- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Audit report on Ayushman Bharat-PM Jan Arogya Yojna
Audit report on Ayushman Bharat-PM Jan Arogya Yojna
09-08-2023
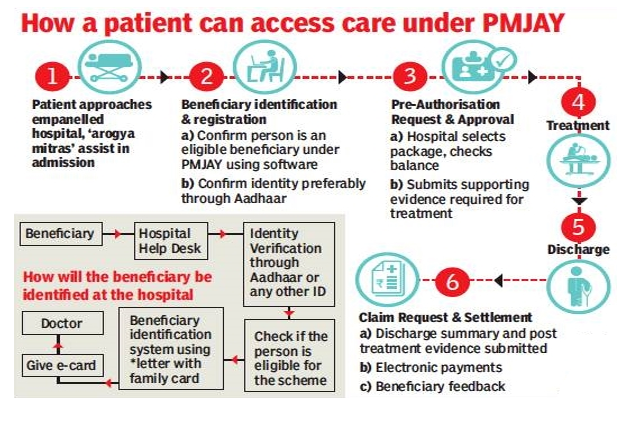
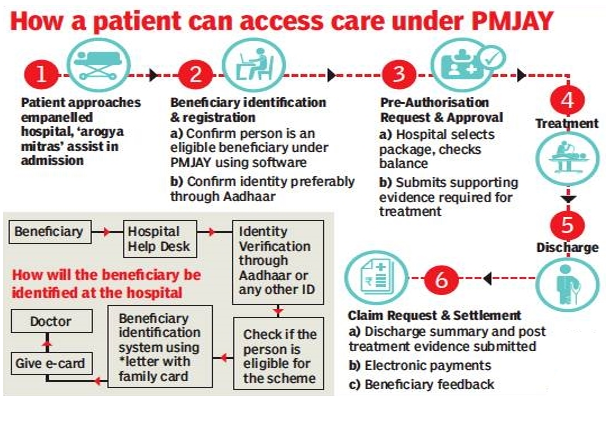
Latest Context:
Recently, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India released an audit report on Ayushman Bharat - PM Jan Arogya Yojna (PMJAY).
About Ayushman Bharat - PM Jan Arogya Yojna (PMJAY)
- PMJAY is a flagship healthcare scheme launched by the Government of India in September 2018.
- It is a part of the broader Ayushman Bharat program, which aims to provide accessible and affordable healthcare to millions of Indian citizens.
- The scheme primarily targets poor and vulnerable families in India.
Key features of PMJAY are:
- Health Coverage: PMJAY provides health insurance coverage of up to ₹5 lakhs per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization. This coverage is meant to take care of most medical expenses for major illnesses and surgeries.
- Beneficiary Identification: Beneficiaries under PMJAY are identified based on the Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) database. The SECC database helps in identifying and selecting eligible families who are socio-economically deprived and in need of healthcare support.
- Cashless Transactions: The scheme aims to facilitate cashless transactions at empanelled hospitals. Beneficiaries can receive treatment without worrying about immediate out-of-pocket expenses, as the hospital bills are directly settled by the insurance provider.
- Portability: PMJAY provides the flexibility of availing services across India. Beneficiaries can access healthcare services at any empanelled hospital in any part of the country, making it especially beneficial for individuals who need medical attention, while away from their home state.
- Coverage of Medical Procedures: The scheme covers a wide range of medical procedures, including surgeries, diagnostics, and treatments for various illnesses and medical conditions.
- No Enrolment or Premiums: Beneficiaries do not need to pay any enrolment fee or premium to get the benefits of PMJAY. The government covers the cost of insurance for eligible families.
- Empanelled Hospitals: The scheme has a network of empanelled private and public hospitals. Hospitals that meet certain criteria are enlisted under the scheme to provide services to the beneficiaries.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): PMJAY aims to maintain electronic health records of beneficiaries to ensure smooth and efficient healthcare delivery across different healthcare facilities.
- Focus on Women and Children: PMJAY has a special focus on providing healthcare services to women and children, with specific packages designed for maternity and childcare.
- Preventive Healthcare: The scheme also emphasizes preventive healthcare measures to promote overall well-being and reduce the burden of disease.
Key findings of the audit report are:
- As per the report, only around 73% of the targeted households are actual beneficiaries.
- A lot of errors like invalid names, duplicate IDs, etc. have been found.
- Many empanelled hospitals are charging for treatments and they even lack basic infrastructure, biomedical waste management etc.
- In many states, an overlap of beneficiaries with the state-sponsored schemes have been found.
- Few other mismanagements have also been noticed like release of excess grants to some states, diversion of funds, non-compliance with the rules and regulations.
- Only around 10% of the complaints were redressed within the given timeframe.
Recommendations of the report are:
- Cross-check mechanism should be there to increase the accuracy and reliability of the data.
- To encourage more private hospitals to join the scheme.
- Regular audits on the processing and payment of the claims.
- To constitute ‘District Implementing Units’ in every district of the country.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi


