- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
A Sicilian Volcano is Blowing Smoke Rings: Volcanic Vortex Rings
A Sicilian Volcano is Blowing Smoke Rings: Volcanic Vortex Rings
13-04-2024
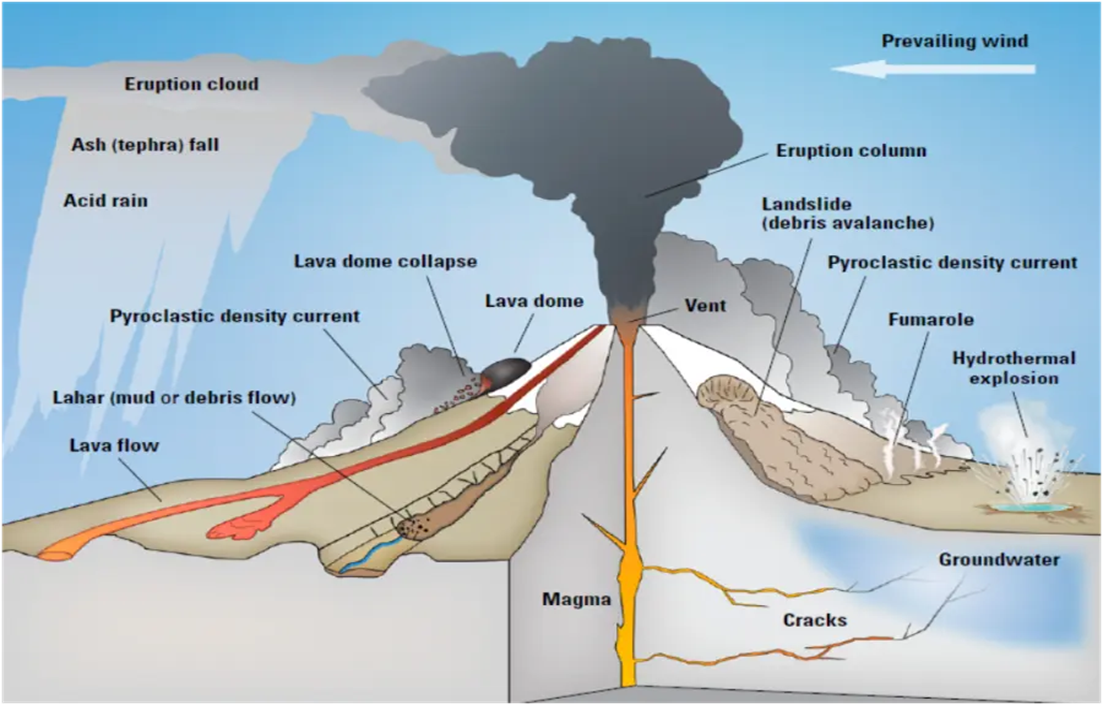
Since April 5, 2024, Mount Etna, the largest volcano in Europe, and among the world’s most active and iconic volcanoes, has been sending up almost perfect rings of smoke into the air.
- The rings are a rare phenomenon that scientists refer to as volcanic vortex rings, which are produced roughly in the same way as the smoke rings that some cigarette smokers are able to blow out of their mouths.
Characteristics of Volcanic Vortex Rings:
Vortex rings are generated when gas, predominantly water vapour, is released rapidly through a vent in the crater. The vent that has opened up in Etna’s crater is almost perfectly circular
-
Formation: Volcanic vortex rings are created when a fast-moving gas, usually steam, is forcefully ejected through a circular opening.
-
Air Time: Under ideal weather conditions, these rings can remain suspended in the air for up to 10 minutes. However, strong winds and turbulence shorten their lifespan.
-
Historical Observations: The presence of volcanic vortex rings was first documented in Italy, at Mount Etna and Mount Vesuvius, in the year 1724.
-
Global Occurrences: In more recent times, similar phenomena have been seen at volcanoes worldwide, including Redoubt in Alaska, Tungurahua in Ecuador, Pacaya in Guatemala, and many others.
Mount Etna's Significance:
-
Location and Status: Mount Etna, also simply known as Etna, is an active volcano situated on the eastern coast of Sicily, the largest Mediterranean island.
-
Height and Rank: Etna's peak stands as the highest point in Italy south of the Alps, making it the tallest and one of the most active volcanoes in Europe.
-
Summit and Eruptions: The summit of Etna has 5 craters that contribute to most of its eruptions.
-
Heritage Recognition: Mount Etna was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2013 for its exceptional natural and cultural significance.
FAQs:
What are Volcanoes?
Volcanoes are landforms where molten rocks erupt from the Earth's surface. They form when pressure builds in the Earth's crust, causing eruptions that can last for days, months, or years.
Here are some facts about volcanoes:
|
|
|
Active volcanoes
|
|
Dormant volcanoes
|
|
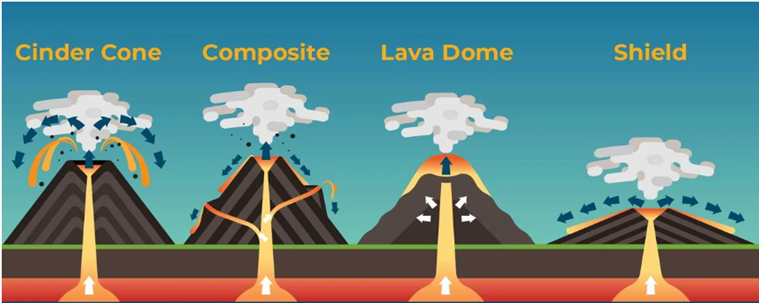
Composite volcanoes
|
Lava domes
-
These are small volcanoes that form from slow eruptions of thick lava. They can produce explosive eruptions, but the lava doesn't flow far.
Shield Volcanoes
Shield volcanoes are the largest type of volcano. They are wider than they are tall, and are called shield volcanoes because they look like the shield of a medieval knight.
The Ring of Fire
-
This 25,000-mile horseshoe-shaped zone contains 75% of the world's active volcanoes. It stretches from the southern tip of South America to New Zealand, where the Pacific and Nazca plates meet other tectonic plates.
Other facts about volcanoes:
-
Ash from volcanoes can cause lightning.
-
Lava from volcanoes creates new land.
-
Olympus Mons is the largest volcano in the solar system.
-
Mauna Loa is taller than Mount Everest.
-
Volcanoes release water vapor for drinking.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi