- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
African Union joins as a permanent member of G20
African Union joins as a permanent member of G20
11-09-2023
Latest Context:
Recently, the African Union (AU) joined as a permanent member of G20 under India’s presidency.
About the African Union (AU)
- AU is a continental organization consisting of 55 African countries.
- It was established in 2001 at Durban (South Africa) and was officially launched in 2002 at Durban, to replace the Organization of African Unity (OAU), which had been in existence since 1963.
- The AU was formed with the aim of promoting unity and cooperation among African nations and addressing the various social, economic, political, and security challenges facing the continent.
- AU is the largest intergovernmental organization on the African continent. All African countries are eligible to join it.
- The AU plays a critical role in promoting peace and security on the continent. It has established the African Standby Force (ASF) and the Peace and Security Council (PSC) to address conflicts and crisis in Africa.
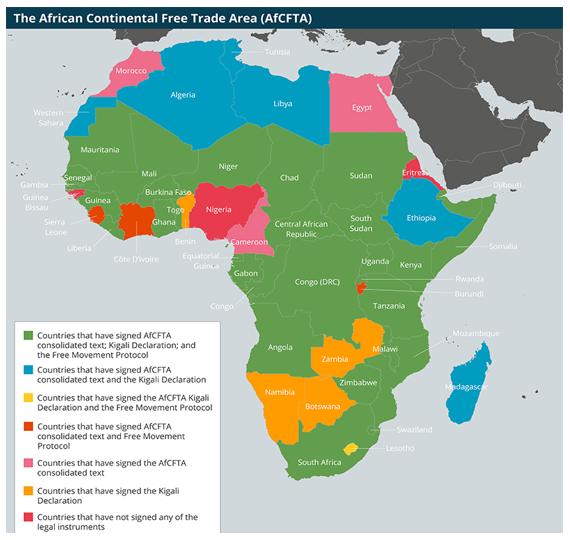
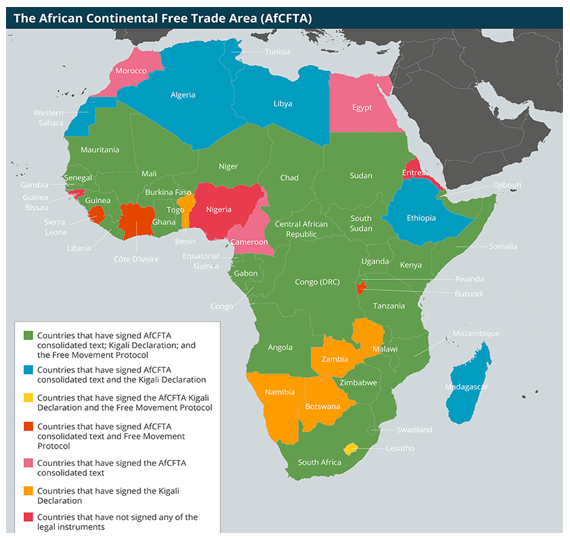
- The AU works to promote economic integration through initiatives like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which aims to create a single market for goods and services across the continent.
- The AU facilitates political cooperation among member states, including promoting democratic governance and human rights.
- The AU promotes cultural exchange and social development initiatives to strengthen the bonds among African nations and celebrate the diversity of African cultures.
Significance of inclusion of African Union into G20
- Economic Significance: Africa is home to some of the world's fastest-growing economies, with vast natural resources and a young, dynamic population. Inclusion of the AU in the G20 reflects the continent's growing economic importance on the global stage.
- Development Challenges: Many African countries face significant development challenges, including poverty, infrastructure deficits, and healthcare issues. Inclusion in the G20 will provide a platform for discussing and addressing these challenges with the world's major economies.
- Trade and Investment: Enhanced participation in the G20 could facilitate discussions on trade and investment between African nations and G20 members, potentially leading to increased economic cooperation and opportunities for African countries.
- Global Governance and Representation: Advocates argue that the G20 should be more representative of the global community, including regions that are traditionally underrepresented in international forums. The inclusion of the AU can contribute to a more balanced representation in global governance.
- Global Challenges: Many global challenges, such as climate change, pandemic preparedness, and terrorism, require international cooperation and coordination. African nations can play a significant role in addressing these challenges, and their inclusion in the G20 can promote cooperation on these critical issues.
About the G20
- It’s an international forum comprising 19 individual countries and the European Union.
- It was established in 1999 and its first meeting took place in Berlin (Germany) in 1999 only.
- It brings together major advanced and emerging economies to discuss and address global economic issues.
- The group represents around 80% of the world's economic output and two-thirds of its population.
- Its members are: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom and the United States.
- Additionally, the European Union is represented by the European Commission and the European Central Bank in the G20 meetings.
- The G20 organises annual summits where leaders from member countries, as well as representatives from international organizations such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, gather to discuss and coordinate on various global economic issues, including financial stability, trade, climate change, and the development.
- One of the main strengths of the G20 is its inclusiveness, as it includes both developed and developing economies, making it a significant platform for dialogue and cooperation. However, the G20's decisions are not legally binding and its effectiveness depends on the willingness of its member countries to implement agreed-upon measures.
Ques. Which of the following organisation has been granted permanent membership in G20?
a) ASEAN
b) Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
c) NATO
d) African Union (AU)
Ans. (d)
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi



