- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 1st APRIL 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 1st APRIL 2025
01-04-2025

Bodh Gaya Temple
Why in news?
- Since February 2024, Buddhist monks under the All India Buddhist Forum (AIBF) have been protesting, demanding the repeal of the Bodh Gaya Temple Act (BTA), 1949.
About Bodh Gaya Temple:
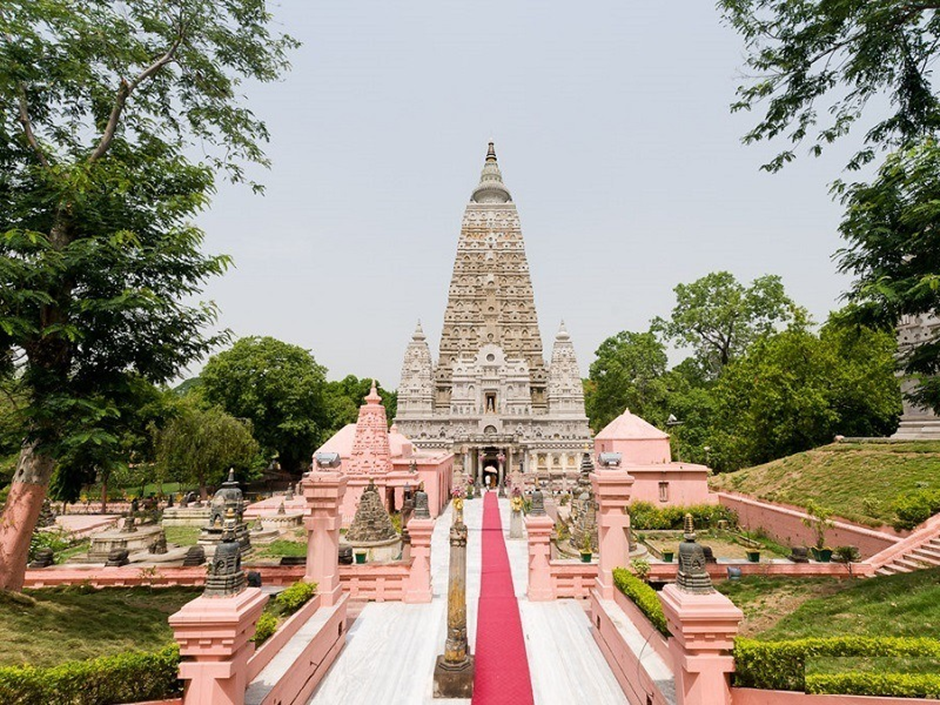

- Location:
- The Bodh Gaya Temple is located in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, on the banks of the Niranjana River.
- It is one of the four most sacred Buddhist sites, along with Lumbini (Buddha’s birthplace), Sarnath (Buddha’s first sermon), and Kushinagar (Buddha’s parinirvana).
- Establishment and Historical Significance:
- Emperor Ashoka built the original temple in the 3rd century BCE, marking the site where Gautama Buddha attained enlightenment under the Bodhi Tree.
- The present structure dates to the 5th–6th centuries CE and is one of the oldest surviving brick structures in India.
- Over centuries, the temple remained a centre of Buddhist learning, especially during the Pala Dynasty, but declined after Bakhtiyar Khilji’s invasion in the 13th century.
- In 1590, a Hindu monk established the Bodh Gaya Mutt, leading to Hindu control over the temple.
- The British-era records continued to refer to Bodh Gaya as a Hindu-controlled site until India’s independence.
- The temple complex was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2002.
- Architectural Features:
- Grand Temple: A 50-metre-high pyramidal shikhara (tower) with intricate carvings and motifs.
- Four smaller towers surround the main temple, each topped with an umbrella-like dome.
- Sacred Bodhi Tree: Believed to be a direct descendant of the original tree under which Buddha attained enlightenment.
- Vajrasana (Diamond Throne): A stone slab marking the exact meditation spot of Buddha.
- Temple Shrine: Houses a yellow sandstone statue of Buddha, encased in glass.
- The 4.8-hectare complex includes ancient shrines and modern Buddhist structures built by devotees.
- The Bodh Gaya Temple Act (BTA), 1949:
- Passed by the Bihar Assembly, the Act aimed to formalise temple management, transferring control to a management committee instead of a single Hindu authority.
- The Act established an eight-member management committee with equal representation for Hindus and Buddhists, but the District Magistrate (DM) was made the ex-officio chairperson.
- Historically, since the DM was often a Hindu, it created a perceived Hindu majority in temple administration.
- Protests Against the Act:
- Buddhist organisations, including the All India Buddhist Forum (AIBF), have long demanded full control over the temple, calling it Bodh Gaya Mahavihara.
- Since February 2024, Buddhist monks have been protesting, seeking repeal of the BTA, 1949, arguing that the temple should be administered solely by Buddhists.
- In the early 1990s, Bihar CM Lalu Prasad Yadav draughted the Bodh Gaya Mahavihara Bill to transfer temple management to Buddhists, but the bill was never passed.
- The 2013 amendment allowed the ex-officio chairman (DM) to be from any faith, but Buddhist groups continue to demand full control.
Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- A Forest Department survey discovered 63 new species of odonates, butterflies, and birds in Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary.
About Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary:
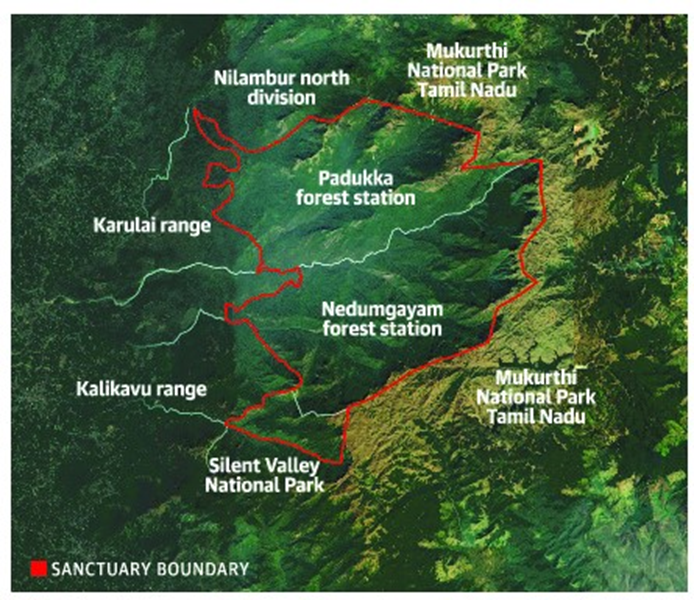
- Geography:
- Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Malappuram district of Kerala, spanning 227.97 sq. km on the western slopes of the Nilgiri Hills.
- It forms part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (NBR), recognised under UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere Programme.
- The sanctuary shares its boundary with Mukurthi National Park (Tamil Nadu) to the east and Silent Valley National Park (Kerala) to the south.
- The Karimpuzha River, a tributary of the Chaliyar River, flows through the sanctuary, contributing to its rich biodiversity.
- The landscape includes steep hills, deep valleys, marshlands, grasslands, and shola forests, with altitudes ranging from 40 m to 2550 m, creating diverse habitats.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The sanctuary is unique as it hosts all seven forest types found in Kerala, including evergreen rainforest, semi-evergreen forest, moist deciduous forest, sub-tropical hill forest, montane wet grasslands, and montane wet temperate forest.
- It is home to endemic species of the Western Ghats, such as the Nilgiri Tahr, Lion-tailed Macaque, Slender Loris, Tiger, and Gaur.
- The sanctuary supports nomadic Cholanaikan tribes, classified as Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) by the Government of India.
- The diverse ecosystem, coupled with perennial water sources, makes it an ideal habitat for a wide variety of species, including newly recorded odonates, butterflies, and birds.
Tonga
Why in news?
- A powerful 7.1 magnitude earthquake struck near Tonga, triggering a tsunami warning for the region.
About Tonga:
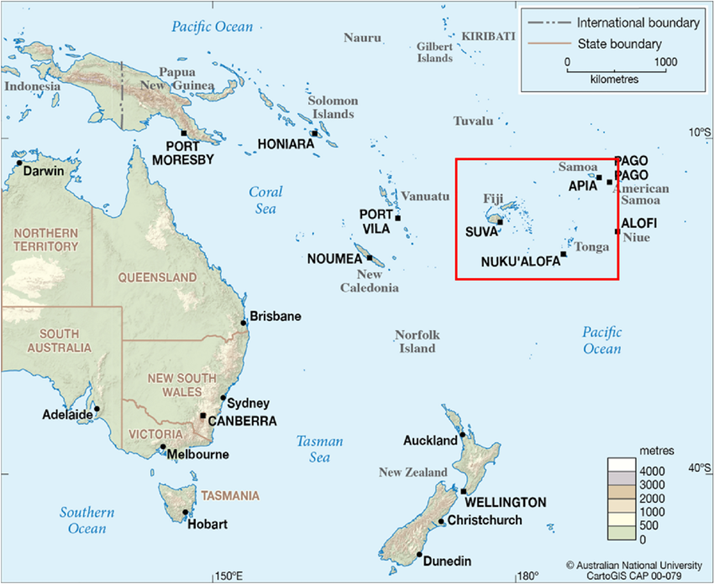
- Location:
- Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an archipelago of 169 islands, with only 36 inhabited.
- It is located in the South Pacific Ocean, south of Samoa, east of Fiji, and just north of the Tropic of Capricorn.
- The three largest islands are Tongatapu, Ha'apai, and Vava'u, with Nuku‘alofa as the capital on Tongatapu.
- Geophysical Characteristics:
- Tonga’s western islands are volcanic, with four active volcanoes, while its eastern islands are low-lying coral formations.
- The nation is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a seismically active region prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- Due to its tectonic setting, Tonga frequently experiences seismic activity, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
- Reason Behind the Earthquake:
- Tonga is located near the Tonga Trench, a subduction zone where the Pacific Plate is forced under the Indo-Australian Plate.
- This subduction results in intense seismic activity, leading to frequent earthquakes and tsunamis.
- The recent 7.1 magnitude earthquake was caused by tectonic stress release along this subduction zone.
- Impact of the Earthquake:
- The earthquake triggered a tsunami warning, raising concerns for coastal communities.
- It caused infrastructure damage and disrupted communication and transportation networks.
- Local authorities advised evacuations in vulnerable areas due to the risk of aftershocks and potential tsunamis.
Netravati River
Why in news?
- Sewage inflow into the Netravati River in Mangaluru has raised environmental concerns, highlighting ongoing water pollution issues and ecosystem threats.
About Netravati River:
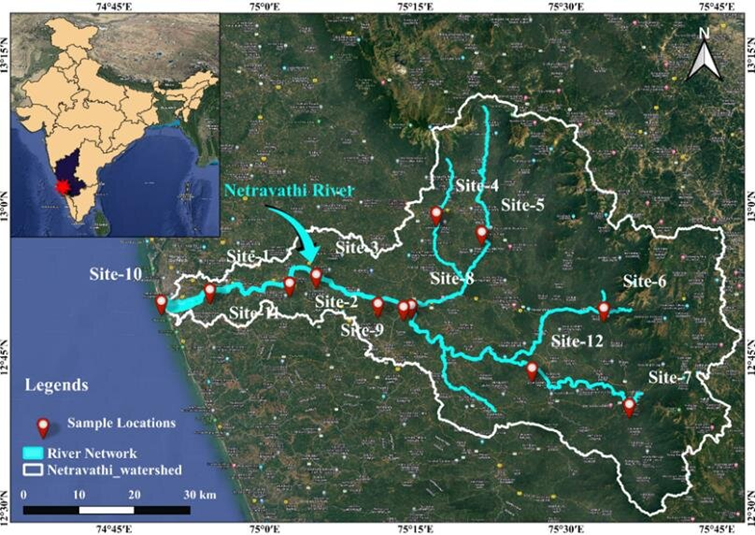
- Origin and Course:
- The Netravati River originates in the Bangrabalige Valley, Yelaneeru Ghat, in the Kudremukha range of Chikkamagaluru district, Karnataka.
- It flows through Dharmasthala, a famous pilgrimage site, before merging with the Kumaradhara River at Uppinangadi.
- The river ultimately drains into the Arabian Sea, south of Mangalore.
- It covers a drainage area of 1,353 square miles, with over 100 TMC of water flowing annually to the sea.
- Historical and Geographical Significance:
- Earlier known as the Bantwal River, it played a crucial role in the trade and economy of the region.
- The 1855 Gazetteer of Southern India described it as an unfordable river during the South-West Monsoon.
- The riverbed consists of hornblende rock, mica, garnets, and pegmatite fragments.
- It is navigable by small country boats for several miles.
- The river supports agriculture and fishing, providing water for irrigation during non-monsoon periods.
- The riverbed is a source of fine sand used in construction.
- Environmental Concerns:
- Flooding is a recurring problem, with major floods recorded in 1928 and 1974, submerging Bantwal town.
- Several mini hydroelectric and river diversion projects threaten the ecological balance of the region.
- Experts warn that altering the river’s course could impact marine biodiversity and rainforest continuity in the Western Ghats.
- Opposition has risen against hydroelectric projects due to potential environmental damage.
Similipal Biosphere Reserve
Why in news?
-
- A new wild ginger species has been discovered in Odisha's Similipal Biosphere Reserve.
About Similipal Biosphere Reserve:
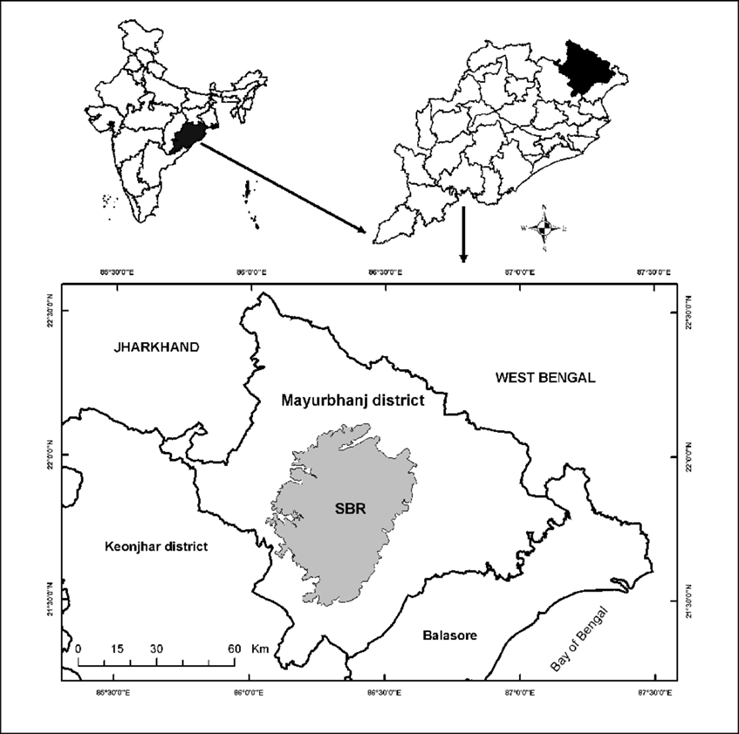
- Location and Geography:
- Similipal Biosphere Reserve is located in the Mayurbhanj district of Odisha, India.
- It covers an area of 5,569 sq. km, with Similipal National Park forming its core.
- The reserve is part of the Eastern Ghats and is characterised by hills, valleys, plateaus, and dense forests.
- Several rivers, like Budhabalanga, Khairi, and Salandi, originate from Similipal, providing water to the region.
- The region experiences a tropical monsoon climate, with heavy rainfall and dense vegetation.
- Flora and Fauna:
- Similipal is home to tropical moist deciduous forests, dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and savannahs.
- It supports over 1,000 species of plants, including medicinal and rare tree species.
- The reserve is famous for its rich biodiversity, including elephants, tigers, leopards, deer, gaur, and wild boars.
- It is also a habitat for mugger crocodiles, reptiles, and over 200 species of birds.
- Recent discoveries, like new wild ginger species, highlight its botanical richness.
- Other Protected Areas within Similipal Biosphere Reserve:
- Similipal National Park: The core area of the biosphere, known for its diverse wildlife and dense forests.
- Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary: Located in Keonjhar district, known for its water bodies and bird species.
- Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary: Situated in Balasore district, an important corridor for elephants.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |




