- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
Why Climate Change Poses an Existential Threat to the Panama Canal
Why Climate Change Poses an Existential Threat to the Panama Canal
22-08-2024
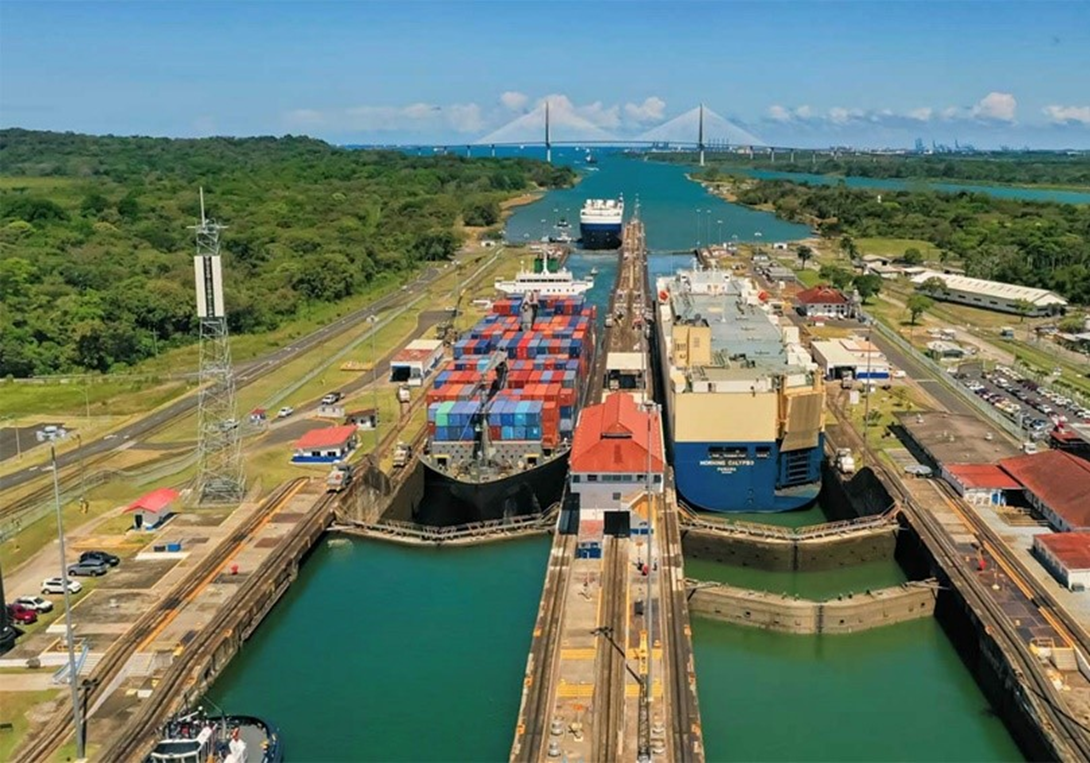

The Panama Canal, a key global shipping route, is facing serious issues because of long-term drought conditions worsened by climate change. This has led to lower water levels in Lake Gatun, an essential part of the canal’s operation. This situation is prompting discussions on how to ensure the canal’s future functionality.
- The Panama Canal, which opened on August 15, 1914, is a remarkable engineering achievement. Stretching 82 kilometers, it allows ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans without navigating the lengthy route around South America.
- This shortcut saves about 12,600 kilometers on a voyage between New York and San Francisco, making it one of the world's most crucial shipping routes.
Current Situation
- Daily Traffic:
- Average: Around 36 to 38 ships pass through daily.
- Recent Drop: In December, traffic fell to just 22 ships per day due to a drought causing low water levels in Lake Gatun, an essential reservoir for the canal.
- Temporary Improvement:
- Current Traffic: Restored to about 35 ships a day.
- Concerns: Experts believe this is a short-term improvement, with climate change threatening the canal’s future.
How the Panama Canal Works?
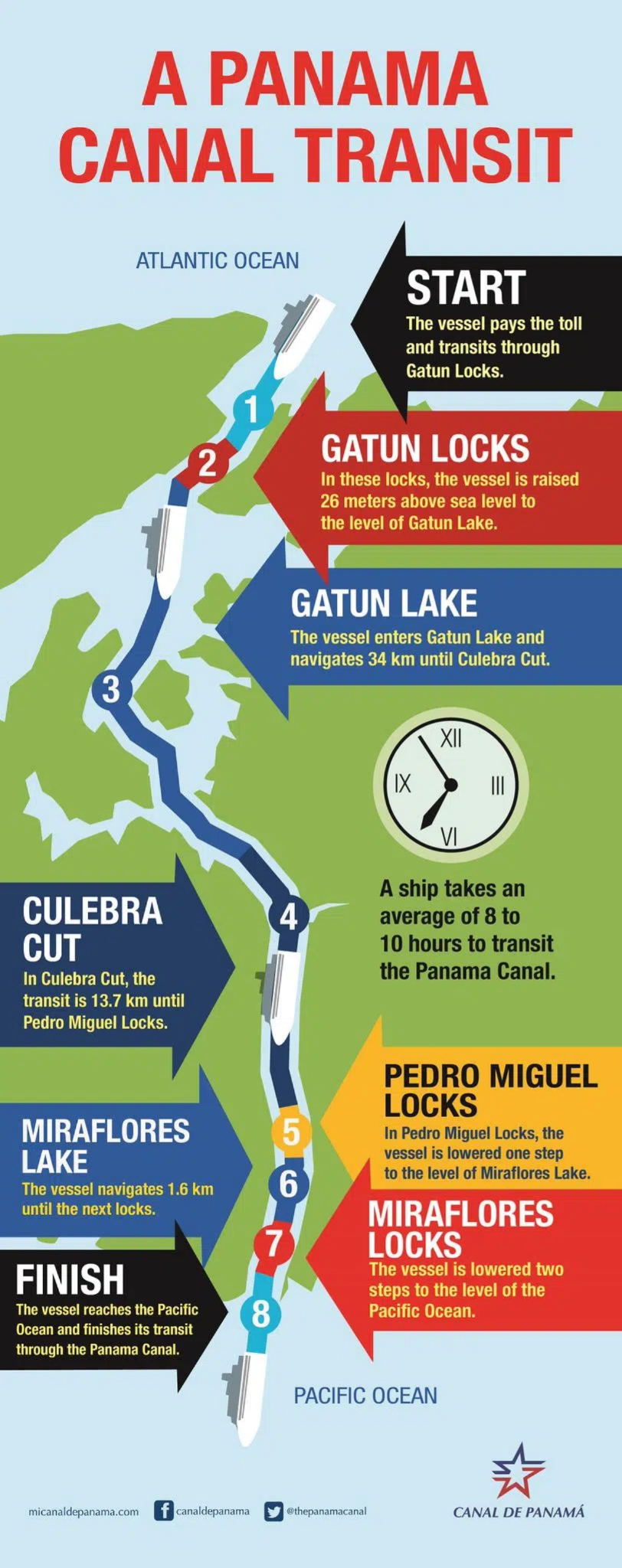
- Lock System:
- Purpose: The canal uses locks to lift and lower ships because the Pacific Ocean is slightly higher than the Atlantic.
- Process:
- A ship enters the lowest lock chamber.
- The lock gate closes, and water from a higher chamber floods the chamber.
- Once the water levels are equal, the ship moves to the next chamber.
- The process is reversed to lower the ship when moving back.
- Water Requirement:
- Volume: A single ship passage uses over 50 million gallons (about 200 million liters) of water.
- Comparison: This is more than twice the daily water use of New York City’s 8 million residents.
Threats from Climate Change
- Impact of Drought:
- Water Levels: Lower water levels in Lake Gatun last year led to fewer ships passing through and reduced cargo loads.
- Salinity Issues: Using ocean water to compensate for lower lake levels increases salinity, affecting Lake Gatun’s role as a drinking water source for more than half of Panama’s population.
- Changing Rainfall Patterns:
- Past vs. Present: Historically, significant rainfall deficits occurred about once every 20 years due to major El Niño events. Recently, such events are becoming more frequent.
- Future Predictions: As global temperatures rise, extreme rainfall shortages may become even more common.
- Steven Paton from the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute noted that recent rainfall deficits have no precedent in the past century’s data.
Proposed Solutions
- New Water Source:
- Plan: Construct a $1.6 billion dam on the Rio Indio to provide an additional water source for the canal.
- Legal Changes: Panama’s Supreme Court recently overturned a law that previously protected the river from such projects.
- Controversy:
- Displacement: Building the dam will displace about 2,000 people, mostly from lower-income communities, who will lose their homes and livelihoods.
- Local Opposition: Affected residents, like Olegario Hernandez, feel that relocating them will not improve their situation.
Key Facts About the Panama Canal
Isthmus of Panama
Other Important Canals Around the World
|
Conclusion:
Climate change poses a serious risk to the Panama Canal by affecting water levels in Lake Gatun and altering rainfall patterns. While temporary fixes are being implemented, such as the potential new dam, the long-term survival of this vital waterway depends on addressing the broader impacts of climate change.
Must Check: Best IAS Coaching In Delhi
UPSC Prelims Result 2024 Out: Expected Cut Off & Other Details, UPSC Prelims 2024 Answer with Explanation, Daily Prelims Quiz, Daily Current Affairs, MONTHLY CURRENT AFFAIRS TOTAL (CAT) MAGAZINE, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Karol Bagh, Best IAS Coaching Institute in Delhi, Daily Mains Question Answer Practice, ENSURE IAS UPSC Toppers, UPSC Toppers Marksheet, Previous Year Interview Questions, UPSC Syllabus