- Courses
- GS Full Course 1 Year
- GS Full Course 2 Year
- GS Full Course 3 Year
- GS Full Course Till Selection
- Answer Alpha: Mains 2025 Mentorship
- MEP (Mains Enrichment Programme) Data, Facts
- Essay Target – 150+ Marks
- Online Program
- GS Recorded Course
- Polity
- Geography
- Economy
- Ancient, Medieval and Art & Culture AMAC
- Modern India, Post Independence & World History
- Environment
- Governance
- Science & Technology
- International Relations and Internal Security
- Disaster Management
- Ethics
- NCERT Current Affairs
- Indian Society and Social Issue
- NCERT- Science and Technology
- NCERT - Geography
- NCERT - Ancient History
- NCERT- World History
- NCERT Modern History
- CSAT
- 5 LAYERED ARJUNA Mentorship
- Public Administration Optional
- ABOUT US
- OUR TOPPERS
- TEST SERIES
- FREE STUDY MATERIAL
- VIDEOS
- CONTACT US
US Considers Solar Geoengineering to Counter Global Warming
US Considers Solar Geoengineering to Counter Global Warming
03-07-2023
Latest Context
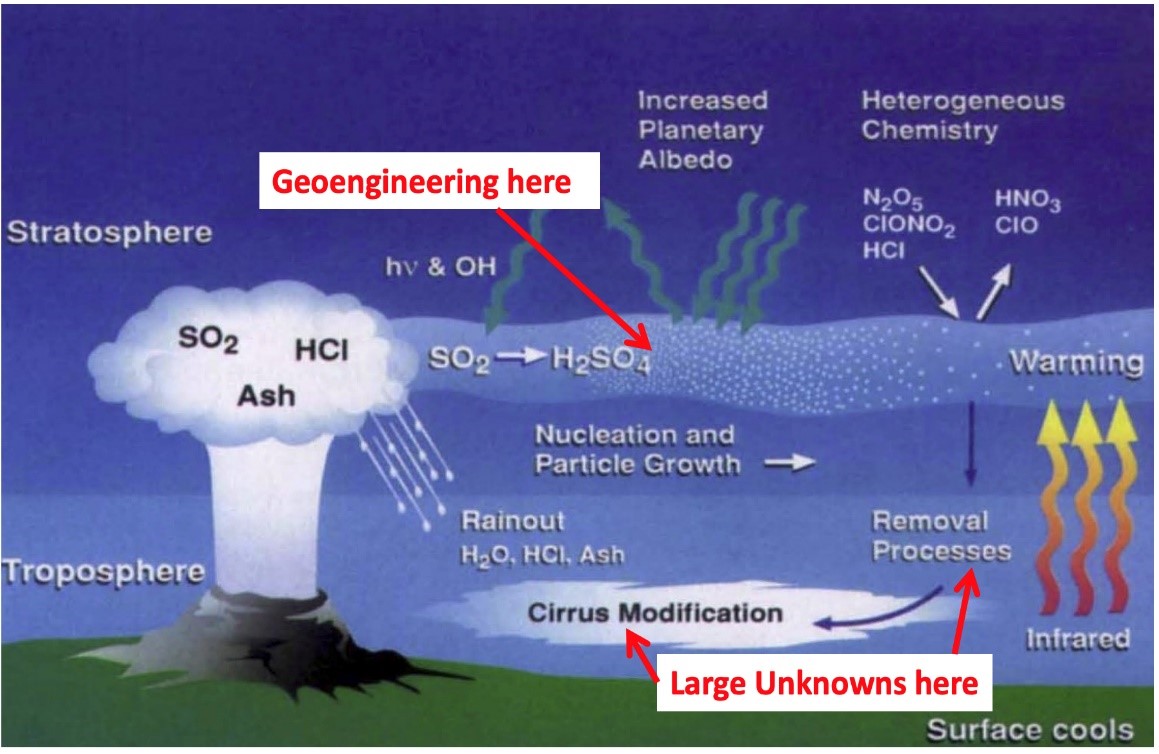
Recently, the White House issued a federally mandated report on Solar Geo-Engineering (SGE), or solar radiation management in order to study how blocking sunlight can save Earth from climate change. SGE is an umbrella term that describes methods (refer to image) of reflecting sunlight away from Earth to cool the atmosphere.
Main Highlights of the Report:
It lays emphasis on two methods of SGE.
- Stratospheric Aerosol Injection (SAI): It releases particles of Sulfur Dioxide into the upper atmosphere to reflect sunlight away from Earth.
- Marine cloud brightening: By infusing sea salt using ships, to improve the reflectivity of certain clouds.
Other proposed methods of SGE: It comprises the following methods.
- High-albedo crops and buildings: It enhances the albedo of buildings to reflect more sunlight back to space.
- Ocean mirror: In this method, a fleet of sea vessels is used to add tiny microbubbles on the ocean surface to act as a mirror.
- Cloud thinning: Their absorption of long wavelength radiations can be curtailed by removing cirrus clouds from the atmosphere,
- Space sunshades: Under this method, it comprises sending a fleet of mirrors into orbit in order to reflect away more sunlight from Earth.
Significance of SGE: It decreases climate impacts like changes in water availability, extreme temperatures, and intensity of tropical storms in addition to creating employment opportunities
Solar Geoengineering: It refers to solar radiation management (SRM) which prescribes a set of proposed approaches in order to reflect sunlight (back to space) to rapidly cool the Earth. Within solar geoengineering, researchers are considering two main approaches.
Various Methods of Soar Radiation Management:
-
Marine cloud brightening (MCB): It utilizes sea salt for stimulating cloud formation over the ocean that helps in reflecting the sunlight in the region.
-
Stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI): Under this method, tiny reflecting particles, known as aerosols inject into the upper atmosphere to cool the planet.
Reasons for using Solar Geoengineering
- Under the Paris Agreement, the target is to require keeping the global temperature increase well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and making efforts to keep the temperature below 1.5°C.
- Another reason is that nations are required to bring net global CO2 emissions to zero by no later than mid-century.
- Despite these ambitious goals, solar geoengineering is being considered to prepare for the possibility that global efforts may fall short.
The Plan of the USA:
- Public or private actors could carry out activities like injecting aerosols and MCB to reflect more sunlight into space as per the White House.
- It recommends conducting research to enable better-informed decisions about the potential risks and benefits of the tool as part of its climate policy, in addition to mitigation and adaptation.
- Social Geoengineering comes with the concerns raised by the experts over the high environmental (changes in precipitation patterns, ozone amounts, sea-level rise, ocean acidification, etc), social, and geopolitical risks that come with SRM.
Solar geoengineering risks:
- Moral hazard: The risk is that the technology will become an excuse to slow emissions reductions and stop moving toward a low-carbon economy.
- Very few efforts in terms of research to know the risks and potential of solar geoengineering have been made and have mostly been conducted through computer-based modeling and natural observations (volcanic eruption).
Way ahead: Solar geoengineering has global implications, and its consideration for climate mitigation response requires –
- There should be effective international governance/ Mechanisms for oversight.
- Governments must fund outdoor experimentation and funding for experiments.
- Emphasis should lay upon devising ways to involve the public in decision-making.
Must Check: IAS Coaching Centre In Delhi



