- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Challenges and Strategic Adjustments for ARCs
Challenges and Strategic Adjustments for ARCs

Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) are facing a slowdown in growth, primarily due to a reduction in Non-Performing Assets (NPAs), which have fallen to a 12-year low of 2.8% as of March 2024. According to Crisil, assets under management (AUM) by ARCs are expected to contract by 7-10% in 2024-25, following a stagnant performance in 2023-24.
Concerns of Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs)
Low Business Potential
- Decrease in new non-performing corporate assets has led ARCs to target smaller, less profitable retail loans.
- Despite this focus, there has not been a significant increase in retail NPAs, limiting opportunities for ARCs.
Increased Investment Mandate
- RBI's directive in October 2022 requires ARCs to invest at least 15% of bank investments in security receipts or 2.5% of total security receipts issued, whichever is higher.
- This has placed additional constraints on ARCs' capital usage, with many struggling to meet the new ₹300 crore minimum net owned funds requirement.
Net Owned Funds Requirements
- The RBI raised the minimum net owned funds requirement for ARCs from ₹100 crore to ₹300 crore in October 2022 to ensure robust balance sheets.
- Many ARCs are struggling to meet this requirement, leading to potential mergers or exits.
Competition from NARCL
- The state-owned National Asset Reconstruction Company Ltd (NARCL) offers security receipts guaranteed by the government, making them more attractive to financial institutions.
- This creates significant competition for private ARCs.
Regulatory Challenges
- ARCs must now obtain approval from an independent advisory committee for all settlement proposals, leading to delays.
- Increased RBI scrutiny, including the banning of Edelweiss ARC from new loans for bypassing regulations, has impacted major ARCs.
- Trust deficit between the RBI and ARCs, with concerns about transactions potentially helping defaulting promoters regain control of assets, violating Section 29A of the IBC.
What are ARCs?
- Definition: An asset reconstruction company (ARC) buys distressed debts from banks at an agreed value and attempts to recover the debts or associated securities.
- Background: ARCs were introduced by the Narsimham Committee – II (1998) and established under the SARFAESI Act, 2002.
- Current Status: 27 ARCs are registered with the RBI, including prominent ones like NARCL, Edelweiss ARC, and Arcil.
- Registration and Regulation: ARCs must be registered under the Companies Act, 2013 and with the RBI under the SARFAESI Act.
- Funding: ARCs raise funds from Qualified Buyers (QBs) including insurance companies, banks, and asset management companies.
Working of ARCs
Asset Reconstruction
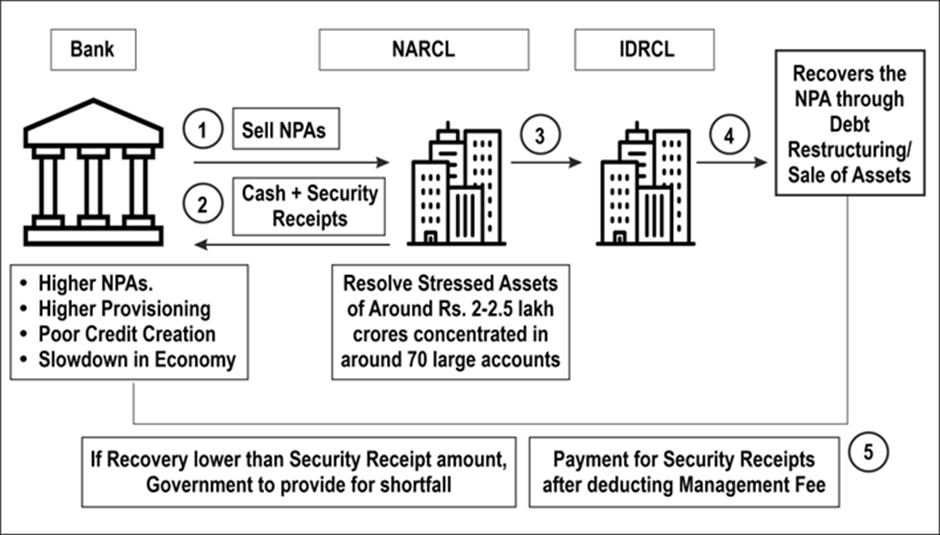
- Acquiring rights in distressed loans or credit facilities for recovery.
- Buying distressed loans at a discount, redeemable within eight years.
Securitisation
- Acquiring financial assets by issuing security receipts to Qualified Buyers.
Non-Performing Asset (NPA)
- Definition: A loan classified as NPA when payments are overdue for 90 days; for agriculture, if overdue for two cropping seasons.
- Categories:
- Sub-standard Assets: Non-performing for ≤12 months.
- Doubtful Assets: Non-performing for >12 months.
- Loss Assets: Uncollectible and needing to be written off.
Recent Changes in ARCs Regulations by RBI
- Strengthening Governance Structure: Chair and at least half of the board must be independent directors.
- Enhancing Transparency: Disclosure of track record of returns and collaboration with rating agencies for schemes launched in the past eight years.
- Revised Investment Requirements: ARCs must invest at least 15% of the transferor’s investment or 2.5% of total receipts issued, whichever is higher.
Measures to Address Challenges Faced by ARCs
- Diversification of Asset Portfolios: Explore sectors beyond traditional corporate and retail loans, such as infrastructure and MSMEs.
- Improving Regulatory Transparency and Collaboration: Work closely with the RBI and other regulatory bodies for transparent operations and compliance.
- Enhancing Efficiency in Settlements: Use technology, such as AI-driven analytics, to speed up settlement processes.
- Adopting Strategic Competition with NARCL: Offer specialized solutions or focus on faster recovery mechanisms to differentiate from NARCL.
Conclusion
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) are facing multiple challenges, including a reduced pool of non-performing assets, increased regulatory requirements, and competition from the state-owned NARCL. Addressing these challenges requires diversification, improved regulatory collaboration, and enhanced operational efficiency.




