- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Five Eyes: The World’s Oldest Intelligence Network and Its Global Impact
Five Eyes: The World’s Oldest Intelligence Network and Its Global Impact


Five Eyes member’s Flag
The Five Eyes Alliance: An Overview
In 1946, a covert partnership was established, laying the foundation for the world's oldest and most secretive intelligence-sharing network: the Five Eyes (FVEY) Alliance. Though born out of the chaos of World War II, this alliance would go on to shape not only military strategy but also influence global politics, economics, and major international conflicts over the course of the 20th and 21st centuries.
Today, the Five Eyes remains a formidable force in international intelligence activities, having played critical roles in the Cold War, the War on Terror, and the age of global surveillance. However, the methods and operations of the alliance have often sparked heated debates and controversy. Its influence is felt in ways that many may not fully realize, raising questions about privacy, sovereignty, and ethics.

Must Read: Heard Island and McDonald Islands: U.S. Tariff Announcement & Significance
The term "Five Eyes" is shorthand for the partnership’s original classification, denoted as "AUS/CAN/NZ/UK/US Eyes Only" (AUSCANNZUKUS), referring to the strict limits on how intelligence could be shared among these nations.
The Origins of the Five Eyes
The seeds of the Five Eyes were planted much earlier than 1946. The collaboration between the United Kingdom and the United States began during World War II when the two nations exchanged critical intelligence. In February 1941, Scottish codebreaker Alastair Denniston made a cryptic entry in his diary: "The Ys (Yanks) are coming!" This was a reference to the increasing collaboration between the UK and the US in cracking sophisticated enemy codes. The UK had managed to break the German Enigma cipher, while the US cracked the Japanese Purple code. This alliance proved essential in the success of the Allies during the war.
After the war, the geopolitical landscape dramatically shifted. The former ally, the Soviet Union, emerged as a new threat. To counter this, the UK and US formalized their intelligence-sharing agreement in 1946, an arrangement that eventually became known as the Five Eyes. The primary goal was to share vital information related to the growing threat of the Soviet Union, particularly in areas of nuclear weapons and espionage. This led to the creation of a unique intelligence-sharing pact based on mutual trust and transparency—one that would evolve into a “no-spy” agreement between its members.
The Expansion of the Alliance
The partnership soon expanded as other nations recognized the value of participating in the intelligence network. Canada, Australia, and New Zealand joined the alliance, each country taking responsibility for intelligence gathering in different regions of the world. Australia focused on South and East Asia, Canada took charge of Latin America, the North Atlantic, and Eastern Russia, while New Zealand focused on the Pacific.
With all five nations involved, the Five Eyes developed a near-constant global surveillance apparatus, covering virtually every corner of the Earth. The alliance’s intelligence-gathering capabilities expanded far beyond its initial UK-US cooperation, creating a 24/7 watch over the globe. Despite the secrecy surrounding this collaboration, it wasn’t until 2010 that the public was officially made aware of its existence when a heavily redacted document confirmed the alliance’s operations.
Tensions and Disputes Within the Five Eyes
Despite its remarkable success, the Five Eyes alliance has not been free of friction. Throughout the years, political disagreements and intelligence disputes have arisen among the member nations.
One significant tension occurred during the 1960s when the Soviet-backed Cambridge Five spy ring in the UK led the US to question the reliability of British intelligence. This incident sowed distrust, showing that even within such a closely-knit alliance, confidence could be shaken.
At times, intelligence-sharing was interrupted due to political differences. For example, in 1990, Canada found itself temporarily excluded from intelligence-sharing during the Gulf War because of its hesitation to send troops. Similarly, in 1973, Richard Nixon and Henry Kissinger suspended cooperation with the UK due to Prime Minister Edward Heath’s pro-European policies.
Perhaps the most famous example of internal friction occurred in 2013, when Edward Snowden, a former contractor for the US National Security Agency (NSA), leaked classified information about global surveillance programs. The NSA’s failure to inform its allies about the leak, despite knowing Snowden’s identity, highlighted the lack of transparency within the alliance and created further distrust.
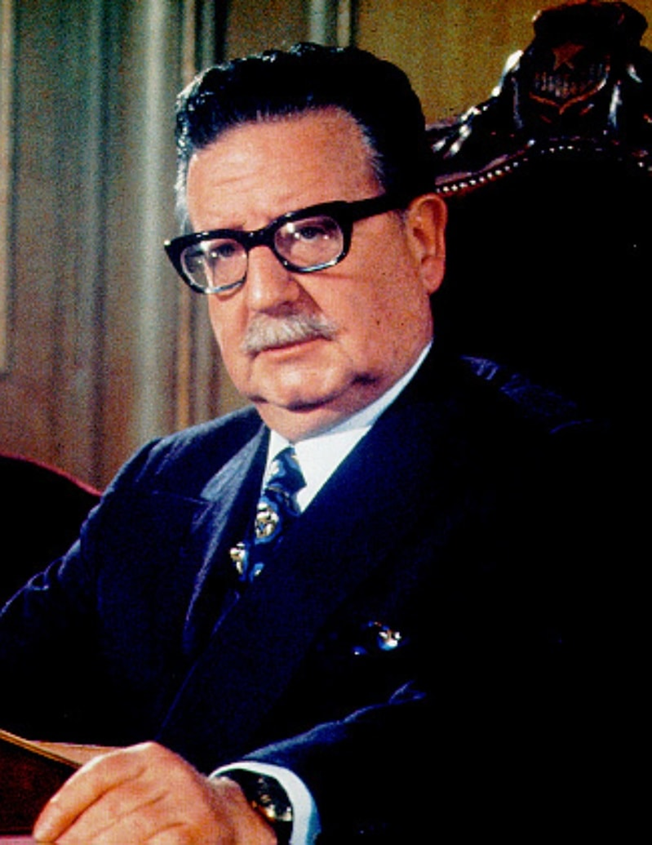

Ousted Chilean President Salvador Allende
Covert Operations: A Legacy of Intervention
The Five Eyes have been deeply involved in numerous covert operations that have shaped world history, often intervening in foreign governments and influencing political outcomes. One of the most infamous operations occurred in Chile in the early 1970s. After the election of Salvador Allende, a Marxist president, the US viewed him as a direct threat to its interests in Latin America. With the support of Australia's ASIS (Australian Secret Intelligence Service), the CIA worked to undermine Allende’s government. Despite these efforts, Allende narrowly won re-election in 1973, only to be overthrown later that year by General Augusto Pinochet’s military coup. Pinochet would go on to rule Chile with an iron fist for 17 years.
Another high-profile covert operation took place in 1953 when the CIA and MI6 (the UK’s intelligence service) orchestrated the coup in Iran to overthrow Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh. The operation, driven by concerns over Mosaddegh’s move to nationalize Iran's oil industry, resulted in the installation of the pro-Western Shah of Iran. This coup set the stage for decades of instability in the region, which has had lasting geopolitical consequences.
Throughout the Cold War and beyond, the Five Eyes were involved in numerous such interventions, often in the name of preserving Western interests. These covert actions extended far beyond the borders of Europe and North America, particularly influencing political landscapes in the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America.
Intelligence Failures and Manipulations
While the Five Eyes’ covert operations are often seen as successful, they have also been marked by significant failures and instances of intelligence manipulation. One of the most notorious failures occurred in 2003 when the US invaded Iraq based on the premise that Saddam Hussein possessed weapons of mass destruction (WMDs). The invasion, which led to a devastating conflict and regional instability, was later revealed to have been based on faulty or fabricated intelligence.
The actions of whistleblower Katharine Gun, a British intelligence officer, shed light on the extent to which the Five Eyes manipulated intelligence to achieve political goals. Gun leaked a memo revealing that the NSA and MI6 had been spying on UN diplomats to pressure them into supporting the invasion of Iraq, demonstrating the willingness of the alliance to manipulate global intelligence for political ends.
The Backlash: Global Concerns Over Surveillance
In recent years, the surveillance overreach of the Five Eyes has become a subject of global backlash. One of the most prominent controversies occurred in 2013 when it was revealed that the NSA had been tapping the phone of German Chancellor Angela Merkel. This revelation shocked the international community, raising questions about whether the Five Eyes had crossed ethical boundaries and violated the sovereignty of other nations.
The alliance's surveillance activities also extended to other nations, including Brazil, South Africa, and Timor-Leste. In 2004, Australia was caught spying on Timor-Leste during critical oil and gas negotiations, which were worth billions of dollars. This led to legal challenges, and the International Court of Justice ultimately ordered Australia to cease its spying activities.
The disclosures made by Edward Snowden further revealed the true extent of the Five Eyes' global surveillance reach, undermining the privacy of individuals and governments worldwide.
Must Read: India-Canada standoff: Five Eyes Alliance
The Enduring Legacy of the Five Eyes
The Five Eyes Alliance has left an indelible mark on global intelligence, geopolitics, and international relations. From influencing the outcome of Cold War-era conflicts to its involvement in the War on Terror, the alliance has shaped global events through its covert operations and intelligence-gathering capabilities. However, its secretive nature and surveillance activities have also led to significant controversy, with concerns over privacy violations and the manipulation of intelligence for political gain.
As global interconnectedness grows, the Five Eyes will likely remain a pivotal player in international intelligence operations. But the alliance’s methods and consequences will undoubtedly continue to be scrutinized as the world grapples with issues of privacy, sovereignty, and ethical intelligence practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Five Eyes Alliance?
The Five Eyes Alliance is a long-standing intelligence-sharing network composed of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. It plays a significant role in global intelligence operations, including surveillance, military interventions, and covert operations.
2. How did the Five Eyes Alliance originate?
The origins of the Five Eyes trace back to World War II when the UK and US began sharing intelligence on German and Japanese codes. This partnership formalized in 1946, with Canada, Australia, and New Zealand joining the alliance in subsequent years.
3. What countries are part of the Five Eyes?
The Five Eyes Alliance consists of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
4. How many QUAD nations are members of the Five Eyes?
Out of the four countries in the Quad (United States, India, Australia, and Japan), two— the United States and Australia—are members of the Five Eyes intelligence network.
5. Why is the Five Eyes controversial?
The Five Eyes has been criticized for its widespread surveillance activities, interventions in foreign governments, and alleged violations of privacy rights. Its role in operations like espionage against Germany, Brazil, and East Timor has sparked significant backlash.
6. How does the Five Eyes influence global politics?
The Five Eyes has shaped international conflicts and politics, playing roles in regime changes, military interventions, and economic policies, including involvement in the Vietnam War, the Gulf War, and the War on Terror.
7. Is India a member of the Five Eyes?
No, India is not part of the Five Eyes Alliance. However, it maintains strong intelligence-sharing relationships with several of the alliance’s members, including the United States.
8. What covert operations have the Five Eyes been involved in?
The Five Eyes have been involved in several high-profile covert operations, such as the overthrow of Chile’s President Allende in 1973, the 1953 coup in Iran, and spying on foreign governments like Germany, Brazil, and Indonesia.
9. What intelligence failures has the Five Eyes been linked to?
A major intelligence failure occurred in the lead-up to the Iraq War in 2003, where the invasion was based on false intelligence about weapons of mass destruction. Whistleblower Katharine Gun’s leak revealed the manipulation of intelligence by the Five Eyes to push for military action.
|
Also Read |
|
| FREE NIOS Books | |