- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 7th MAY 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 7th MAY 2025

Sanjay Gandhi National Park
Why in news?
a. A recent census found 54 leopards in Sanjay Gandhi National Park, showcasing wildlife coexistence with urbanisation and conservation success.
About Sanjay Gandhi National Park:
|
|
- Location and Geography:
- Sanjay Gandhi National Park (SGNP), covering an area of 103 sq km, is one of the largest protected areas within city limits globally.
- It is located near Borivali in the northern part of Mumbai, spanning both the
Thane District and Mumbai Suburban District of Maharashtra.
-
- Initially known as Krishnagiri National Park, it was renamed Borivali National Park in 1974 and finally Sanjay Gandhi National Park in 1981, in honour of the late Indian leader Sanjay Gandhi.
- A notable historical feature of the park is the Kanheri Caves, carved by Buddhist monks between the 1st and 10th century CE, which served as monasteries, temples, and schools.
- These caves are remarkable examples of Buddhist art and architecture, carved out of basaltic rock.
- The park also contains two important artificial lakes—Tulsi Lake and Vihar Lake—which supply water to South Mumbai.
- Flora and Fauna:
- SGNP hosts a rich variety of tropical flora such as Kadamba, Teak, Karanj, Shisham, Acacia, Ziziphus, and Euphorbias species.
- It is home to diverse fauna, including leopards, sambars, chitals, barking deer, rusty spotted cats, hyenas, and Indian civets.
- Other species include the Indian hare, porcupine, flying fox, and primates like
bonnet macaque and the common langur.
-
- The park also supports 251 bird species and a wide range of butterflies, highlighting its ecological richness.
Alcatraz Island
Why in news?
- The US President ordered the reconstruction and expansion of the prison on Alcatraz Island, closed for over 60 years near San Francisco.
About Alcatraz Island:
- Alcatraz Island, also known as "The Rock," is a rocky island in San Francisco Bay, off the coast of California, USA.
- It covers 22 acres (9 hectares) and is located within the Golden Gate National Recreation Area.
- The island was sold to the U.S. government in 1849 and became the site of California’s first lighthouse in 1854.
- Permanent army troops were stationed there in 1859, and it was converted into a
military prison by 1861.
- In 1907, it was named the Pacific Branch of the U.S. Military Prison.
- The U.S. Army vacated the island in 1933, and in 1934, Alcatraz became a federal prison.
- It housed America’s most dangerous criminals until it was closed in 1963 due to high maintenance costs.
- Though it had 330 cells, usually no more than 260 inmates were held at a time.
- Known for being inescapable, few escape attempts were made, but survival was unlikely due to strong bay currents.
- In 1972, it became a public tourist site and remains a popular historical attraction
today.
Port Sudan
Why in news?
- Drone strikes and fire caused a total blackout in Port Sudan amid conflict involving the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and the Sudanese military.
About Port Sudan:
- Location and Geography:
- Port Sudan is a vital port city located on the Red Sea coast in the northeastern region of Sudan.
- It serves as the capital of the Red Sea State and lies approximately 800 kilometres northeast of Khartoum, the national capital.
- Established in the early 20th century, it replaced Suakin as Sudan’s principal seaport and has grown into the country's main maritime gateway.
- The city is situated in a semi-arid zone, bordered by the Red Sea to the east and desert terrain inland.
-
- Its strategic coastal location makes it a key node for international trade and naval access.
- Strategic Importance:
- Port Sudan holds immense economic and geopolitical significance. It is Sudan’s primary seaport, handling the bulk of the country’s imports and exports, including oil, livestock, and agricultural products.
- The oil pipelines and transport routes connecting Port Sudan to Khartoum make it a logistical lifeline.
- Due to its proximity to global shipping lanes, the city is also of interest to regional powers and international actors.
- In recent years, foreign military and economic interests, including those from Russia and Gulf nations, have eyed Port Sudan for naval bases or commercial investments, highlighting its geostrategic relevance in the Red Sea region.
- Conflict and the RSF:
- Since the outbreak of the Sudanese civil conflict in April 2023, Port Sudan has become a focal point of power and survival.
- The war pits the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) against the Rapid Support Forces (RSF)—a powerful paramilitary group that evolved from the Janjaweed militias.
- While Khartoum and other regions descended into violence, Port Sudan initially remained under SAF control and became the de facto administrative capital.
- However, recent drone strikes and attacks, reportedly linked to the RSF, have escalated tensions, leading to events such as a total blackout and widespread fear.
- The conflict in Port Sudan reflects the broader instability in Sudan, with both factions vying for control over critical infrastructure and international legitimacy.
- As the humanitarian crisis deepens, Port Sudan’s role as a refuge and a battleground underscores the fragility of peace and governance in the country.
Paraná River
Why in news?
a. Declining water levels in the Paraná River in Argentina have disrupted soybean oil transport, raising prices in Brazil and impacting the agricultural export economy.
About Paraná River:
- Origin and Course:
- The Paraná River is one of South America’s major waterways, stretching about
4,880 km, making it the second-longest river on the continent after the Amazon.
-
- The river originates in southern Brazil at the confluence of the Paranaíba and Rio Grande rivers.
- It flows southwest, forming part of the border between Brazil and Paraguay, and passes notable landmarks such as the former Guaíra Falls (now submerged by the Itaipu Dam, one of the world’s largest hydroelectric plants).
- The Paraná then merges with the Iguazu River, becoming the natural border between Paraguay and Argentina.
- Continuing southward, it flows through Argentina, passing cities like Rosario, before finally joining the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata, which empties into the Atlantic Ocean.
- Economic and Ecological Importance:
- The Paraná River is economically vital, serving as a major transportation route for agricultural exports such as soybeans and grains, particularly from landlocked Paraguay and inland Argentina.
- The river supports massive hydroelectric infrastructure, including the Itaipu and Yacyretá dams, which provide a significant portion of electricity for Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina.
- Ecologically, the Paraná sustains a rich biodiversity, especially in the Paraná Delta, a vast wetland system supporting migratory birds, fish, and native vegetation.
- However, the construction of dams and pollution from agricultural runoff threaten its ecological balance.
- A severe drought in 2021 highlighted the river's vulnerability, as it reached its
lowest level in 77 years, disrupting navigation and power generation.
Carpathian Mountains
Why in news?
a. The 2025 Mountain Running World Cup commenced in May with a new destination: the Zmeu Xfest in Romania's northern Carpathian Mountains.
About Carpathian Mountains:
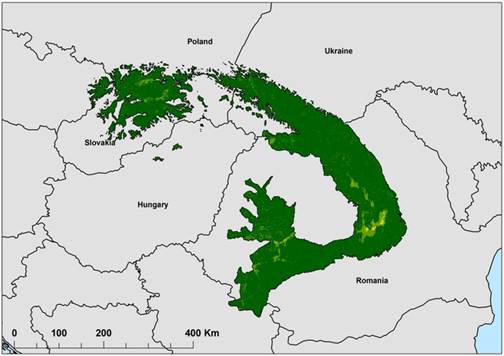
- Location and Extent:
- The Carpathian Mountains are a prominent mountain range in Central and Southeast Europe, forming a sweeping arc that spans about 1,500 km (930 mi).
- They are the third-longest mountain range in Europe, after the Urals and the
Scandinavian Mountains.
-
- The Carpathians extend through Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Ukraine, Romania, and Serbia. Romania holds the largest share—about 50% of the range—followed by Slovakia and Poland.
- Formation and Geography:
- The Carpathians are not a single uninterrupted chain but a series of orographically and geologically distinct groups, including the Western, Eastern, and Southern Carpathians.
- The highest peak is Gerlachovský štít in Slovakia at 2,655 m, located in the
Tatra Mountains.
-
- The mountains encircle the Transylvanian Plateau and stretch southeastward to the Danube River near Orșova in Romania.
- They cover a total area of approximately 190,000 km² and vary in width from 12 km to 500 km.
- Climate and Natural Features:
- While no region was previously thought to have year-round snow, recent discoveries in the Tatra Mountains revealed the presence of permafrost and glacial areas.
-
- The Carpathians are rich in thermal and mineral springs, with Romania alone containing one-third of Europe’s total.
- The mountains support Europe’s largest populations of brown bears, wolves, lynxes, and chamois, especially in Romania. They are also home to over one-third of European plant species.
- The Southern Carpathians host Europe’s largest unfragmented forest area, including virgin forests, second only to those in Russia. However, the region faces threats from deforestation and illegal logging.
|
Also Read |
|
| NCERT Books For UPSC | |
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | Best IAS Coaching in Delhi |