- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
BOT Model for Highway Projects
BOT Model for Highway Projects
05-09-2023
Latest Context:
Recently, the Minister of Road Transport and Highways has said that the projects costing less than Rs 1,000 crore should be awarded through the Build Operate and Transfer (BOT) model.
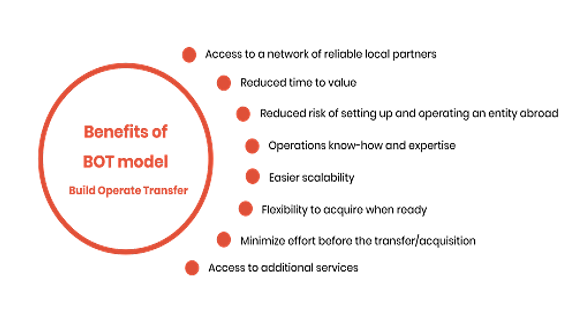
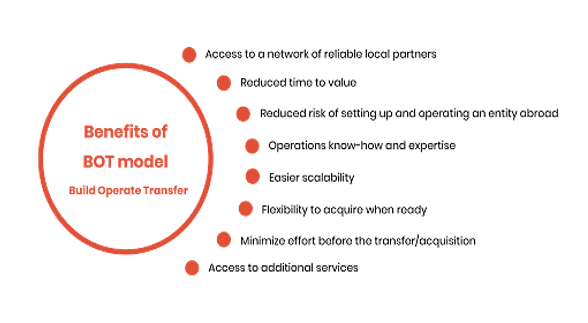
About Build Operate and Transfer (BOT) model
- BOT model is a type of public-private partnership used for infrastructure development projects.
- It is a popular approach for financing and implementing large-scale infrastructure projects, such as highways, bridges, ports, airports, power plants, and more.
The BOT model typically involves 3 main phases:
- Build: In this phase, a private sector entity, often referred to as the "private partner" or "developer," is responsible for designing, financing, and constructing the infrastructure project. The private partner usually enters into a contractual agreement with the government or a public authority, which grants it the right to develop the project according to certain specifications and within a defined timeframe.
- Operate: Once the infrastructure project is completed, the private partner operates and maintains it for a specified concession period, which can range from several years to several decades. During this phase, the private partner is responsible for the day-to-day management, upkeep, and operation of the facility. The private partner generates revenue from user fees, tolls, or other revenue streams, and it is expected to cover its operational and maintenance costs during this period.
- Transfer: At the end of the concession period or the agreed-upon timeframe, ownership and control of the infrastructure project are typically transferred back to the government or the public authority. This transfer is often done at no additional cost (hence the term "transfer"), and the public sector assumes full responsibility for the facility's operation and maintenance.
Significance of BOT Model
- Infrastructure Development: BOT projects enable the development of critical infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, ports, airports, power plants, water treatment facilities, and more. This is especially important in developing countries or regions where governments may lack the necessary funds and expertise to undertake such large-scale projects on their own.
- Private Investment: The BOT model attracts private sector investment into infrastructure development. Private companies bring their capital, technology, and expertise to fund and execute these projects. This reduces the burden on public finances and allows governments to allocate their resources to other pressing needs.
- Risk Allocation: The BOT model allows for the efficient allocation of risks between the public and private sectors. Private partners take on risks related to design, construction, and operation, incentivizing them to deliver projects on time and within budget. Meanwhile, governments can focus on their role of regulation, oversight, and ensuring the public interest is protected.
- Efficiency and Innovation: Competition among private bidders often leads to cost savings and innovative solutions in project design and execution. Private partners are motivated to find the most efficient and cost-effective ways to deliver services because their profits depend on it.
- Timely Delivery: BOT projects are often completed more quickly than traditional government-funded projects. Private partners have a strong incentive to complete construction on time to begin generating revenue during the operational phase.
- Quality Maintenance: During the operational phase, private partners are responsible for maintenance and upkeep. This can result in better quality maintenance than some publicly managed facilities might receive.
- Technology Transfer: BOT arrangements often involve the transfer of technology and best practices from the private sector to the public sector, which can enhance the government's capacity to manage and operate infrastructure.
Conclusion and Way Forward:
- The success of BOT projects depends on careful planning, transparent and well-structured contracts, and effective regulation to balance the interests of both parties and protect the public interest.
- While poorly executed, BOT projects can lead to issues such as high user fees, disputes, or inadequate service quality. Therefore, governments need to carefully consider the specific circumstances and objectives of each project when choosing the BOT model as a means of infrastructure development.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



