- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- NCERT (Recorded 500+ Hours)
- Polity Recorded Course
- Geography Recorded Course
- Economy Recorded Course
- AMAC Recorded Course
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment Recoded Course
- Governance Recoded Course
- Science & Tech. Recoded Course
- International Relations and Internal Security Recorded Course
- Disaster Management Module Course
- Ethics Recoded Course
- Essay Recoded Course
- Current Affairs Recoded Course
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
75th Anniversary of India-Indonesia Diplomatic Relations
75th Anniversary of India-Indonesia Diplomatic Relations

To commemorate the 75th Anniversary of India-Indonesia Diplomatic Relations, the Indonesian President visited India in January, 2025. This visit marked a significant milestone in the strengthening of bilateral ties between the two nations.
During this visit, several key developments took place.
Key Developments During the Indonesian President's Visit
- Agreements Signed:
- Health Cooperation: Strengthening collaborative health initiatives.
- Traditional Medicine: Promoting the sharing of knowledge and practices.
- Maritime Safety and Security: Enhancing cooperation on regional maritime security issues.
- Digital Development: Exploring opportunities for digital transformation and collaboration.
- Cultural Exchange Programme (2025-2028): Initiating a long-term cultural exchange to deepen mutual understanding.
- Third India-Indonesia CEOs Forum: A joint report was presented at the 3rd India-Indonesia CEOs Forum, highlighting collaborative efforts to boost trade and investment.
- Republic Day Celebrations: The Indonesian President was the chief guest at India’s 76th Republic Day celebrations, showcasing the growing political and diplomatic ties between the two countries.
- Joint Statement: A joint statement was issued, highlighting the shared areas of cooperation and mutual goals.
Significance of India-Indonesia Relations
1. Mutual Benefits of Bilateral Cooperation
- Economic Engagement: The India–Indonesia Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD Dialogue) (2023) aims to enhance economic collaboration and develop a shared understanding of global economic issues.
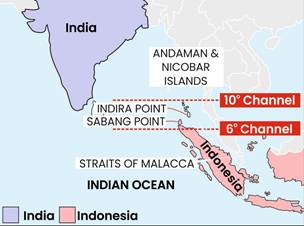
- Maritime Security: The countries are working together to ensure the security of key maritime routes like the Straits of Malacca and Singapore (SOMS), enhancing cooperation in regional maritime mechanisms.
- Defence and Security:
- Strategic and operational cooperation between defence forces is evident through joint exercises like Garuda Shakti (Army), Samudra Shakti (Navy), and India-Indonesia Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT).
- Progress on technology transfer, including discussions on Brahmos missile collaboration, showcases deepening defence ties.
- Multilateral Cooperation:
- Both nations coordinate closely on multilateral forums like the United Nations (UN) and G20, focusing on reformed multilateralism.
- Indonesia’s membership in BRICS further strengthens the alignment of the two countries in global governance.
- Infrastructure & Connectivity: India’s Development Partnership with the Indonesia-Malaysia-Thailand Growth Triangle (IMT-GT) helps enhance regional infrastructure and connectivity.
- Cultural and Heritage Cooperation: The Cultural Exchange Programme (2025-2028) promotes deeper cultural ties, while the annual Bali Jatra festival commemorates the historic maritime trade and cultural exchange between India (Odisha) and Indonesia (Bali).
- Other Areas of Collaboration: Both nations condemn all forms of terrorism, and collaborate in Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), cybersecurity, and global health initiatives.
2. India’s Key Interests in the Relationship
- Trade:
- Indonesia is India’s second-largest trading partner in the ASEAN region (after Singapore). Bilateral trade has grown significantly from $4.3 billion in 2005-06 to $29.40 billion in 2023-24.
- Despite the growth, the target of $50 billion in bilateral trade by 2025 remains a work in progress.
- Geostrategic Significance: India’s assistance in the development of Sabang Port in Aceh (Indonesia) aligns with its SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) initiative, boosting maritime connectivity and providing a strategic advantage in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Internationalization of the Indian Rupee: A MoU on Local Currency Settlement Systems (LCSS) was signed to facilitate the use of local currencies for bilateral trade, reducing reliance on the dollar.
- Health and Pharmaceuticals: India and Indonesia are collaborating on Digital Health initiatives, and India is sharing its best practices and capacity-building programs for Indonesian healthcare professionals.
3. Indonesia’s Key Interests in the Relationship
- Market Access: India is a key export destination for Indonesia, particularly as the second-largest buyer of coal and crude palm oil.
- Investment: Indian companies have made substantial investments in infrastructure, power, textiles, steel, and automotive sectors in Indonesia.
- Notably, GMR Airports Limited is involved in developing and operating the Kualanamu International Airport in Medan.
- Climate Change and Disaster Resilience:
- Indonesia is vulnerable to natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis.
- India has been involved in Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) activities and Indonesia is part of India-led initiatives like the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Food Security: India has supported Indonesia’s mid-day meal scheme, sharing knowledge and experience to ensure food security for its population.
- Space Cooperation: India’s ISRO is working with Indonesia's BRIN (National Research and Innovation Agency) on satellite telemetry and tracking systems, enhancing space cooperation.
- Education and Skill Development: India offers training through the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Programme and under the ASEAN-India Network of Universities (AINU), contributing to skill development in Indonesia.
Challenges in India-Indonesia Relations
- Unrealized Trade Potential:
- Despite the growing economic engagement, the bilateral trade potential between India and Indonesia stands at $61 billion, which is about 33% higher than the current trade volume.
- Factors like high tariffs, non-tariff barriers, and limited utilization of the India-ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (FTA) are hindering full trade potential.
- China’s Influence: China’s significant presence in Indonesia, particularly through investments under the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), raises concerns for India, especially in strategic sectors like infrastructure and energy.
- Slow Progress of Strategic Projects: Strategic initiatives like Brahmos missile deals and Sabang Port development have faced slow progress due to various economic and geopolitical challenges.
Way Forward: Enhancing India-Indonesia Cooperation
- Identifying Areas for Convergence:
- India and Indonesia can create an "ASEAN Plus" policy, aligning ASEAN’s Indo-Pacific outlook with India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Indonesia has committed to supporting the maritime resources pillar under IPOI.
- Trade Reforms: Rationalizing FTAs and accelerating the negotiation of a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) can help achieve the trade target of $50 billion by 2025.
- Regional Cooperation:
- India can engage more actively in regional forums such as ASEAN, the East Asia Summit (EAS), BRICS, and the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Inviting Indonesia to join forums like BIMSTEC could be beneficial for realizing India’s Act East Policy.
- Cooperation in the Global South: India and Indonesia should work together on issues crucial to the Global South, including climate change, sustainable development, and economic integration, using platforms for South-South Cooperation.
- Minilaterals and People-to-People Ties:
- Promoting minilateral forums, like the India-Indonesia-Australia trilateral in specific sectors, will help deepen collaboration.
- Cultural exchanges, education opportunities, and tourism (capitalizing on the ASEAN-India Year of Tourism 2025) can further strengthen people-to-people ties.
India-Indonesia relations have grown significantly over the years, with mutual benefits in trade, defence, regional security, infrastructure, and cultural cooperation. By addressing challenges like unrealized trade potential, slow strategic project implementation, and connectivity issues, the two nations can build an even stronger and more dynamic partnership in the future.
|
Also Read |
|
| Public Administration Optional | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Question Answer Practice For UPSC |