- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
PLACES IN NEWS 18th APRIL 2025
PLACES IN NEWS 18th APRIL 2025
18-04-2025

Alaknanda River
Why in news?
- A family of five, including three children, died as their car plunged into the Alaknanda River in Uttarakhand.
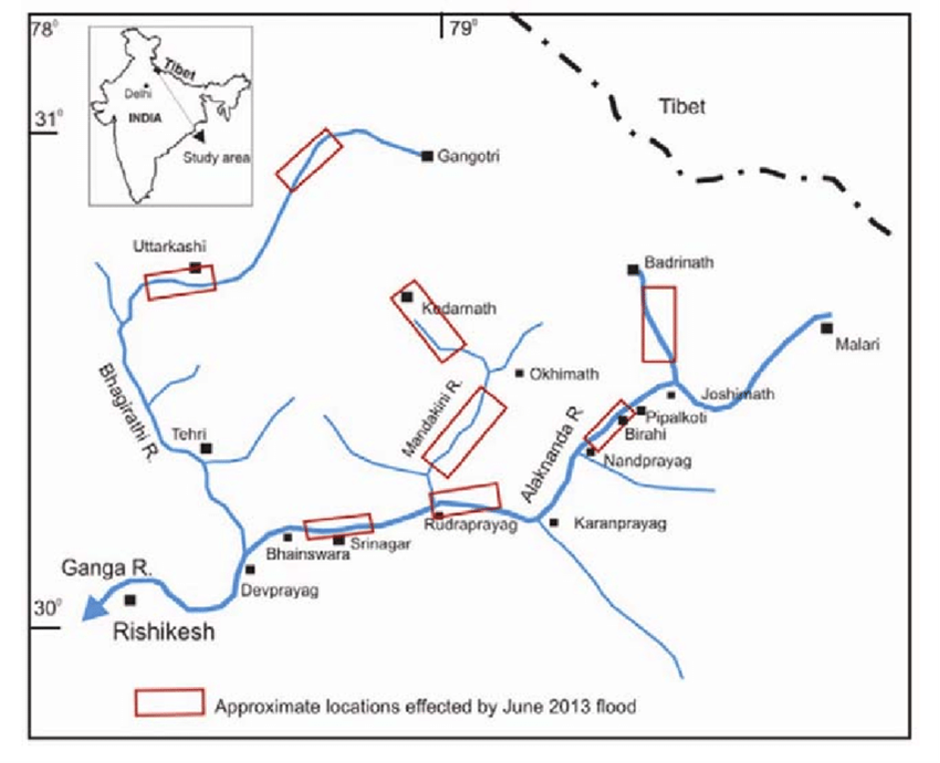
About Alaknanda River:
-
- Geographical location:
- The Alaknanda River originates from the Satopanth Glacier in Uttarakhand, India, located at an altitude of about 3,600 meters near the base of the Chaukhamba massif.
- This glacier is nestled in the Garhwal region of the Himalayas, a region known for its pristine natural beauty and significant hydrological systems.
- Flowing in a southeast direction, the Alaknanda passes through key towns like Badrinath, Joshimath, Rudraprayag, and Srinagar in Uttarakhand. Along its path, it is fed by several tributaries, including the Dhauliganga, Nandakini, Pindar, and Mandakini rivers.
- The Alaknanda merges with the Bhagirathi River at Devprayag, marking the official beginning of the Ganga River, which is one of the most revered rivers in India.
- The river traverses some of Uttarakhand’s most spiritually significant regions, including Badrinath, one of the Char Dham pilgrimage sites. This reinforces its profound cultural importance and draws thousands of devotees annually.
- Economic and cultural significance:
- The Alaknanda River is pivotal for hydroelectric power generation. Major projects like the Vishnuprayag Hydroelectric Project, Srinagar Hydroelectric Project, and Tapovan-Vishnugad Hydropower Plant harness the river’s flow to generate electricity, supporting Uttarakhand’s energy needs and contributing to India’s renewable energy goals.
- Additionally, the river supports agriculture and local livelihoods by providing irrigation to the fertile valleys along its course.
- The Alaknanda holds immense cultural significance as a sacred river in Hinduism. Its confluence points, known as the Panch Prayags—Vishnuprayag, Nandaprayag, Karnaprayag, Rudraprayag, and Devprayag—are sites of deep religious reverence.
- These locations are believed to cleanse sins and offer spiritual liberation. The river is also central to numerous rituals, festivals, and practices, cementing its place in the cultural and spiritual ethos of the region.
Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean
Why in news?
- Tensions between Türkiye and Greece have escalated following Greece's recent submission of Maritime Spatial Planning (MSP) to the European Union, aiming to organize maritime activities such as fishing, tourism, and energy exploration in its waters.
- Türkiye has criticized these plans, asserting that parts of the proposed maritime zones infringe upon its jurisdiction in the Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean.
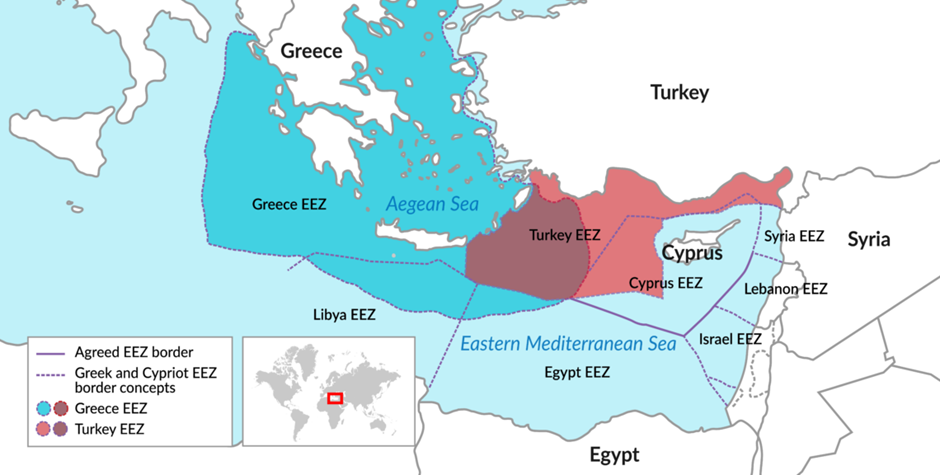
About Aegean Sea:
-
-
- The Aegean Sea is a part of the Mediterranean Sea, located between mainland Greece and western Türkiye (Anatolia).
- It spans approximately 610 kilometers north to south and 300 kilometers east to west.
- The sea is bordered to the north by the Dardanelles Strait, linking it to the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea via the Bosphorus.
- To the south, it connects to the Mediterranean Sea near the island of Crete.
- The Aegean Islands, including the Cyclades, Dodecanese, and North Aegean Islands, are mostly under Greek sovereignty.
- The region has a rugged coastline, deep waters, and is rich in marine biodiversity.
- It is shaped by ongoing tectonic activity, contributing to its complex underwater topography.
-
About Eastern Mediterranean:
- The Eastern Mediterranean is a historically and geographically significant region, renowned for its rich cultural heritage and strategic importance.
- Historically referred to as the Levant, this region includes modern-day countries like Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, parts of Turkey, and stretches into Egypt.
- The term "Levant" originates from the French word meaning "rising," alluding to the direction of the rising sun in the east and its position relative to Europe.
- Geographically, the Eastern Mediterranean borders the Middle East to the east, and is framed by the Anatolian Peninsula in the north and the Sinai Peninsula in the south.
- This region serves as a crossroads between Europe, Asia, and Africa, facilitating trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of civilizations for millennia.
- Major waterways such as the Suez Canal and the Bosporus Strait enhance its global connectivity, further cementing its importance in geopolitics and commerce.
What is Maritime Spatial Planning (MSP) and Jurisdictional Disputes regarding the Greece’s planning?
- Maritime Spatial Planning (MSP) is a framework used by coastal states to manage marine resources and activities in their territorial waters and Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs).
- Greece has recently advanced its MSP initiative by submitting maritime spatial plans to the European Union, aiming to regulate activities like fishing, tourism, shipping, and energy exploration.
- These plans are designed to promote sustainable use of marine resources and environmental protection.
- However, Greece's MSP has triggered strong objections from Türkiye, which claims that certain proposed zones overlap with areas where Turkish sovereign rights exist, particularly in the Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean.
- The core of the jurisdictional dispute lies in conflicting interpretations of international maritime law, especially the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), which Türkiye has not signed.
- Greece asserts its right to extend its territorial waters and EEZ based on UNCLOS provisions, including around its many islands.
- Türkiye, however, argues that such moves disregard its continental shelf rights and could restrict its access to international waters and resources.
Mount Lewotobi
Why in news?
- Indonesia's Mount Lewotobi in East Nusa Tenggara erupted recently, prompting flight alerts and issuing safety warnings for nearby residents.
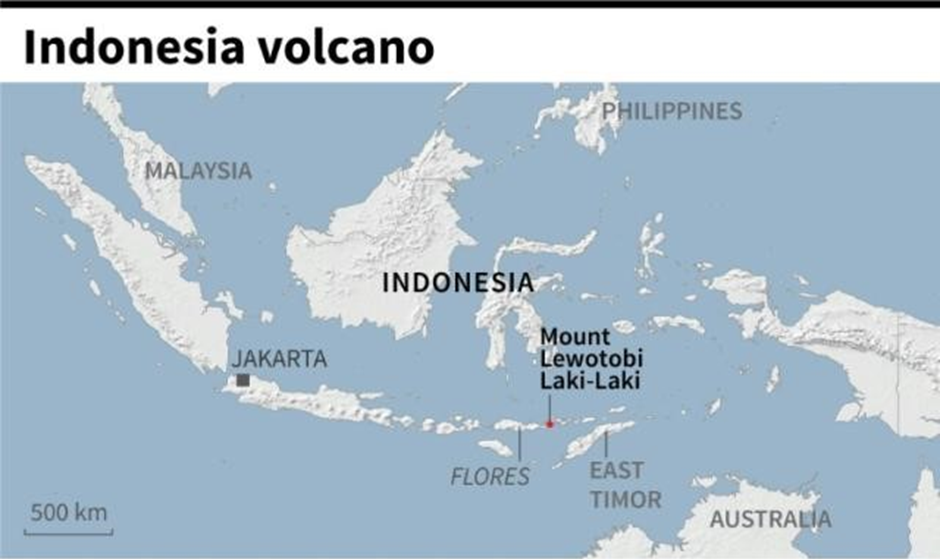
About Mount Lewotobi:
-
-
- Mount Lewotobi is a twin stratovolcano located on Flores Island in East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia.
- It lies along the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone known for frequent seismic and volcanic activity.
- The volcano features two distinct peaks, aligned northwest to southeast, separated by a 1232-meter-high saddle.
- These peaks are known as Lewotobi Lakilaki (male) and Lewotobi Perempuan (female), giving rise to the name "Lewotobi," meaning "husband and wife."
- Lewotobi Lakilaki, standing at 1584 meters, has a 400-meter-wide summit crater open to the north and has shown frequent eruptions in the 19th and 20th centuries.
- Lewotobi Perempuan, at 1703 meters, has a 700-meter-wide crater and has erupted only twice in recorded history.
- Lava domes have formed in both summit craters during the 20th century, indicating ongoing magmatic activity.
-
Tanzania
Why in news?
- In 2024, Tanzania's average annual temperature hit a record 24.3°C, surpassing the long-term norm by 0.7°C.
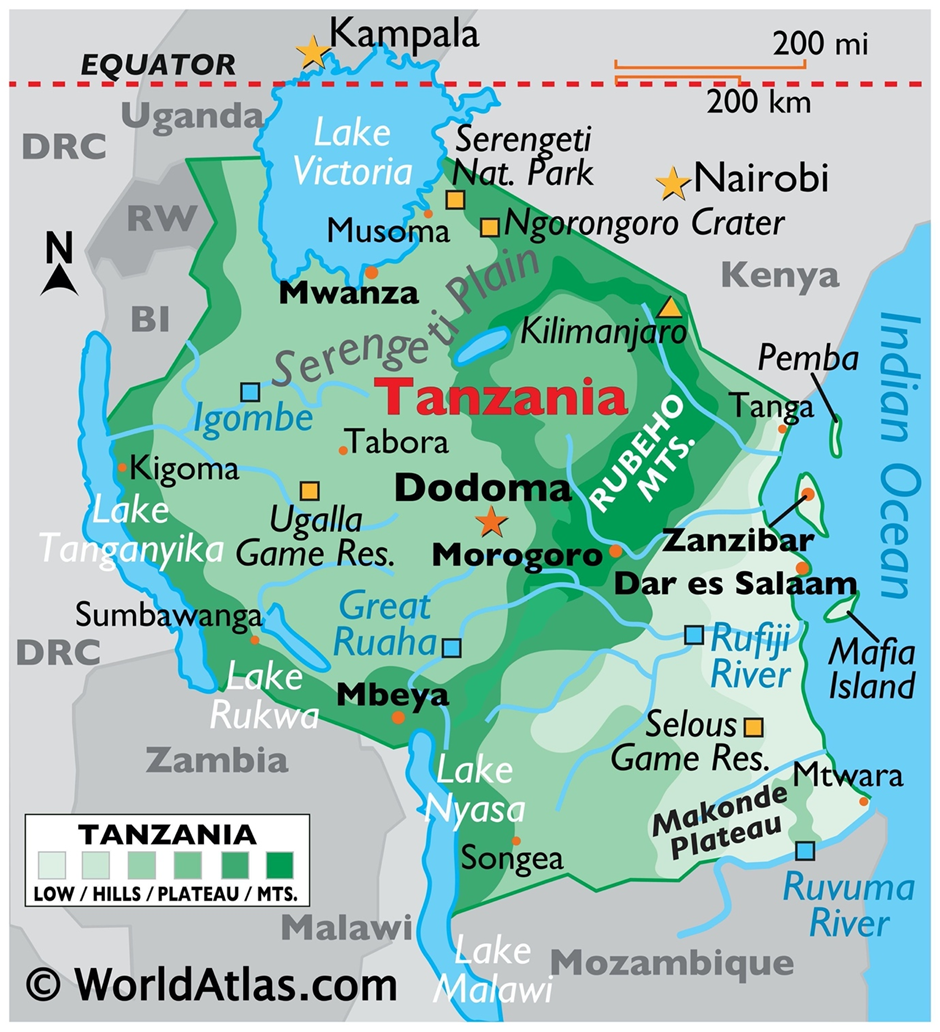
About Tanzania:
- Geographical location:
- Tanzania is located in East Africa, just south of the equator, with the Indian Ocean forming its eastern coastline.
- It shares borders with Kenya and Uganda to the north; Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to the west; and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south.
- The country is known for its diverse topography, ranging from coastal plains and inland plateaus to volcanic highlands.
- Tanzania is home to Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak and a dormant volcano, which draws climbers and researchers from across the globe.
- Several major lakes define Tanzania’s borders—Lake Victoria (the world’s second-largest freshwater lake) in the north, Lake Tanganyika (the second deepest in the world) in the west, and Lake Nyasa in the southwest.
- The country’s major rivers include the Ruvuma and Rufiji, vital for agriculture, transport, and hydroelectric power.
- Natural resources:
- Tanzania is rich in natural resources such as gold, diamonds, natural gas, uranium, and fertile land for agriculture.
- It has vast forests, wildlife, and marine resources, supporting both biodiversity and ecotourism.
- The country’s economy benefits from mining, farming, and tourism, with Serengeti National Park and Ngorongoro Crater attracting global visitors.
- Impact of rise in temperature:
- In 2024, Tanzania recorded its highest average annual temperature of 24.3°C, which is 0.7°C above the long-term normal.
- Rising temperatures threaten agricultural productivity, especially crops like maize and coffee that are sensitive to heat stress.
- It increases the risk of droughts, water scarcity, and vector-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue.
- Glacial retreat on Mount Kilimanjaro and coastal erosion along the Indian Ocean are visible signs of climate change impact.
- The shift in rainfall patterns disrupts the two seasonal rains, affecting food security and rural livelihoods.
|
Also Read |
|
UPSC Foundation Course |
|
| UPSC Monthly Magazine | CSAT Foundation Course |




