- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 21st APRIL 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 21st APRIL 2025

Tapi River
Why in news?
a. A minor boy and his parents recently died by jumping off a bridge into the Tapi River at Kamrej, Surat district.
About Tapi River:
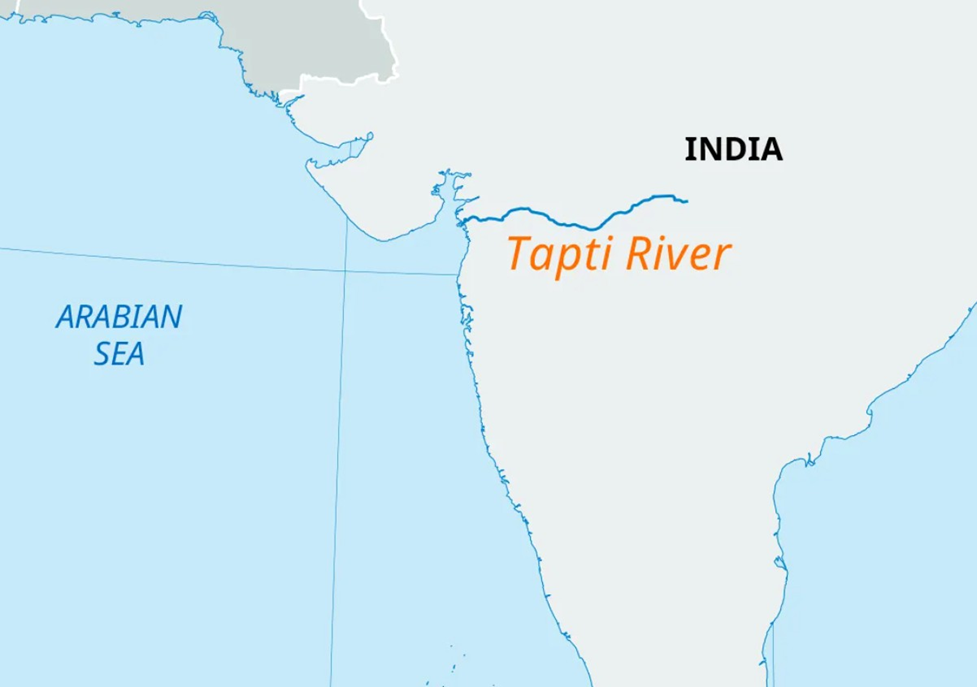
- Geography and Location:
- The Tapi River, also known as Tapti, originates from Multai in Madhya Pradesh at an elevation of 752 metres in the Satpura range.
- It flows westward for about 724 km, making it the second-longest west-flowing river in India after the Narmada. The river travels through Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat before draining into the Gulf of Khambhat in the Arabian Sea.
-
- The river basin is spread across parts of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat, with 14 major tributaries — including Aner, Arunavati, Gomai (right bank) and Purna, Girna, and Waghur (left bank) — originating from various ranges like the Satpuras, Ajanta Hills, and Western Ghats.
- Economic Significance:
- The river is vital for agriculture, drinking water, and industrial use, especially in regions like Surat and Jalgaon.
- Major hydroelectric and irrigation projects include the Ukai Dam in Gujarat, which helps control floods, generate power, and support irrigation.
- The river’s flooding history, especially the 1968 Surat flood, led to critical infrastructure development to mitigate future disasters. Post-flood, the Ukai Dam was crucial in regulating water flow and boosting regional resilience.
Davis Strait
Why in news?
a. A hidden landmass, the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, was discovered beneath the waters between Canada’s Baffin Island and Greenland.
About Davis Strait:
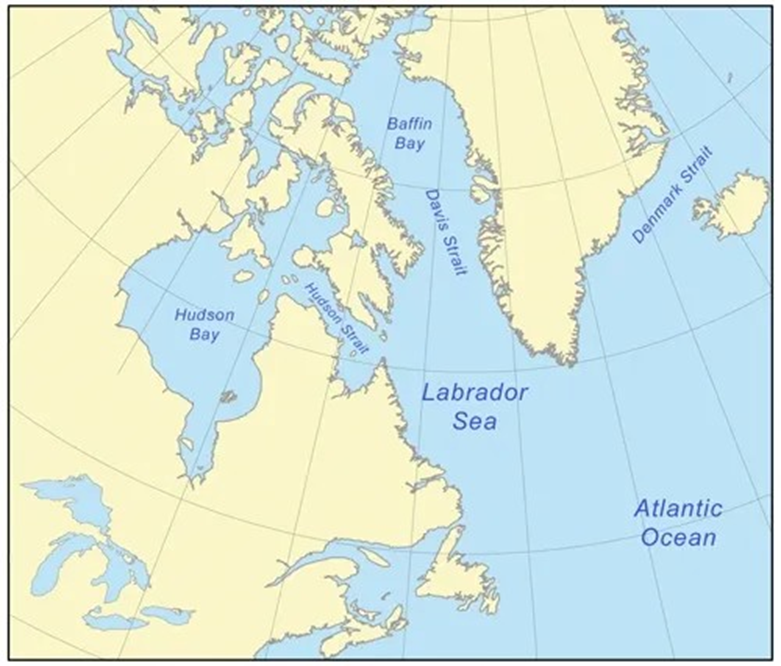
- Geography and Location:
- The Davis Strait is a broad, shallow arm of the Arctic Ocean, located between western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada.
- It connects the Labrador Sea in the south with Baffin Bay to the north and lies between latitudes 60°N and 70°N. The strait is the world’s broadest, with depths ranging from 1,000 to 2,000 metres, shallower than the adjacent Labrador Sea.
- Characterised by complex geological features, it is underlain by ancient grabens and ridges, the result of strike-slip faulting from tectonic plate movements 45–62 million years ago.
- Recent Discovery:
- In a landmark study, scientists from Uppsala University and the University of Derby discovered a hidden proto-microcontinent beneath the Davis Strait.
- This 19–24 km thick block of continental crust, named the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent, likely separated from Greenland due to east-west tectonic extension around 58 million years ago.
- The discovery enhances understanding of microcontinent formation, revealing the role of a newly identified Pre-Ungava Transform Margin, and may help predict future tectonic evolution and resource potential in similar regions.
Subansiri River
Why in news?
a. NHPC's plan to begin power generation from the 2000 MW Lower Subansiri Hydroelectric Project raises downstream impact concerns in Assam.
About Subansiri River:
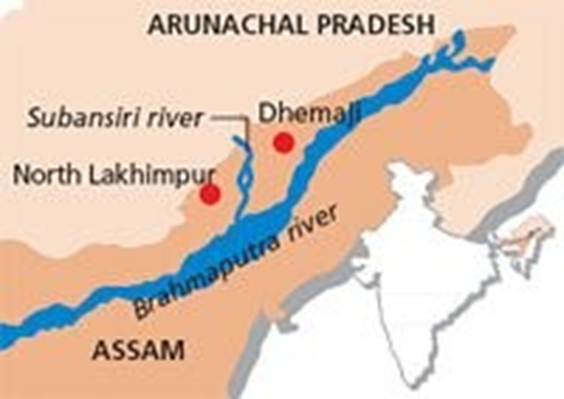
- Origin and Course:
- The Subansiri River, known as Chayul Chu in Tibet and Obonori in the Mising language, is a prominent trans-Himalayan tributary of the Brahmaputra River, spanning approximately 518 km with a drainage basin of 32,640 sq km.
- Originating near Chayul Dzong in southwestern Tibet, the river is formed by the confluence of the Nye Chu and Loro Chu rivers.
- After flowing through the mountainous terrains of Lhuntse County, it enters India in Arunachal Pradesh near Taksing, meandering through the Miri Hills, and finally enters Assam at Dulangmukh, where it merges with the Brahmaputra at Jamurighat in Lakhimpur district.
- The Subansiri contributes nearly 7.92% of the Brahmaputra's total flow, making it its largest tributary.
- With a peak discharge of 18,799 cubic metres per second, the river plays a crucial role in the region’s hydrology and ecology.
- About Lower Subansiri Hydroelectric Project (LSHP) and its impact:
-
- A significant development on the river is the Lower Subansiri Hydroelectric Project (LSHP) — a 2000 MW gravity dam under construction at Gerukamukh.
- This ambitious project, managed by NHPC, is the largest hydroelectric venture in Northeast India. However, it has faced continuous opposition due to environmental, seismic, and downstream impact concerns, especially in Assam.
- Critics argue that the dam’s operation could alter natural flow regimes, disrupt aquatic biodiversity, and aggravate flood risks, as evidenced by the devastating flash flood caused by a landslide blockade in 1950.
- Local communities and organisations highlight the lack of credible downstream impact assessments and fear the destruction of livelihoods dependent on the river.
- Thus, while the LSHP promises clean energy, it has sparked a larger debate on sustainable development, ecological sensitivity, and people’s participation in infrastructure planning in ecologically fragile zones like the Northeast.
Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
a. Green Task Force (GTF) pledges strong resistance against any threat to Meghalaya’s Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary, aiming to safeguard its biodiversity and ecology.
About Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary:
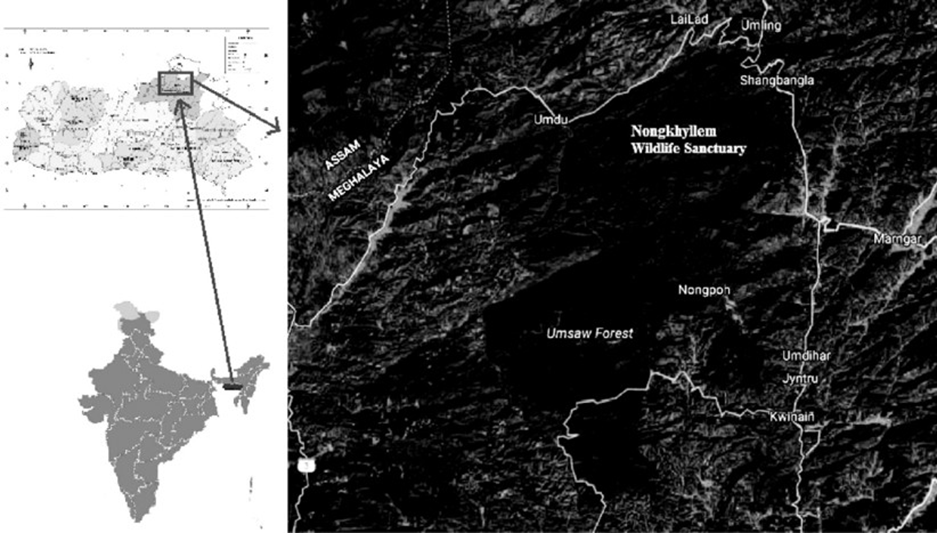
- Geography and Location:
- Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Ri-Bhoi district of
Meghalaya, in the northeastern region of India.
-
- It forms part of the Eastern Himalayan Global Biodiversity Hotspot, a region globally recognised for its extraordinary biological richness.
- Spanning an area of approximately 200 square kilometres, the sanctuary features diverse landscapes including dense tropical forests, grasslands, and freshwater streams.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary boasts a remarkable diversity of vegetation, with over 1,000 plant taxa documented by botanist J. Joseph in 1982, spanning 639 genera and 159 families. The region includes tropical moist evergreen, semi-evergreen, and moist deciduous forests.
- Nongkhyllem is a haven for birdwatchers, having recorded over 400 avian species. Notable among them is the rufous-necked hornbill, an endangered bird that symbolises the sanctuary's ecological importance.
- It is also home to a wide variety of mammals such as clouded leopards, barking deer, and Himalayan black bears, along with numerous reptiles and amphibians, reflecting the ecological richness of the Eastern Himalayas.
- Ecotourism and Seasonality:
- The best time to visit Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary is during the monsoon season, when the forest thrives with dense greenery and vibrant wildlife activity.
-
- The sanctuary offers opportunities for ecotourism, birding, and nature-based education while promoting conservation awareness.
- Its rich biodiversity and scenic landscapes make it a critical site for both
scientific research and sustainable tourism in Meghalaya.
Ras Isa oil port
Why in news?
- On April 18, 2025, U.S. airstrikes targeted the Houthi-controlled Ras Isa oil port in Yemen, resulting in at least 74 deaths and 171 injuries, according to Houthi officials.
About Ras Isa oil port:
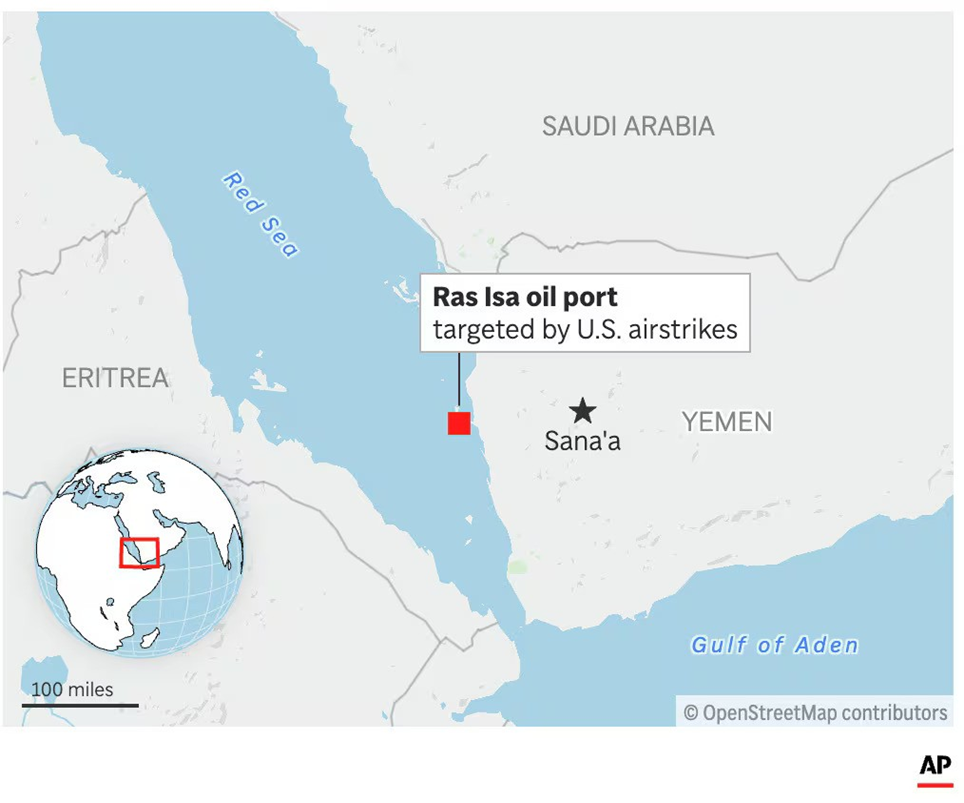
- Ras Isa Oil Port is a critical energy infrastructure located on Yemen’s western coast, approximately 55 km north of the port city of Hodeidah, along the Red Sea.
- It serves as a major export terminal for crude oil from Yemen’s inland oil fields, particularly those in the Marib region.
- The port includes facilities such as the Floating Storage and Offloading (FSO) Safer, a 48-year-old vessel that has been central to Yemen’s oil export operations.
- Ras Isa plays a vital role in Yemen's economy, with around 70% of imports and 80% of humanitarian aid passing through this and nearby ports.
- Currently, Ras Isa is under the control of the Houthi movement, an Iran-aligned group that governs significant portions of northern Yemen, including the capital, Sanaa.
- The Houthis have utilised revenues from fuel imports and exports at Ras Isa to fund their military activities.
- This control has made the port a focal point in the ongoing conflict, as it provides both economic and strategic advantages to the Houthis.
- On April 18, 2025, the United States conducted a series of 14 airstrikes on the Ras Isa oil terminal.
- These strikes resulted in the deaths of at least 80 individuals and injuries to over 170 others, marking it as the deadliest attack in the U.S. campaign against the Houthis.
- The U.S. military stated that the objective was to disrupt the Houthis' economic resources and diminish their capacity to threaten regional stability.
- In response, the Houthis condemned the strikes as a war crime and launched retaliatory attacks, including missile strikes on U.S. and Israeli targets.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




