- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Biobank Laws: Key to Advancing Precision Medicine in India
Biobank Laws: Key to Advancing Precision Medicine in India
15-10-2024
- Precision medicine is bringing in a new era of personalised healthcare.
- In India, despite significant advancements in this area, the absence of strong biobank regulations poses a key challenge to further progress in precision medicine.
What is meant by the Precision Medicine?
- Precision medicine is an emerging personalized healthcare approach that customizes treatment according to a person’s genetic makeup, environment, and lifestyle.
- Precision medicine began with the completion of the Human Genome Project.
- Human Genome Project is a research effort aimed at determining the chemical makeup of the entire human genetic code (genome), and identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome.
- It plays a key role in diagnosing and treating cancers, chronic diseases, and immunological, cardiovascular, and liver diseases.
- Emerging technologies like gene-editing and mRNA therapeutics also contribute to precision medicine.
- Key Technological Successes:
- Gene therapy restored vision in people with genetic mutations. In the U.K., researchers reversed diabetes using reengineered stem cells.
- mRNA vaccines were rapidly developed during the COVID-19 pandemic, earning a Nobel Prize.
- Organ-on-chips allows testing drugs on microfluidic devices replicating human cells, aiding in drug testing.
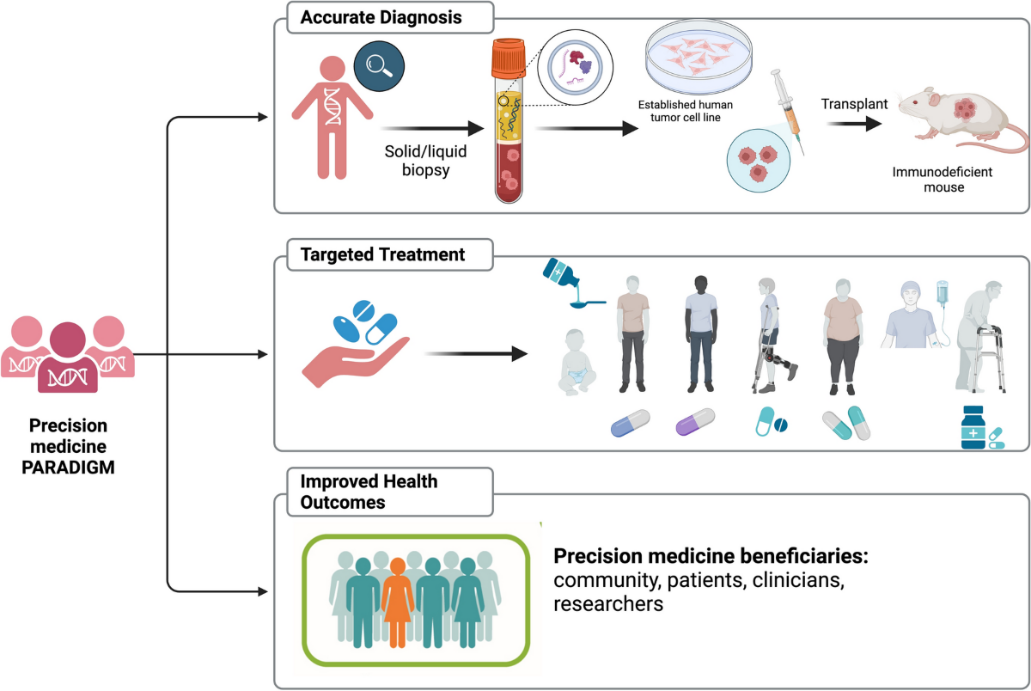
Precision Medicine in India
- India’s precision medicine market is growing rapidly and projected to reach over $5 billion by 2030.
- Currently, it contributes 36% to the national bioeconomy, focusing on cancer immunotherapy, gene editing, and biologics.
- The development of precision therapeutics is also part of the new ‘BioE3’ (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy.
- BioE3’ policy aims to promote high-performance biomanufacturing, which is the use of advanced biotechnological processes to produce products like medicine and materials.
- Recent Developments in India: In October 2023, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization approved NexCAR19, a domestically developed CAR-T cell therapy.
- CAR T-cell therapy (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy) is a type of treatment in which a patient's T cells (a type of immune system cell) are changed in the laboratory so they will attack cancer cells.
Benefits of Precision Medicine
- Better diagnosis: Precision medicine can help doctors diagnose diseases more accurately and understand the causes of a patient's illness.
- More effective treatments: Precision medicine can help doctors identify the best treatments for each patient, which can help slow, stop, or reverse disease.
- Better understanding of disease: It can help doctors understand the underlying mechanisms of disease.
- Reduced adverse effects: Precision medicine can reduce the risk of adverse effects for patients.
- Improved healthcare systems: Precision medicine can improve the sustainability and efficiency of healthcare systems.
Biobanks in Precision Medicine
- Biobanks store biological samples like blood, DNA, and tissues, along with genetic data for research.
- Large, diverse biobanks are critical for precision medicine; otherwise, benefits will reach only a limited population.
- India has 19 registered biobanks with diverse biological specimens.
- Major initiatives like the Genome India Project, Phenome India and Paediatric Rare Genetic Disorders (PRaGeD) mission have begun collecting large-scale genetic data.
- Biobank regulations in India are insufficient, which hampers growth in precision medicine.
International vs. India’s Biobank Regulation:
- Countries like the U.K., U.S., Japan, and China have comprehensive biobank regulations covering informed consent, privacy, and data protection.
- India lacks consistent regulation, leading to gaps in public trust and limiting precision medicine’s growth.
Key Issues with Biobank Regulations in India
- Lack of Legal Protection: There is no law that safeguards individuals' rights related to how their biological samples are used, ensuring data privacy, or securing informed consent.
- Incomplete Consent: Participants often agree to share their samples without fully understanding how their data will be used or who will access it.
- No Central Oversight: India lacks a central regulatory body to monitor biobank activities, leading to no penalties for ethical breaches like mishandling or unauthorized sharing of samples.
- Risk of Foreign Access: Foreign pharmaceutical companies can access Indian samples without proper supervision, leading to potential loss of ownership and profits from research outcomes.
Leadership Opportunity for India
- Enhancing Data Privacy: Strengthening data privacy rules and introducing better oversight will encourage more people to participate in biobank research and ensure ethical practices.
- Aligning with Global Standards: Bringing India's biobank regulations in line with international standards will boost trust and position India as a leader in next-generation therapies.
- Leadership in Global Health: India's active participation in global groups like Quad and BRICS, along with its strong pharmaceutical presence, requires updated biobank laws to grow its influence in global healthcare advancements.
Previous Year UPSC Prelims Question
What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news? (UPSC Prelims 2019)
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
Answer: (a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
Practice Question
Consider the following statements regarding biobanks:
1. Biobanks are repositories that store biological samples like blood, DNA, and tissues for research purposes.
2. Large, diverse biobanks are essential for precision medicine to benefit all sections of society.
3. Biobanks in India are well-regulated, with comprehensive laws ensuring informed consent and data protection.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus




