- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
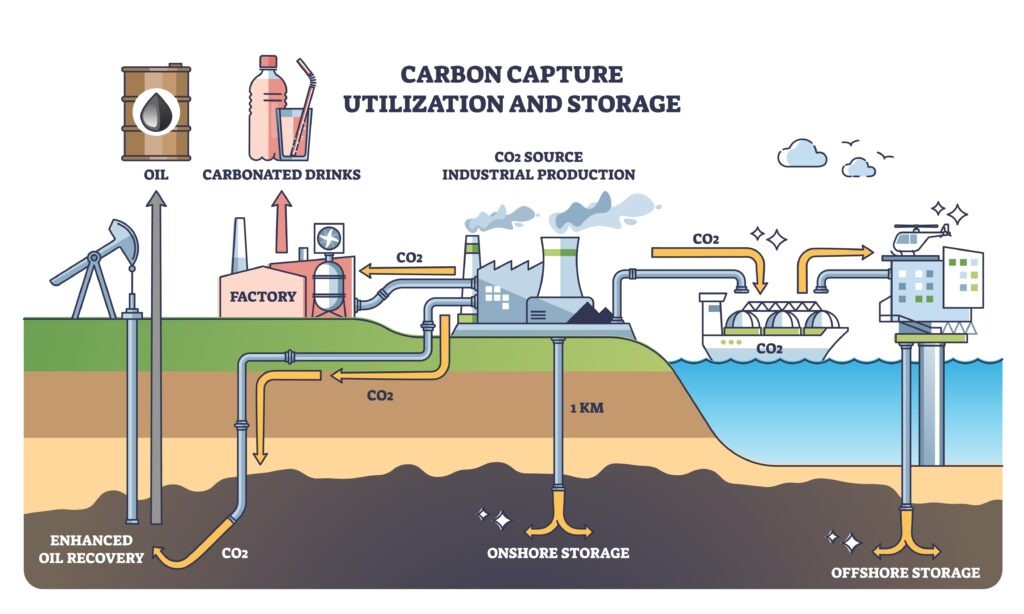
Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) Testbeds
Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) Testbeds
20-05-2025
Why in News?
Recently, the Department of Science and Technology (DST) has launched a new initiative to reduce pollution from the cement industry on National Technology Day, 11th May 2015.
- It involves setting up five Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) Testbeds in the cement sector to promote Green Cement.
What is Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU)?
- About:
- CCU is a modern technology that captures CO₂ released during industrial processes.
- It is promoting the reuse of emitted CO2 .
- Uses:
- Synthetic fuels: CCU can be used to produce synthetic fuels like kerosene, which can be used in aviation or other sectors.
- Chemicals: CO2 can be converted into chemicals like urea, which is used in fertilizers.
- Building materials: CO2 can be used to manufacture concrete and cement, reducing the carbon footprint of these materials.
- Other products: CCU can also be used to create materials like carbon nanotubes and graphene, which have various applications in technology.
- Benefits of CCU:
- Reduced emissions: CCU helps to reduce CO2 emissions from industrial sources.
- Resource efficiency: CCU can reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and other resources.
- Economic growth: It can create new industries and jobs in the carbon capture and utilization sector.
- Environmental benefits: It can help to mitigate climate change and improve air quality.
What are the Importance of CCU?
- The CCU initiative is a significant step towards helping India to achieve its climate objectives.
- Achiveing net-zero carbon emissions by 2070.
- Fulfilling the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) under the Paris Agreement.
- This initiative will contribute to creating new employment opportunities, fostering innovation, and building a cleaner, greener economy for future generations.
What is Green Cement?
- Green cement is a kind of cement that is better for the environment.
- It is made using a process that produces much less carbon dioxide (CO₂), which helps in controlling the pollution.
- Green cement uses waste leftovers from industries, like slag from blast furnaces and fly ash instead of using only new raw materials.
- The technology used to make green cement saves a lot of energy and releases much less CO₂ about 40% less compared to regular cement.
- Green cement also costs less to make and is cheaper to buy because it uses waste materials.
What are the Testbeds?
- A testbed is like a small project or experiment where new ideas and technologies are tested.
- These five testbeds will test different ways to capture carbon dioxide (CO₂) which is a major green house gas that causes global warming.
What will Each Testbed Do?
- Each testbed is trying a different method to reduce CO₂ from cement factories.
- Testbed 1 (JK Cement Ballabhgarh):
- It will capture two tonnes of CO₂ every day.
- The CO2 will turn into lightweight blocks (Concrete Block) and olefins (alkene used in making plastics).
- It uses a method called oxygen calcination.
- Testbed 2 (IIT Kanpur and JSW Cement):
- It will test CO₂ mineralisation.
- Mineralisation means turning CO₂ into solid materials like rocks or bricks.
- Testbed 3 (IIT Bombay and Dalmia Cement):
- It will use catalysts to capture CO₂ more efficiently. The catalyst will help the chemical reaction happen more quickly.
- Testbed 4 (CSIR-IIP, IIT Tirupati, IISc and JSW Cement):
- It will use vacuum swing adsorption.
- This is a method where CO₂ is pulled out of the air using a vacuum and special materials.
- Testbed 5 ( IIT Madras, BITS Pilani Goa and UltraTech Cement)
- It will work on new process ideas to lower carbon emissions at every step of cement production.
- Testbed 1 (JK Cement Ballabhgarh):
Why Focus on the Cement Sector?
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) pollution from cement factories in India has increased almost four times since the year 2000.
- Cement production in India released about 177 million tonnes of CO₂ in the year 2023.
- This was around 6% of all CO₂ pollution from fossile fuel use and industries in India that year.
- India's cement industry alone caused 6% of the country’s industrial pollution and 11% of the world’s cement pollution in 2023.
How does Public-Private Partnership promote innovation in CCU?
- This CCU project is being done in a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- The top research institutions are working together with Major cement companies.
- This project will be supported by Government funding.
- This collaboration helps in sharing knowledge, testing new technologies in real-world conditions, and making them ready for large-scale use.
What are the Challenges Associated with CCU?
- High Costs: Implementing CCU technology requires significant investment, making it expensive for many industries to adopt.
- Technical Complexity: Capturing and converting CO₂ efficiently involves complex processes that need advanced technology and expertise.
- Energy Requirements: CCU processes can consume a lot of energy, which may reduce overall efficiency if not managed properly.
- Limited Infrastructure: There is a lack of widespread infrastructure to capture, transport, and utilize CO₂ on a large scale.
- Market Development: Products made from captured CO₂ are still emerging, and demand for these products is not yet strong enough to sustain large-scale CCU operations.
Way forward:
- Increase Research and Innovation: Support ongoing research to improve CCU technologies, making them more efficient and affordable.
- Government Incentives and Funding: Provide financial support, subsidies, and policy incentives to encourage industries to adopt CCU solutions.
- Capacity Building and Training: Train workers and managers to operate and maintain CCU technologies effectively.
- Develop Infrastructure: Build the necessary facilities for capturing, transporting, and utilizing CO₂ at a larger scale.
- Promote Market Creation: Encourage the use and demand of CO₂-based products through awareness campaigns and industry partnerships to ensure sustainability of CCU initiatives.
Official Secrets Act, 1923; and Section 152 of Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita(BNS)
Official Secrets Act, 1923; and Section 152 of Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita(BNS)