- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- NCERT Medieval History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Civil Services Examination UPSC CSE 2023
Civil Services Examination UPSC CSE 2023

CSE 2023 Notification
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) released the UPSC Civil Services Examination Notification 2023 on 1st February 2023 on their official website. For the year 2023, the commission indicated 1105 vacancies in the notification inclusive of all reserved and non-reserved categories of students.
- The notification mentions the exam application’s start and end dates, information on vacancies, the hiring procedure, syllabus, exam pattern, and other relevant information.
- The candidates are required to submit their duly filled application ONLY IN ONLINE mode before February 21, 2023, at upsconline.nic.in.
- Aspirants can apply for the UPSC Exam from the 1st of February 2023 to till 21st of February 2023.
- UPSC generally releases the UPSC IAS exam notification in the first week of month of February. After the release of the notification, the application filing process starts the next day and continues for a period of 20-25 days.
- The Union Public Service Commission conducts Civil Service Examinations every year to select graduates who want to serve the nation in various All India Services and Central Civil Services.
PROCESS OF REGISTRATION FOR UPSC
- The application for the IAS Exam is made on the UPSC’s official website only and in ONLINE MODE only.
- Aspirants are first required to register themselves on the UPSC Online registration portal (One-time registration [OTR]) by visiting the official website of UPSC. https://www.upsc.gov.in/
- The application process is divided in two separate registrations namely- PART I Registration and PART II Registration.
- Aspirants must first fill PART I registration which requires basic information of the candidates and then move on to PART II registration which required advanced information about the candidates such as Exam center preferences, Photo and signature upload, fee payment and other relevant information.
- Candidates must fill the form very carefully as once the form is submitted; NO CHANGES can be made in the future.
UPSC CSE Prelims 2023 date
UPSC will be conducting the stage one exam called Preliminary Civil Services Examination (UPSC Prelims) on 28th May, 2023 (Sunday) all over India, to fill all the vacancies of the central government as mentioned the official notification.
CSE 2023 Syllabus
STAGE 1 – PRELIMS EXAM
UPSC Civil Services Preliminary Examination Syllabus
Paper I - (200 marks) (GS Paper)
- Current Events of National and International Importance.
- History of India and Indian National Movement.
- Indian and World Geography-Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World.
- Indian Polity and Governance-Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- Economic and Social Development-Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector Initiatives, etc.
- General issues on Environmental ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change - that do not require subject specialization.
- General Science.
Paper II - (200 marks) (CSAT Paper)
- Comprehension; Interpersonal Skills including Communication Skills.
- Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability.
- Decision Making and Problem Solving.
- General Mental Ability.
- Basic Numeracy (Numbers and their Relations, Orders of Magnitude, etc.) (Class X level).
- Data Interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency etc. — Class X level).
Note 1: Paper-II of the Civil Services (Preliminary) Examination will be a qualifying paper with minimum qualifying marks fixed at 33%.
Note 2: The questions will be of multiple choice, objective type.
STAGE 2 – MAINS EXAMINATION
UPSC Civil Services Mains examination Syllabus
Syllabus of General Studies-I (GS-1)
(Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society)
- Indian Culture - Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
- Modern Indian History from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present- significant events, personalities, issues.
- The Freedom Struggle — its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country.
- Post-independence Consolidation and Reorganization within the country.
- History of the World will include events from 18th century such as Industrial Revolution, world wars, Redrawal of National Boundaries, Colonization, Decolonization, political philosophies like Communism, Capitalism, Socialism etc.— their forms and effect on the society.
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
- Role of Women and Women’s Organization, Population and Associated Issues, Poverty and Developmental issues, Urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
- Effects of Globalization on Indian society.
- Social Empowerment, Communalism, Regionalism & Secularism.
- Salient features of World’s Physical Geography.
- Distribution of Key Natural Resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India).
- Important Geophysical Phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
Syllabus of General Studies-II (GS - 2)
(Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International Relations)
- Indian Constitution—Historical Underpinnings, Evolution, Features, Amendments, Significant Provisions and Basic Structure.
- Functions and Responsibilities of the Union and the States, Issues and Challenges Pertaining to the Federal Structure, Devolution of Powers and Finances up to Local Levels and Challenges Therein.
- Separation of Powers between various organs Dispute Redressal Mechanisms and Institutions.
- Comparison of the Indian Constitutional Scheme with that of Other Countries.
- Parliament and State Legislatures—Structure, Functioning, Conduct of Business, Powers & Privileges and Issues Arising out of these.
- Structure, Organization and Functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary—Ministries and Departments of the Government; Pressure Groups and Formal/Informal Associations and their Role in the Polity.
- Salient Features of the Representation of People’s Act.
- Appointment to various Constitutional Posts, Powers, Functions and Responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- Statutory, Regulatory and various Quasi-judicial Bodies.
- Government Policies and Interventions for Development in various sectors and Issues arising out of their Design and Implementation.
- Development Processes and the Development Industry — the Role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders.
- Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable Sections of the population by the Centre and States and the Performance of these Schemes; Mechanisms, Laws, Institutions and Bodies constituted for the Protection and Betterment of these Vulnerable Sections.
- Issues Relating to Development and Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Issues relating to Poverty and Hunger.
- Important Aspects of Governance, Transparency and Accountability, E-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; Citizens Charters, Transparency & Accountability and institutional and other measures.
- Role of Civil Services in a Democracy.
- India and its Neighborhood- Relations.
- Bilateral, Regional and Global Groupings and Agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
- Effect of Policies and Politics of Developed and Developing Countries on India’s interests, Indian Diaspora.
- Important International Institutions, agencies and fora - their Structure, Mandate.
Syllabus of General Studies-III (GS – 3)
(Technology, Economic Development, Bio-diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management)
- Indian Economy and issues relating to Planning, Mobilization of Resources, Growth, Development and Employment.
- Inclusive Growth and issues arising from it.
- Government Budgeting.
- Major Crops - Cropping Patterns in various parts of the country, - Different Types of Irrigation and Irrigation Systems; Storage, Transport and Marketing of Agricultural Produce and Issues and Related Constraints; E-technology in the aid of farmers.
- Issues related to Direct and Indirect Farm Subsidies and Minimum Support Prices; Public Distribution System - Objectives, Functioning, Limitations, Revamping; Issues of Buffer Stocks and Food Security; Technology Missions; Economics of Animal-Rearing.
- Food Processing and Related Industries in India- Scope’ and Significance, Location, Upstream and Downstream Requirements, Supply Chain Management.
- Land Reforms in India.
- Effects of Liberalization on the Economy, Changes in Industrial Policy and their Effects on Industrial Growth.
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
- Investment Models.
- Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday Life.
- Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology; Indigenization of Technology and Developing New Technology.
- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-technology, Bio-technology and issues relating to Intellectual Property Rights.
- Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment.
- Disaster and Disaster Management.
- Linkages between Development and Spread of Extremism.
- Role of External State and Non-state Actors in creating challenges to Internal Security.
- Challenges to Internal Security through Communication Networks, Role of Media and Social Networking Sites in Internal Security Challenges, Basics of Cyber Security; Money-Laundering and its prevention.
- Security Challenges and their Management in Border Areas - Linkages of Organized Crime with Terrorism.
- Various Security Forces and Agencies and their Mandate.
Syllabus of General Studies-IV (GS – 4)
(Ethics, Aptitude and Integrity)
- Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, Determinants and Consequences of Ethics in - Human Actions; Dimensions of Ethics; Ethics - in Private and Public Relationships. Human Values - Lessons from the Lives and Teachings of Great Leaders, Reformers and Administrators; Role of Family Society and Educational Institutions in Inculcating Values.
- Attitude: Content, Structure, Function; its Influence and Relation with Thought and Behaviour; Moral and Political Attitudes; Social Influence and Persuasion.
- Aptitude and Foundational Values for Civil Service, Integrity, Impartiality and Non-partisanship, Objectivity, Dedication to Public Service, Empathy, Tolerance and Compassion towards the weaker-sections.
- Emotional Intelligence-Concepts, and their Utilities and Application in Administration and Governance.
- Contributions of Moral Thinkers and Philosophers from India and World.
- Public/Civil Service Values and Ethics in Public Administration: Status and Problems; Ethical Concerns and Dilemmas in Government and Private Institutions; Laws, Rules, Regulations and Conscience as Sources of Ethical Guidance; Accountability and Ethical Governance; Strengthening of Ethical and Moral Values in Governance; Ethical Issues in International Relations and Funding; Corporate Governance.
- Probity in Governance: Concept of Public Service; Philosophical Basis of Governance and Probity; Information Sharing and Transparency in Government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work Culture, Quality of Service Delivery, Utilization of Public Funds, Challenges of Corruption.
- Case Studies on above issues.
CSE 2023 study resources
- UPSC IAS exam has a vast and diversified syllabus and hence requires a mix of basic books such as school NCERTs as well as standard books for deeper understanding of concepts.
- The table below provide a detailed list of books required to clear UPSC IAS exam.
|
Subject |
Basic + Standard Books |
|
GEOGRAPHY |
1. 11th NCERT- Fundamental of Physical Geography 2. 11th NCERT- Indian Physical Environment 3. 12th NCERT- Fundamentals Of Human Geography 4. 12th NCERT- Indian People and Economy 5. GC LEONG (Oxford India) 6. MAJID HUSSAIN (McGrawHill) |
|
ENVIRONMENT |
1. Environment, ecology and Biodiversity- Ravi Agrahari (McGrawHill) |
|
DISASTER MANAGEMENT |
1. ENSURE IAS Disaster Management Booklet |
|
ANCIENT INDIA |
1. POONAM DALAL DAHIYA (McGrawHill) 2. 11TH NCERT- Ancient India by RS Sharma |
|
MEDIEVAL INDIA |
1. POONAM DALAL DAHIYA (McGrawHill) 2. 11TH NCERT- Medieval India by Satish Chandra |
|
ART AND CULTURE |
1. INDIAN ART AND CULTURE by Nitin Singhania (McGrawHill) 2. 11th NCERT- An introduction to Indian Art |
|
MODERN INDIA |
1. 12TH NCERT- Modern India by Bipin Chandra 2. A Brief History of Modern India (Spectrum Pub) |
|
POLITY |
1. M. LAXMIKANT (McGrawHill) 2. 11TH NCERT-Working with Indian Constitution |
|
GOVERNANCE |
1. ENSURE IAS HANDOUTS |
|
INTERNAL SECURITY |
1. ASHOK KUMAR & VIPUL ANEKANT (McGrawHill) |
|
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY |
1. ENSURE IAS HANDOUTS |
|
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS |
1. PAVNEET SINGH (McGrawHill) 2. ENSURE IAS HANDOUTS |
|
ECONOMY |
1. NITIN SINGHANIA (McGrawHill) 2. 11th NCERT- Indian economic development 3. 12th NCERT- Introductory Macroeconomics |
|
INDIAN SOCIETY AND SOCIAL ISSUES |
1. 12TH NCERT- Indian Society |
|
ETHICS |
1. DECODE ETHICS BY MUDIT JAIN (KBC Publication) |
|
ESSAY |
1. ENSURE IAS HANDOUTS |
|
CSAT |
1. ENSURE IAS HANDOUTS 2. ENSURE IAS concept book |
CSE Cutoff Marks
UPSC Cutoff is the minimum score required by a candidate to clear a particular stage of IAS examination. Cutoff marks actually indicate the marks of the last candidate who has been selected to enter next stage of exam based on number of vacancies in that particular category.
UPSC releases Prelims cutoff, Mains cutoff and final Cutoff of the exam separately only after the completion of the entire examination process and release of the final result.
The prediction of cutoff always remain a highly speculative topic till the final cutoff is released by UPSC.
Interview for UPSC 2022 IAS Exam is currently going on. The cutoff for UPSC 2022 exam is expected to be released in the last week of May 2023.
Below is the list of UPSC cutoffs of past 3 years for each category of candidates.
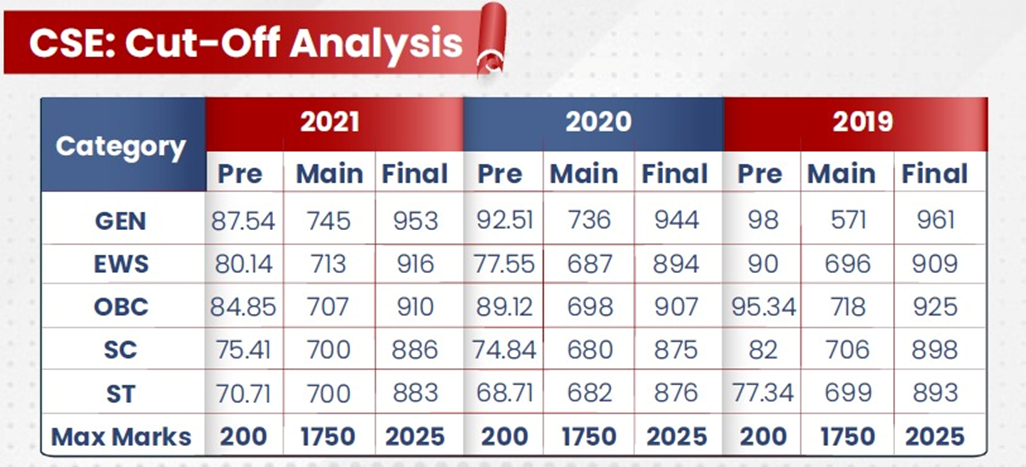
CSE 2023 eligibility
IAS (Indian Administrative Service) is the premier service of India. IAS along with IPS (Indian Police Service) and IFoS (Indian Forest Services) are All India Services and an integral part of Union Services. Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), which is a constitutional body, conducts examinations for recruitment to these services every year.
To sit for the IAS exam, UPSC has specified several eligibilities criteria for education, age, minimum marks, and other requirements for each category of the students.
A) Nationality Criteria
Candidate must be either: -
A citizen of India, or
A subject of Nepal, or
A subject of Bhutan, or
A Tibetan refugee who came to India before 1st January 1962 intending to settle in India permanently, or
A person of Indian origin (PIO) who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka, East African countries of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Malawi, Ethiopia, Zaire and Vietnam intending to settle in India permanently.
B) Education Criteria
The various educational requirements as per the UPSC exam are:
Minimum educational qualification: The candidate must hold a Graduation degree from Government recognised Universities.
Final year/semester students: Candidates who are in their final year or waiting for final graduation results are also eligible to appear for UPSC preliminary Examination. All such candidates must provide proof of having passed the said examination along with the application for the main IAS examination.
Professional and technical degrees: Candidates having professional and technical qualifications recognised by the Government as equivalent to professional and technical degrees.
Medical students: Medical students who have passed the final year of MBBS, but are yet to complete their internship also have eligibility for IAS. Although, along with the Main Examination application, a certificate of course completion (including internship) from the concerned authority of the University/Institution must be submitted.
UPSC does not discriminate against candidates based on their scores in graduation. Hence, there is NO MINIMUM QUALIFYING PERCENTAGE to sit for the IAS exam.
C) Age criteria
The minimum age to sit for the UPSC IAS Exam is 21 years for all categories of students. However, the maximum age for appearing for the exam varies according to the categories as mention in the table below:
|
UPSC Exam Age Limit for General, SC/ST, OBC & Other categories |
||
|
Category |
UPSC Age Limit- Upper Relaxation |
Number of Attempts |
|
General |
32 |
6 |
|
OBC |
35 |
9 |
|
SC/ST |
37 |
Unlimited (Up to age limit) |
|
Disabled Defence Services Personnel |
35 |
9 |
|
Ex-Servicemen |
37 |
9 |
|
Persons with Benchmark Disability – EWS (Economically Weaker Section) |
42 |
9 |
Must Check: IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims 2025 Answer Key Out, Download PDF
Ancient History Previous Year Questions (PYQs) for Prelims
UPSC MAINS EXAM 2024 QUESTION PAPER: [Paper-A : Indian Language- Hindi ]
