Autonomous Districts and Regions with District and Regional Councils.
Council Composition:
- District Council: Up to 30 members, with a maximum of 4 nominated by the Governor.
- Regional Council: Established for autonomous regions with a similar structure.
Conclusion
The formation of 5 new districts in Ladakh represents a significant administrative step aimed at improving governance and development in a region characterized by its vast and challenging terrain. This move is expected to enhance service delivery, support strategic development, and address local governance issues. However, it also raises questions about the adequacy of local governance structures and political representation. As Ladakh continues to navigate its status as a Union Territory and respond to socio-political demands, the effective implementation of these new districts will be crucial for ensuring that the benefits of development and governance reach all corners of this strategically important region.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus