- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Women in Workforce
Women in Workforce
Context: The Central government has initiated a survey to boost women’s role in the Labour Force Participation Rate.
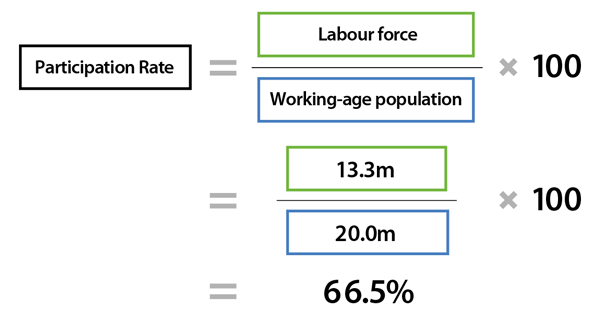
What is the Labour Force Participation Rate?
- It is the percentage of people who are either working or actively looking for work.
- In India, the Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) can be calculated using the following formula:
Formula |
Description |
|
|
Labour Force = Number of people employed + Number of people unemployed but actively seeking employment Working Age Population = Total population aged 15 years and above |
What are the Trends in India's Labor Force Participation?
- Historically, female labour force participation has seen a decline.
Year |
1999-2000 |
2011-12 |
Trend |
|
Female Participation |
34.1% |
27.2% |
Declined by 6.9% |
- But recently the trend has reversed. According to the Periodic Labour Force Survey, the figures are:
Year |
2017-18 |
2018-19 |
2019-20 |
2020-21 |
|
Female Participation |
17.5% |
18.6% |
22.8% |
25.1% |
What has the Trend Reversed?
|
Phase 1 |
Initially in any economy, women's labour force participation remains high due to economic necessity driven by low incomes in agriculture-based economies. |
|
Phase 2 |
As the economy progresses into the second phase, women gain the option to withdraw from participation. Transitioning from agriculture to factory-based economies introduces social barriers for women, including limited access to education, traditional gender roles, workplace discrimination, lack of support services, safety concerns, and social stigma. |
|
Phase 3 |
Increased levels of education, skill development, and rising demand in certain industries like IT and healthcare contribute to increased women's participation in the workforce. |
What are the reasons behind the Low Labour Force Participation of Women in India?
- Informalization of Employment: More than 90% of women in India are employed in the Informal Sector. The informal Sector is one which is not regulated or monitored by the government, due to which workers do not have formal contracts or benefits like healthcare or retirement plans.
- Limited Job Options: There aren't enough job opportunities as the Indian economy transitioned from an Agriculture to a Service sector-led economy. The manufacturing sector could have provided more job opportunities.
- Glass ceiling: Women often face barriers to advancing in their careers, like discrimination in wages or limited promotion opportunities.
- Pink Jobs: Some jobs are seen as "women's work" like teaching, nursing, etc making it harder for women to break into other industries.
- Better Household Incomes: As household incomes rise, there is a choice for women not to work.
- Cultural Norms: Indian culture puts pressure on women to focus on domestic chores and childcare.
- Educated Unemployment: Even with education, some people struggle to find suitable jobs. The overall enrollment of women in higher education is increasing but they are unable to find suitable employment of their qualification.
- Lack of Political Nudge: There's not enough support from policymakers to encourage more women to join the workforce.
Why do we need to increase Women's Labour Force Participation?
- Economic Growth: According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), if women equally participate in the workforce with men, it will add 27% to India’s GDP.
- Feminization of poverty: When women aren't in the workforce, it can contribute to their poverty.
- Improved Social Indicators: Higher female workforce participation leads to improved health and education outcomes, greater financial independence, and improved gender equality.
What are the Steps taken by the Government?
- Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017: Provides maternity benefits like paid leave and medical benefits to women employees.
- Stand Up India: A program aimed at promoting entrepreneurship among women and marginalized groups by providing financial support and guidance.
- Sexual Harassment at Workplace Act, 2013: This act ensures a safe working environment for women by prohibiting and addressing sexual harassment in the workplace.
- Promotion of Self-Help Groups (SHGs): SHGs are like clubs where people, usually women, with similar backgrounds team up. They help each other out with things like saving money, learning new skills, and even starting small businesses. It's a way for them to support each other and improve their lives together. Such SHGs are given financial support by the government.