- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT Batch
- Polity Module Course
- Geography Module Course
- Economy Module Course
- AMAC Module Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History Module Course
- Environment Module Course
- Governance Module Course
- Science & Tech. Module Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Module Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Module Course
- Essay Module Course
- Current Affairs Module Course
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Cook Islands
Cook Islands
16-05-2024

The Cook Islands, located in the South Pacific, are pioneering the exploration of deep-sea mining for minerals crucial to the production of electric car batteries. These mineral deposits have not been extracted on a large scale before, but their vast reserves could potentially enable a transition away from fossil fuels.
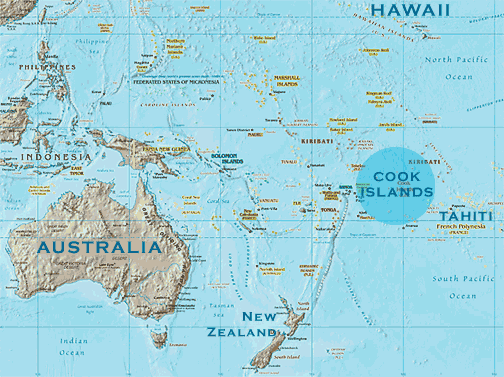
- The Cook Islands, a 15-island chain that was once a colony of New Zealand has been self-governing since 1965.
Location:
- Situated in the South Pacific Ocean, the Cook Islands is a self-governing island state in free association with New Zealand.
- Its 15 islands are divided into two groups: the northern group and the southern group.
Northern Islands:
- The northern islands consist of 6 low-lying and sparsely populated coral atolls: Manihiki, Nassau, Penrhyn, Pukapuka, Rakahanga, and Suwarrow.
- These islands are characterised by their white sand beaches, light vegetation, and crystal-clear waters.
Southern Islands:
- The southern islands are generally larger and higher, with volcanic origins.
- They are also more densely populated than the northern islands.
- The southern island group includes Rarotonga, Aitutaki, Atiu, Mangaia, Manuae, Mauke, Mitiaro, Palmerston, and Takutea.
Highest Point:
- The highest point in the Cook Islands is Te Manga, which rises to 652m on the island of Rarotonga.
- Population: The majority of the population resides on the island of Rarotonga, which serves as the administrative and economic center of the Cook Islands.
Capital City:
- The capital city of the Cook Islands is Avarua, located on the island of Rarotonga.
- It is a vibrant hub of activity, with a blend of traditional Polynesian culture and modern amenities.
Volcanic Islands:
- The southern islands of the Cook Islands are of volcanic origin, formed when volcanoes erupted underwater and built up new land above the water's surface.
- These islands are characterised by their vegetation, fertile soils, and rugged landscapes.
Significance of Volcanic Islands:
- Volcanic islands play an important role in the ecosystem, providing habitats for diverse flora and fauna.
- They also contribute to the formation of coral reefs, which support marine biodiversity and protect coastlines from erosion.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



